Table of Contents
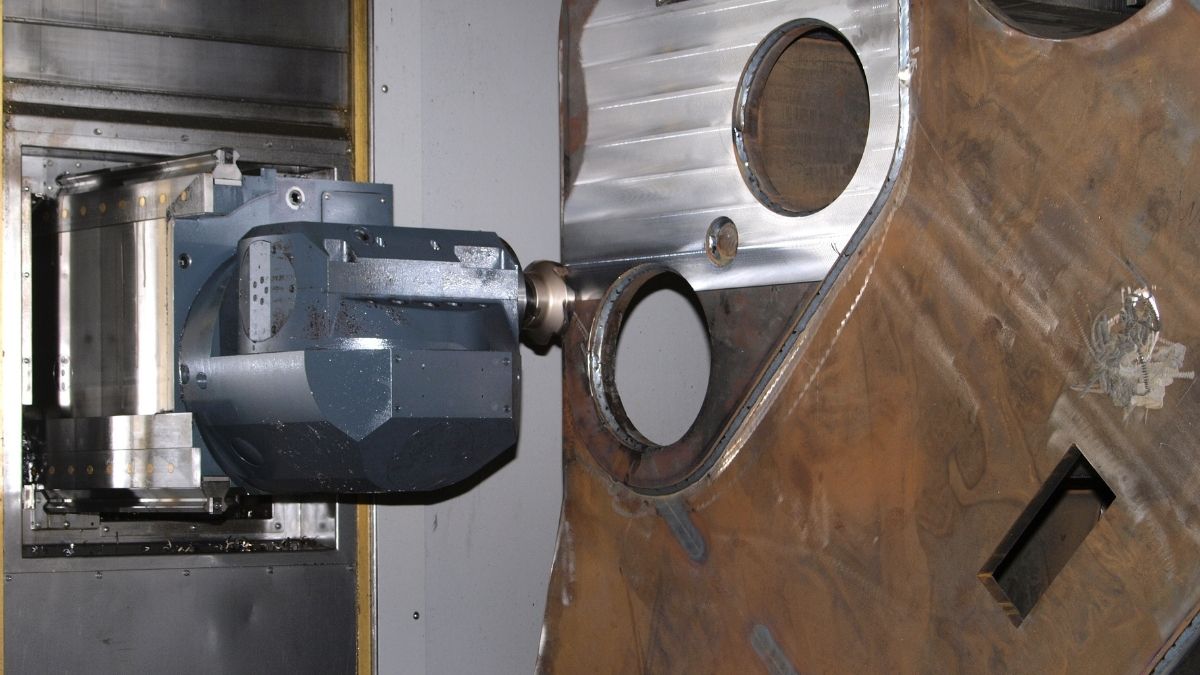
Ultrasonic machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from the surface of a part through low-amplitude, high-frequency vibrations of a tool against the material surface in the presence of fine abrasive particles. Ultrasonic vibration machining physically operates through the mechanism of microchip or erosion on the surface of the workpiece.
As the abrasive slurry is kept in motion by low amplitude and high-frequency vibrations, the impact forces of the slurry are significant and cause high contact stresses. These high contact stresses are achieved by the small contact area between the mud particles and the workpiece surface. Brittle materials fail by crack mechanics and these high stresses are sufficient to cause microparticles to be removed from their surface. The material as a whole does not fail due to extremely localized stress regions.
Ultrasonic Machining in Industries:
Ultrasonic machining is changing manufacturing industries with its superlative performance. The main reason this machining process is used in the manufacturing area is that it involves less heat in the process. All operations carried out with the ultrasonic machining method are economical and with better results.
Ultrasonic machining is an abrasive process that can convert any material into a hard and brittle form with the help of its vibrating tool and the indirect passage of abrasive particles into the workpiece. It is a low material removal rate machining process.
Also known as ultrasonic impact grinding, it is an operation that involves a vibrating tool that fluctuates ultrasonic frequencies to remove material from the workpiece. The process involves an abrasive paste that runs between the tool and the workpiece. Because of this, the tool and part never interact with each other. The process rarely exceeds two pounds.
