Table of Contents
Boilers can be classified in several ways based on their design, fuel source, and purpose. Following are some common classifications:
Based on Design:
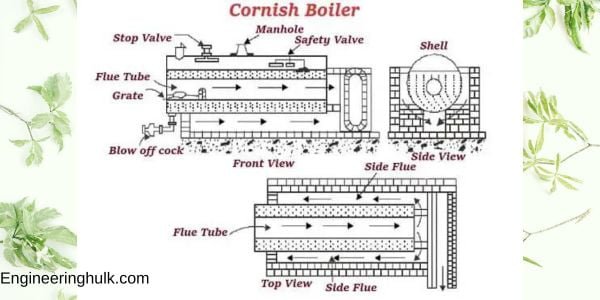
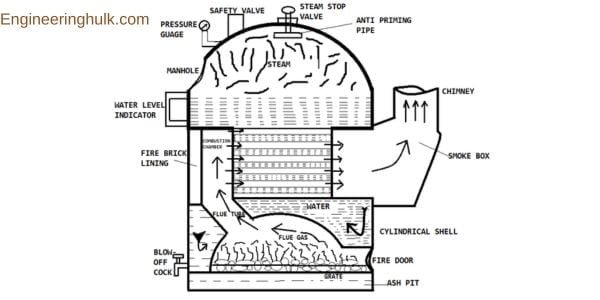
a) Fire Tube Boilers:
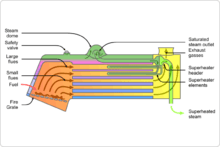
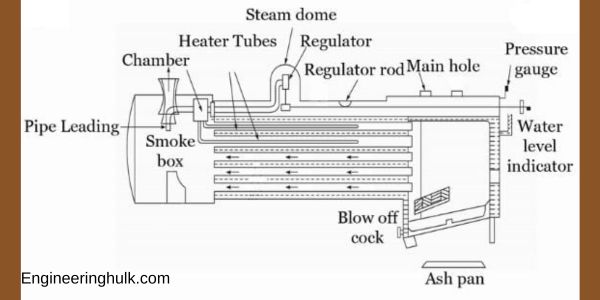
Fire Tube Boilers are a popular type of boiler that utilizes hot gases produced by combustion to heat water passing through tubes within a cylindrical shell. As the hot gases flow through the tubes, they transfer their heat to the water surrounding the tubes, causing it to turn into steam.
The basic structure of a fire tube boiler consists of a tube bundle enclosed by a cylindrical shell. The tubes are arranged in a manner that maximizes the surface area available for heat transfer, while the flue gases produced during combustion exit the boiler through a chimney or stack.
Fire tube boilers are generally used for low-pressure applications that require steam or hot water. They are straightforward to operate and maintain, making them suitable for use in small to medium-sized facilities. However, they are less efficient than water tube boilers and are not appropriate for high-pressure applications.
Fire tube boilers are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings for heating and process applications. Their simplicity of operation and compact size make them ideal for use in steam locomotives and ships.
