Table of Contents
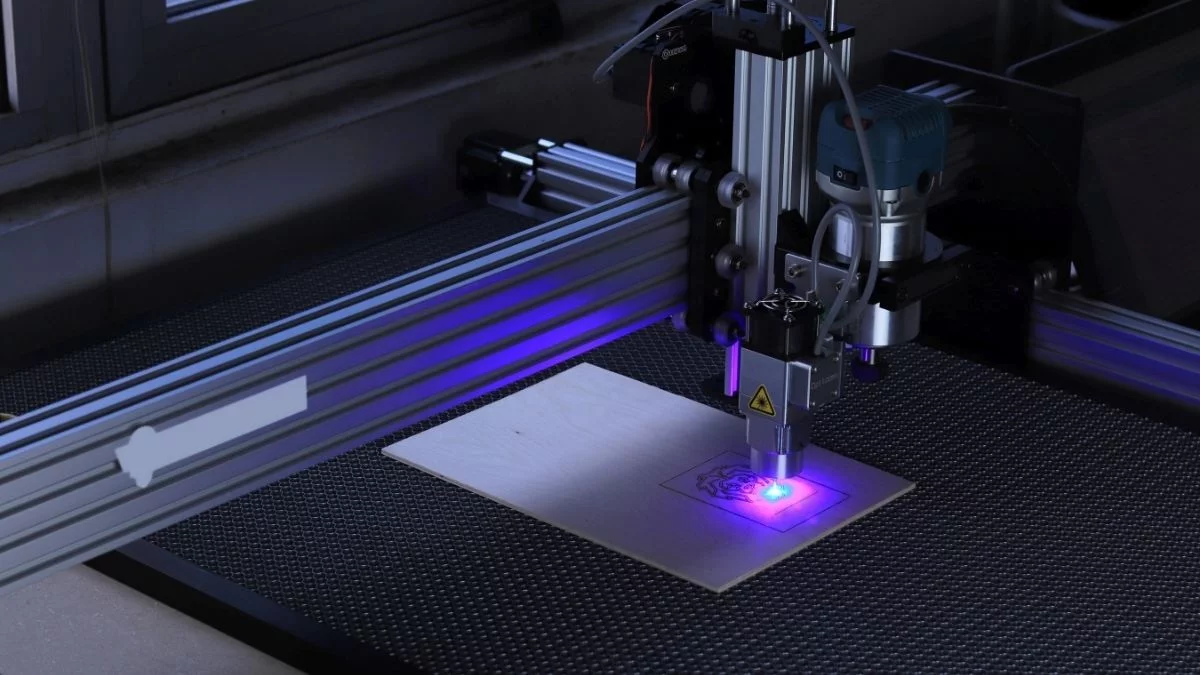
CNC, which stands for Computer Numerical Control, is an automation technology utilized in the manufacturing industry. It involves the use of computers to control machine tools. CNC machines are capable of executing precise and intricate movements to cut, shape, and form a variety of materials like metal, wood, plastic, and composites.
A typical CNC system comprises several components:
- CNC Machine: This refers to the physical equipment or tool responsible for carrying out machining operations. Examples include milling machines, lathes, routers, plasma cutters, and 3D printers.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software is utilized to create a digital 3D model or design of the part or product to be manufactured. The design is typically saved in standardized file formats like DXF or STEP.
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) Software: CAM software takes the CAD design and converts it into instructions that can be understood by the CNC machine. It generates tool paths and specifies cutting operations, speeds, feeds, and other parameters.
- Controller: The controller acts as the central processing unit of the CNC system. It receives instructions from the CAM software and translates them into electrical signals that drive the motors and actuators on the CNC machine. The controller also monitors machine position and movement through feedback sensors.
- Motors and Drives: CNC machines utilize various types of motors (such as stepper motors or servo motors) and motor drives to control the movement of machine axes (X, Y, Z, and sometimes additional rotational axes).
CNC technology enables manufacturers to achieve high precision, repeatability, and efficiency in their production processes. It finds applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and furniture, where accurate and automated manufacturing processes are essential.