Ultrasonic Machining Process:
The tool present in the machine for cutting the materials is made of a material that is soft to the workpiece. The tool is usually made of materials such as mild steel and nickel. When the tool vibrates, abrasive suspension (liquid) containing abrasive particles and grains is added. The abrasive slurry is added until the parts interact with the grains. Due to the added liquid particles, the workpiece’s fragility wears out the surface as the tool gradually deforms.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Machining:
- Machining of all types of hard materials
- Produces fine, structured results.
- Produces less heat Various ways to cut holes due to vibrating tool movement
- Various ways to cut holes due to vibrating tool movement
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Machining:
- It requires a greater degree of integrity and skills.
- No certified X-ray record
- Unnecessarily large grain sizes cause defects
- Additional repairs may be required due to false signals and misunderstanding of the process
Ultrasonic machines are the future of machining and are used all over the world to create hard and brittle materials for industrial use. Many operations can be performed with the ultrasonic machine which can benefit industrialists in many ways. Advanced technology creates a solution that helps open up market opportunities and makes things easier.
Main four types of abrasive solutions: –
- Aluminium oxide.
- Silicon Carbide
- Boron carbide
- Diamond dust
These four types of solutions are used in ultrasonic machining depending on the material to be machined. Aluminum oxide is very light and loses its intensity very quickly. Diamond powder is the hardest of these four slurries and is used to machine very fragile materials.
Silicon carbide and boron carbide have a hardness between diamond dust and aluminum oxides. Two slimes can be used individually, or mixtures of these two can be used as slimes. Ultrasonic machining works based on the magnetostrictive action of machining.
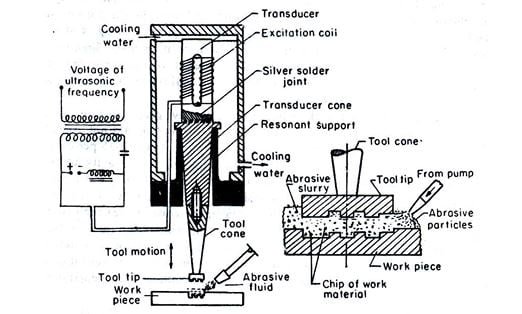
In magnetostrictive action, when we send a frequency to the transducer, the transducer will change those frequencies to vibration. These transducers are a kind of electromagnet; when we give an electrical signal, it converts it into mechanical vibration.
It will work at over 20,000 oscillations per second. It is a silent process because the human ear cannot hear this high frequency and that is why it is called ultrasonic frequency. The equipment that will be used in this process will be made of soft metal so that we can easily mold the tool into any shape. The cavity created in the machining will be proportional to the size of the respective tool. Therefore, the tool is selected from soft metal so that it can be molded into any shape.
Working principle of ultrasonic machining process:
In an ultrasonic machining operation, the difference between the tool and the part is 0.25 mm. The device is made of ductile material. Between the tool and the workpiece, there is an abrasive solution. This material will flow out of the machining area, causing the paste tool to flow slightly thinner to create a perpendicular hole.
The abrasive is incorporated into the tool, and during the downward stroke of the tool, the removal of the abrasive material hits the workpiece; the rate decreases due to the difficulty of flushing when the viscosity of the carrier fluid material increases. Increasing the frequency will increase the MRR as the number of effects per unit of time increases.
As the amplitude increases, the MRR will increase as the speed of the abrasive increases. The vibration amplitude varies from 5 to 75 μm, and the frequency can vary from 19 to 25 kHz. By increasing the abrasive concentration, the effect will be in more places, which increases the MRR.
As the size of the abrasive increases, an effect will be seen over a larger area. But when the sizes increase beyond certain values, the abrasive speed decreases. But when the concentration increases beyond a certain value, the MRR decreases due to a collision between the abrasive moments.
High-frequency electrical currents (in the ultrasonic range, i.e. 18 kHz to 40 kHz) are used to generate high-frequency, low-amplitude mechanical vibrations. The mechanical vibrations generated are used for the surface machining of a part in the presence of particles of abrasive grain in the form of paste.
The slurry flows through the equipment and workpiece as the tool presses against the W/P, the slurry contains the abrasive particle chips of the material on the surface.