Table of Contents
Introduction to vapor compression refrigeration:
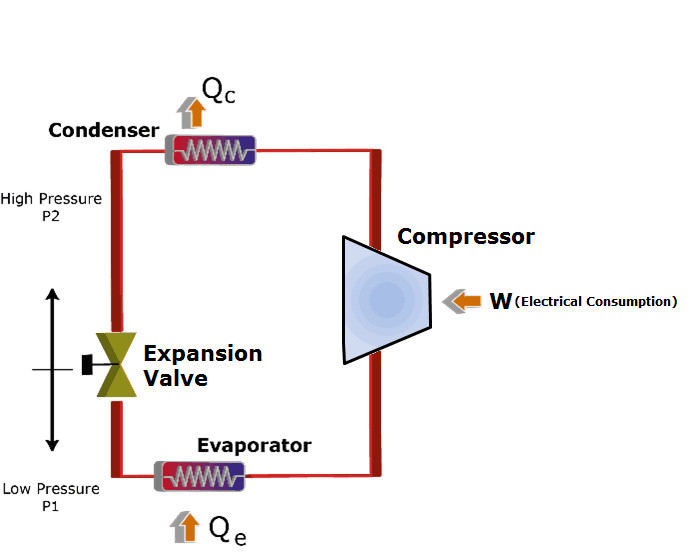
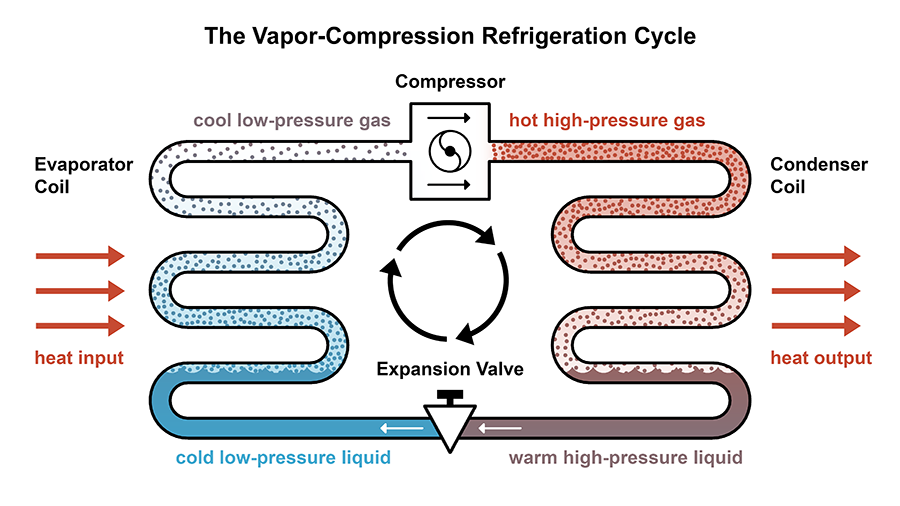
The compression refrigeration cycle consists of circulating a liquid refrigerant through four stages of an unrestricted system. As the refrigerant circulates through the system, it alternatively compresses and expands, changing its state from liquid to vapor. As the refrigerant changes state, the system absorbs and expels heat, reducing the temperature of the conditioned space.
Components used in the vapor compression refrigeration system:
All parts of the vapour compression refrigeration system are connected via a tube. The detailed explanation is as follows.
Compressor :
At low pressures and low temperatures, Vapour enters the compressor from the evaporator, where it’s compressed to high pressures and high temperatures.
condenser :
The condenser may also be called a cooler, as it cools and condensed the very high pressure and temperature vapour refrigerants.
This high-pressure, high-temperature vapour refrigerant is discharged through the discharge stopcock into the condenser. As it passes through the condenser, the refrigerant releases its idle heat into the girding condensing medium, generally air or water.
Receiver:
The condensed liquid refrigerant from the condensers is deposited in a vessel known as a receiver, from where it’s supplied to the evaporators through an expansion stopcock.
Expansion valve:
It’s also called a butterfly valve. Its functions are to allow the passage of liquid refrigerant at high pressures and temperatures, where it reduces its temperature and pressure.
Evaporator:
It also includes tubular coils in which liquid vapor coolers dematerialize at low pressures and temperatures and come into vapor coolers at low pressures and temperatures.