The difference between conventional numerical control and computerized numerical control systems is that in the case of conventional systems, the tape goes through the reader for each job, however, in the case of computer systems, the program is entered once and then stored permanently in the computer’s memory. Additional and computational flexibility capability is offered by CNC systems compared to conventional control systems.
Working of CNC
- A CNC machine, also known as a Computer Numerical Control machine, operates by following a specific sequence of actions to perform various tasks with precision and accuracy. The CNC machine receives instructions from a computer program, which controls its movements and operations.
2. Initially, the operator creates a design or model of the desired object using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This design is then converted into a machine-readable format, usually a G-code, which contains a series of commands that the CNC machine can understand.
3. Next, the operator loads the G-code program into the CNC machine’s computer control system. The machine consists of various components such as motors, drives, and a controller, which work together to execute the instructions.
4. Once the program is loaded, the operator secures the workpiece onto the machine’s worktable or fixture. The workpiece could be made of various materials, including metal, plastic, or wood.
5. When the machine is activated, the controller interprets the G-code instructions and sends signals to the appropriate motors and drives. These signals control the movement of the machine’s axes, which typically include X, Y, and Z axes representing horizontal, vertical, and depth movements respectively.
6. The cutting tool, attached to a spindle, moves according to the programmed instructions. The spindle can rotate at high speeds, allowing the cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece. The precise movements of the axes and the rotation of the spindle enable the CNC machine to shape and form the workpiece according to the design specifications.
7. Throughout the process, sensors and feedback systems may be incorporated to ensure accuracy. These systems can measure variables such as tool position, workpiece dimensions, and cutting forces, providing real-time data to the controller.
8. The CNC machine continues executing the programmed instructions until the entire design is produced or the required operations are completed. Once finished, the operator unloads the workpiece and inspects it for quality and accuracy.
9. A CNC machine works by utilizing a computer program to control the movement and operation of various components, allowing for precise and automated manufacturing processes. It combines the power of computer control with mechanical precision to efficiently produce complex parts and objects.

Advantages of CNC Systems
CNC systems have a number of advantages. The following discussion lists some of the advantages of CNC systems over conventional NC systems:
• In-place machining tape editing: the instruction program on the tape can be optimized for parameters such as feed, speeds, and tool path during machine tool operation.
• Limited tape usage: the tape is read once and the instruction program written on it is stored in the computer’s memory. Reliability is therefore increased as a result of limited tape usage.
• Metric Conversion: CNC machining systems have the ability to convert tape to international systems of units starting from inches.
• Greater flexibility: CNC machining systems are flexible compared to conventional NC systems. New control features, such as new interpolation schemes, can be adopted easily and at the lowest cost. Furthermore, the risk of CNC systems becoming obsolete is also reduced.
• Total fabrication systems: CNC systems can be conveniently used with factory-wide computerized fabrication systems, which is one of the main advantages of CNC over conventional NC systems.
CNC FAQ
What is the difference between CNC milling and CNC turning?
CNC milling involves rotating the cutting tool while the workpiece remains stationary, while CNC turning involves rotating the workpiece while the cutting tool moves along the workpiece’s circumference.
What are the advantages of CNC machining over conventional machining?
CNC machining offers increased precision, repeatability, and automation compared to conventional machining. It allows for complex designs, faster production, and reduced human error.
What are the primary axes in a CNC machine?
The primary axes in a CNC machine are typically X, Y, and Z axes, representing horizontal, vertical, and depth movements, respectively. However, some CNC machines may have additional rotational axes.
What is the role of CAM software in CNC machining?
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software is used to generate the toolpaths and instructions necessary for CNC machines to manufacture a specific part. It translates design files into machine-readable code (G-code).
What is multi-axis CNC machining?
Multi-axis CNC machining refers to the use of CNC machines that have more than three axes. These machines can perform complex operations by simultaneously moving the tool along multiple axes, enabling the production of intricate geometries.
How does CNC automation contribute to increased productivity?
CNC automation allows for continuous and unmanned operation of the machines, minimizing downtime between operations. This leads to increased productivity as machines can run 24/7, reducing the need for manual intervention.
What are the different types of CNC machining processes?
CNC machining encompasses various processes, including milling, turning, drilling, boring, grinding, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). Each process is suited for specific applications and materials.
What is CNC retrofitting?
CNC retrofitting involves upgrading or modernizing existing conventional machines by adding CNC controls and systems. It is a cost-effective way to improve the capabilities and performance of older machines.
What are the common materials used in CNC machining?
CNC machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics (e.g., ABS, acrylic, PVC), composites, wood, and foam. The material choice depends on the desired properties and application requirements.
What are the limitations of CNC machining?
Despite its numerous advantages, CNC machining has certain limitations. It may not be suitable for very small-scale production due to setup and programming costs. Additionally, complex geometries with undercuts may require specialized techniques or post-machining processes.
























Comments on “What is Computer Numerical Control (CNC)?”