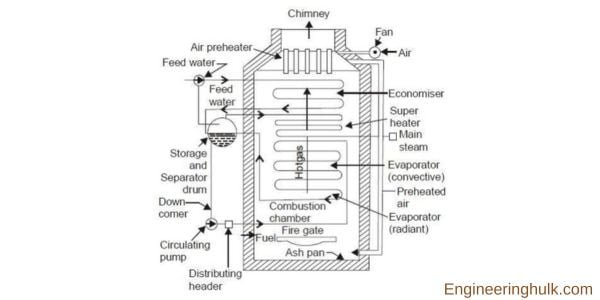
b) Water Tube Boilers:
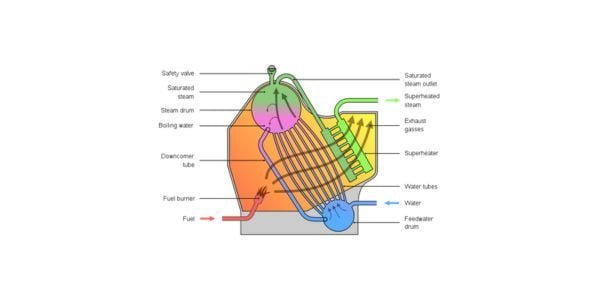
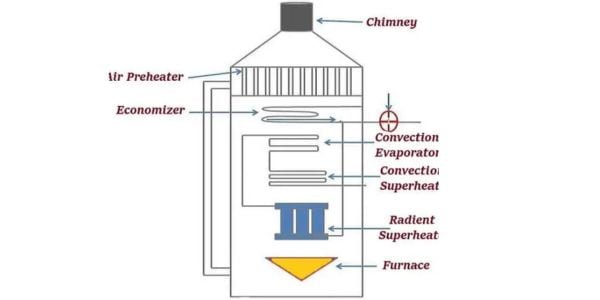
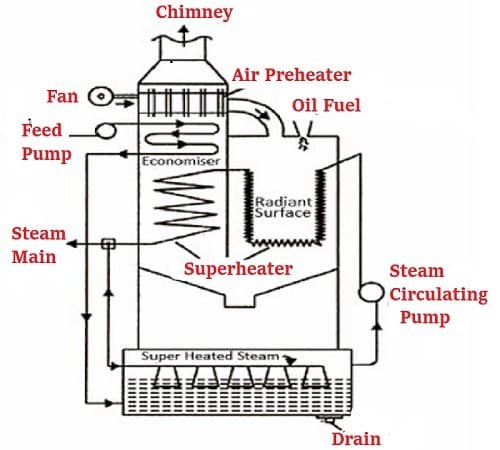
Water tube boilers are a type of boiler commonly used for generating steam or hot water for industrial or heating purposes. These boilers operate by circulating water through tubes that are heated by hot gases produced by a furnace or burner. As the heat from the gases is transferred to the water in the tubes, it produces steam or hot water that can be utilized for various applications.
Compared to fire tube boilers, water tube boilers are generally more efficient as they offer a larger surface area for heat transfer. Moreover, they are considered safer since the water is enclosed in the tubes rather than in a large, pressurized vessel like a fire tube boiler. Furthermore, water tube boilers are capable of handling higher pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for high-pressure applications.
There are several types of water tube boilers, including straight-tube boilers, bent-tube boilers, cyclone-fired boilers, and flex-tube boilers. Straight-tube boilers have straight tubes that run through the boiler and are surrounded by hot gases. Bent tube boilers, on the other hand, have bent tubes that provide greater flexibility in design and can be used in a wide range of applications.
Cyclone-fired boilers utilize a cyclone furnace to burn fuel and generate hot gases, which are then circulated through the tubes. Lastly, flex-tube boilers have flexible tubes that can expand and contract with temperature changes, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Classification Criteria| Types |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Pressure Range | 1. Low-Pressure Boilers |
| | 2. Medium-Pressure Boilers |
| | 3. High-Pressure Boilers |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Construction Type | 1. Fire Tube Boilers |
| | 2. Water Tube Boilers |
| | 3. Packaged Boilers |
| | 4. Compact Boilers |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Circulation Type | 1. Natural Circulation Boilers |
| | 2. Forced Circulation Boilers |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Fuel Type | 1. Coal-Fired Boilers |
| | 2. Oil-Fired Boilers |
| | 3. Gas-Fired Boilers |
| | 4. Biomass Boilers |
| | 5. Electric Boilers |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Application | 1. Power Generation Boilers |
| | 2. Heating Boilers |
| | 3. Industrial Process Boilers |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Type of Steam | 1. Wet Steam Boilers |
| | 2. Dry Steam Boilers |
| | 3. Superheated Steam Boilers |
+------------------------+----------------------------------------+
Based on Fuel Source:
a) Gas Boilers:

A gas boiler is a heating system that uses gas as its fuel source to provide warmth to a building. The process begins by burning natural gas, propane, or other gases in the boiler’s heat exchanger, which generates heat that is transferred to the water. This process heats the water to a high temperature and creates steam, which is then distributed throughout the building via the heating system.
Gas boilers are commonly used in residential and commercial settings because they are efficient and relatively easy to install. They are versatile and can be used for various heating purposes, including providing hot water for showers, baths, and kitchens.