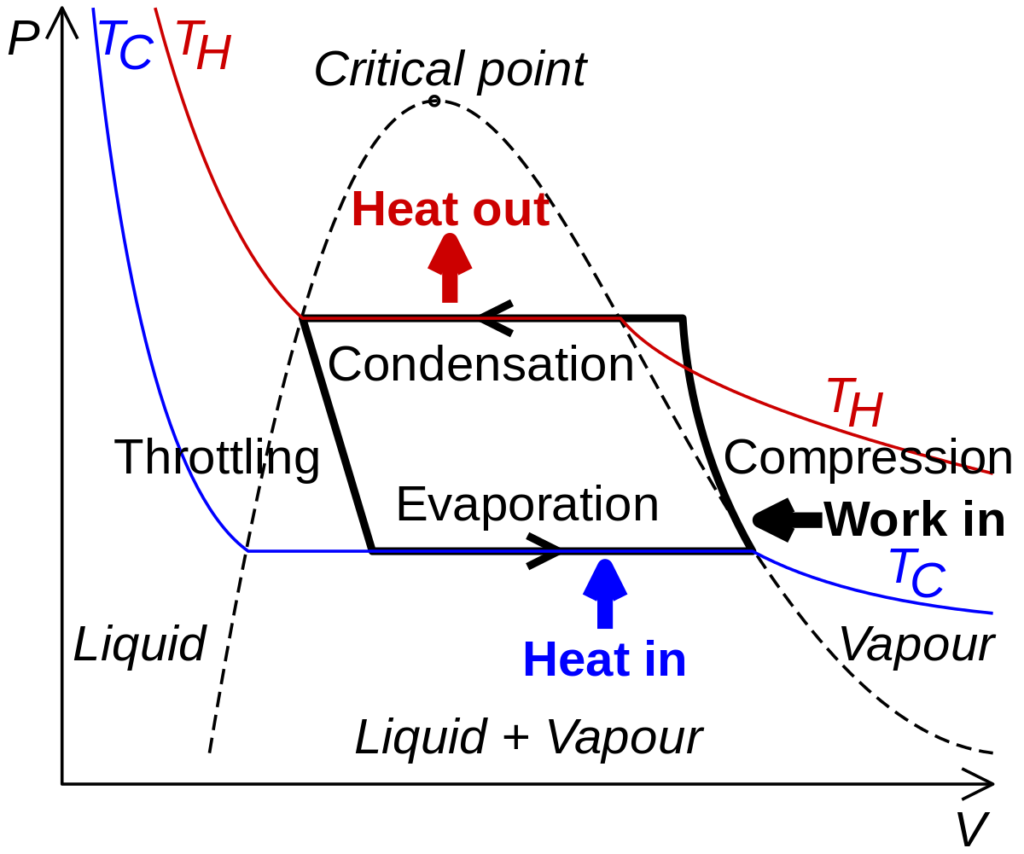
Image credit: Wikipedia
How does the vapor compression refrigeration system work?
The operation of the compression refrigeration system can be completed in 4 processes and they’re as follows.
1. compression process:
Most at low temperature and low pressure enter the compressor where it’s compressed isentropically and latterly its temperature and pressure are increased vastly.
2. Condensation process:
The mist, after leaving the compressor, enters the condenser, where it’s condensed to liquid at high pressure and collected in a receiving tank.
3. Expansion process:
From the receiving tank, it passes through the expansion stopcock, where it’s strangled at low pressure and temperature.
4. Storming process:
After passing through an expansion stopcock, it eventually passes to the evaporator, where it excerpts still from the terrain or the circulation fluid and vaporizes at a lower vapor pressure. still, the temperature position drops to a veritably low position, so it must suffer sensible heat and idle heat to reach the evaporation stage If expansion occurs without strangling.
What are the types of vapor compression refrigeration cooling systems?
Heat flows naturally from a hot body to a cooler one. In the refrigeration system, the contrary must do, that is, heat flows from a cold body to a hotter one. This is done through the use of a substance called refrigerant, which absorbs heat and thus boils or evaporates under low pressure to form a gas. This gas is also compressed to an advanced pressure so that it transfers the heat it has gained to the girding air or water and turns( condenses) into a liquid.
In this way, heat is absorbed or removed from a low-temperature source and transferred to an advanced-temperature source. The refrigeration cycle can be divided into the following stages.
1. The low-pressure liquid refrigerant in the evaporator absorbs heat from the terrain, generally air, water, or some other process fluid. During this process, it changes state from liquid to gas and, at the exit of the evaporator, slightly overheats.
2. Superheated brume enters the compressor where its pressure increases. There will also be a large temperature rise as part of the energy input in the contraction process is transferred to the refrigerant.
3. High-pressure superheated gas passes from the compressor to the condenser. The original part of the cooling process( 3- 3a) removes superheat from the gas before converting it back to liquid( 3a- 3b). Cooling for this process is generally fulfilled using air or water.
There’s also a temperature reduction in the pipes and the liquid force( 3b- 4) so that the coolant liquid is subcooled when entering the expansion device
4. The high-pressure subcooled liquid passes through the expansion device, which reduces its pressure and controls the inflow to the evaporator.
What are the Advantages of vapour compression refrigeration system?
- The size is small compared to a per-air cooling system for a given cooling capacity.
- The operating cost is low.
- High coefficient of performance.
- The operating temperature range is huge.
- The temperature in the evaporator can be easily controlled by adjusting the expansion valve.
- The latent heat involved in the phase change ensures a high heat elimination value, while the air refrigeration system only has sensible heat.
- Requires a smaller evaporator.
What are the disadvantages of a vapor compression refrigeration system?
- High initial cost, expensive soda.
- Dangerous refrigerant for the environment involved.
- You must ensure the prevention of coolant leaks.
Visit the home page for trending topics

















Comment on “The vapor compression refrigeration cycle”
Comments are closed.