It is crucial to maintain gas boilers regularly to ensure they operate safely and efficiently. This includes yearly inspections, cleaning, and servicing by a qualified technician. Carbon monoxide can be produced by gas boilers if they are not adequately maintained, posing a severe health hazard. Therefore, it is essential to have a carbon monoxide detector installed in any building that uses a gas boiler.
b) Oil Boilers:
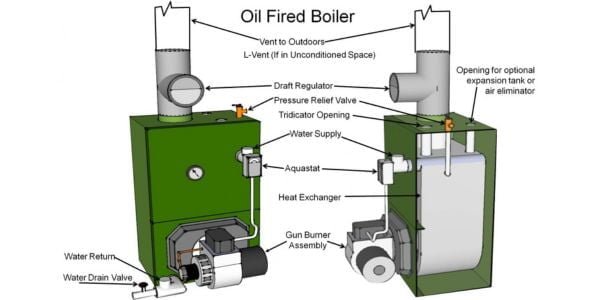
Oil boilers are a type of heating system that uses oil as a fuel source to provide warmth to homes or buildings. This type of boiler is commonly used for both residential and commercial heating purposes.
The way an oil boiler works is through the combustion of oil in a burner, which produces heat that is then transferred to water or air via a heat exchanger. The heated water or air is then circulated throughout the building through pipes or ductwork.
There are two types of oil boilers: regular boilers and combi boilers. Regular boilers require a separate hot water cylinder to store the heated water, while combi boilers provide both heating and hot water on demand without the need for a separate cylinder.
One of the main advantages of oil boilers is their high heating efficiency, especially when used in conjunction with modern controls like thermostats and timers. Additionally, oil is widely available and can be stored on-site, making it a convenient fuel source for those without access to gas lines.
However, oil boilers also have some disadvantages. Regular maintenance and cleaning are required to ensure efficient operation, and there is always the risk of oil spills and environmental pollution. Additionally, oil prices can fluctuate, which can impact the cost of heating a building.
c) Solid Fuel Boilers:
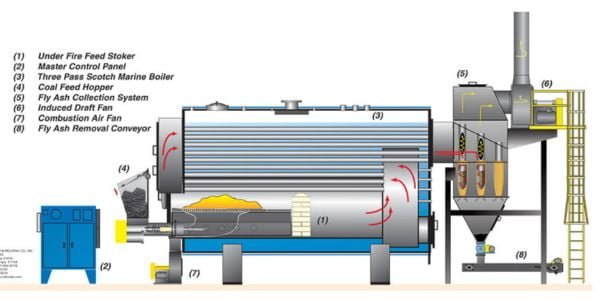
Solid fuel boilers are heating systems that utilize solid fuels such as coal, peat, wood, or biomass to provide warmth. These types of boilers are ideal for areas without access to a gas supply or in locations where electricity prices are high.
Solid fuel boilers work by combusting the fuel in a combustion chamber, which then heats water in a heat exchanger. The heated water is then circulated to radiators or underfloor heating systems to warm up a building or home.
There are various types of solid fuel boilers, including traditional cast iron boilers, modern steel boilers, and boilers that feature automated feeding systems to provide a steady supply of fuel. Some solid fuel boilers can also be fitted with a back boiler, allowing them to heat water for domestic use.
Solid fuel boilers need regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operation. Additionally, they require a constant supply of fuel, which can be a significant expense for some households. However, for those who have a reliable and affordable supply of solid fuel, solid fuel boilers can be an efficient and cost-effective way to heat their homes.
d) Electric Boilers:
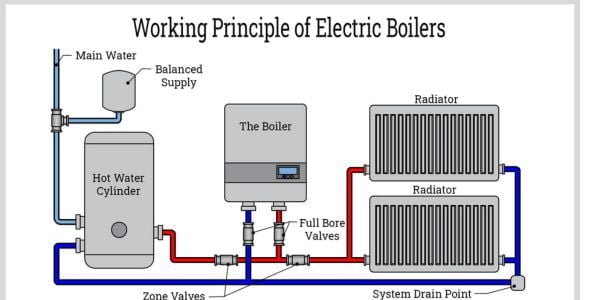
Electric boilers are a type of heating system that uses electricity to heat water, which is then circulated around a property to provide heating and hot water. Unlike gas or oil boilers, electric boilers do not produce any harmful emissions, making them an environmentally friendly option for homeowners.
One of the main benefits of electric boilers is their efficiency. Electric boilers have a very high-efficiency rating, typically around 99%, meaning that almost all of the energy used to heat the water is converted into heat. This makes them one of the most efficient heating systems available and can result in lower energy bills for homeowners.
Another advantage of electric boilers is their compact size. Electric boilers are typically smaller than gas or oil boilers and can be installed in a variety of locations, including in small apartments or homes with limited space. They are also easier to install than traditional boilers, as they do not require a flue or ventilation system.
Electric boilers are also very reliable and require very little maintenance. Unlike gas or oil boilers, which require annual servicing to ensure they are functioning safely and efficiently, electric boilers require minimal maintenance, making them a low-maintenance option for homeowners.
Also, there are also some disadvantages to electric boilers that should be considered. One of the main disadvantages is their cost. Electric boilers can be more expensive to run than gas or oil boilers, as electricity is generally more expensive than gas or oil. However, this can vary depending on the energy tariffs available in your area.
The second disadvantage of electric boilers is their slower heating time. Electric boilers can take longer to heat water than gas or oil boilers, meaning that homeowners may have to wait longer for hot water or heating to be available. However, this can be mitigated by choosing a larger capacity electric boiler, or by using a timer to ensure that the boiler is heating the water in advance.
Based on Purpose:
a) Residential Boilers:
Residential boilers are heating systems used in houses to provide warmth and hot water. They typically run on natural gas, propane, or oil, and operate by heating water, which is then circulated through the house via pipes and radiators.
There are generally two primary types of residential boilers: hot water boilers and steam boilers. The more common type is hot water boilers, which function by heating water to a specific temperature and then distributing it throughout the house via radiators or baseboard heaters. Steam boilers, however, operate by heating water to generate steam, which is then circulated throughout the house via pipes and radiators.
Residential boilers are often more energy-efficient than other heating systems since they can be used for both heating and hot water. Additionally, they can be a more cost-effective option in areas where natural gas prices are lower than electricity prices.
These boilers need regular maintenance to ensure they operate efficiently and avoid potential safety hazards. Homeowners should consult with a professional to determine the best type and size of boiler for their home, as well as to ensure proper installation and ongoing maintenance.
b) Commercial Boilers:
Commercial boilers are heating systems that are specifically designed for use in commercial and industrial settings, such as office buildings, hospitals, schools, and factories. They are used to provide a consistent supply of hot water or steam for a variety of heating applications.
These boilers come in various sizes and types, including both condensing and non-condensing models. Condensing boilers are generally more energy-efficient, as they are able to capture and recycle heat that would otherwise be lost. Non-condensing boilers are often less expensive to purchase, but may not be as efficient overall.
The fuel source for commercial boilers can vary, with options including natural gas, propane, oil, and electricity. The choice of fuel will depend on factors such as availability, local regulations, and cost.
To ensure safe and efficient operation, proper installation and maintenance of commercial boilers are critical. Regular inspections, cleaning, and servicing by a qualified technician can help prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the boiler. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance is also important.
c) Industrial Boilers:
These boilers are designed for use in industrial applications such as power generation, chemical processing, and food production.
d) Marine Boilers:
Marine boilers are specifically designed for use on ships and play a crucial role in the marine propulsion system by generating steam that powers turbines or engines to propel the vessel. Due to limited space on ships and the need for high power output, marine boilers are designed to be compact and efficient. They are also built to withstand harsh marine environments, including saltwater corrosion and vibrations.
There are several types of marine boilers used on ships, including fire-tube boilers, water-tube boilers, and composite boilers that combine elements of both. To ensure safety, marine boilers are equipped with special features like high and low water alarms, pressure relief valves, and automatic controls that prevent overpressure or overheating. Proper maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of marine boilers.
e) Nuclear Boilers:
The term “nuclear boilers” is not commonly used in the nuclear industry, and its meaning is not entirely clear. However, it seems to refer to the process of using a nuclear reactor to generate steam, which is similar to how a boiler works.
In a nuclear reactor, nuclear reactions generate heat which is used to produce steam. The steam then drives a turbine to generate electricity. While this process is similar to how a traditional boiler works, there are important differences between the two. A nuclear reactor uses nuclear fuel, such as uranium, to generate heat through nuclear fission. In contrast, a traditional boiler typically uses fossil fuels or other sources of heat to create steam.
It’s important to note that nuclear reactors are complex devices that require careful controls and safety features to ensure that the nuclear reaction remains safe and controlled. Therefore, while the term “nuclear boiler” may be used to describe the process of generating steam using a nuclear reactor, it is important to understand that nuclear reactors are highly specialized and require extensive safety measures to operate safely.
FAQ
What are the classifications of boilers based on pressure levels?
Boilers can be classified as low pressure (up to 15 psi), medium pressure (between 15 psi and 300 psi), and high pressure (above 300 psi). The pressure level determines the design and construction of the boiler.
What are the classifications of boilers based on the method of heat transfer?
Boilers can be classified as convective, radiant, or combination boilers. Convective boilers transfer heat through convection, radiant boilers transfer heat through radiation, and combination boilers use both convection and radiation for heat transfer.
What is the difference between a boiler and a furnace?
A boiler is a heating system that uses water or steam to generate heat, while a furnace uses air. Boilers are commonly used for heating homes and buildings, while furnaces are typically used for forced-air heating.
What is boiler efficiency?
Boiler efficiency refers to how effectively a boiler converts fuel into usable heat. It is typically measured as a percentage and can be affected by factors such as the design, fuel type, insulation, and maintenance of the boiler. Higher efficiency means less fuel is wasted and lower operating costs.
How do I maintain a boiler?
Boiler maintenance is important to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular tasks may include:
Checking and cleaning the heat exchanger, burner, and flue.
Testing safety controls and pressure levels.
Inspecting and cleaning the system’s water supply and condensate drains.
Removing any sediment or debris from the boiler.
Checking for leaks, rust, or corrosion.
Following manufacturer guidelines and scheduling professional servicing.What is a boiler’s life expectancy?
The life expectancy of a boiler can vary depending on factors such as its type, usage, maintenance, and the quality of its components. On average, well-maintained boilers can last between 15 and 30 years. Regular maintenance and prompt repairs can help extend the lifespan of a boiler.
What are the common boiler problems?
Some common boiler problems include:
Leaks or dripping.
No heat or insufficient heat.
Strange noises, such as banging or whistling.
Pressure loss or fluctuations.
Pilot light or ignition issues.
Frozen condensate pipe (for condensing boilers).
Faulty thermostat or controls.
Scaling or sediment buildup.Can a boiler be used for both heating and hot water?
Yes, many boilers are designed to provide both heating and hot water. These are often referred to as combination or combi boilers. They can heat the water for your radiators or baseboard heaters while also providing hot water for taps and showers.
Are boilers energy efficient?
Boilers can be highly energy efficient, especially newer models with advanced features. Condensing boilers, for example, are designed to capture and reuse heat from exhaust gases, increasing their efficiency. Choosing a high-efficiency boiler, with proper insulation, and regular maintenance can help improve energy efficiency.
What is the difference between a regular boiler and a system boiler?
A regular boiler, also known as a conventional or traditional boiler, requires a separate hot water cylinder and cold-water storage tank. It is suitable for larger properties with higher hot water demands. In contrast, a system boiler incorporates the heating and hot water components into a single unit, eliminating the need for a separate cylinder.
Can boilers use renewable energy sources?
Yes, boilers can be adapted to use renewable energy sources such as biomass, solar thermal energy, or geothermal energy. Biomass boilers burn organic materials like wood pellets or agricultural waste, while solar thermal systems use the sun’s energy to heat water. Geothermal heat pumps utilize the stable temperature of the ground to provide heating and cooling. These renewable options can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Also, read Prospects of geothermal energy in India















Comment on “Boiler Classification: Types, Components & Applications”
Comments are closed.