Table of Contents
1. Noisy gearbox operation:
• The bearings may be worn, in which case they will need to be replaced.
• The countershaft can be worn, bent, or have a large axial play. This must be replaced with a new countershaft.
• Constant-mesh gears can be worn. The only alternative is their replacement.
• Lack or the wrong grade of lubricant. The gearbox must be filled with the specified lubricant.
• The gears can be worn; need to be replaced.
• The gears may be loose on the main shaft. This may be due to worn splines or gears on the main shaft. The worn part must be replaced to remedy the defect.
• The mounting bolts may be loose and may be tightened.
2. Hard shifting:
• The clutch adjustment may be incorrect, which should be correct.
• The clutch connection may be constrained. The same can be repaired or lubricated as needed.
• There may be a misalignment of the clutch housing. The runout at the rear of the clutch housing can be checked and corrected if necessary.
• The main shaft gears may be tightened on the splines. To eliminate the problem, the splines of the main shaft are cleaned and lubricated. If this is not effective, the narrow gear or shaft must be replaced.
• The shifting mechanism may not be properly adjusted or lubricated, which should be done immediately.
• The Synchromesh unit may be jammed or damaged. Damaged parts must be replaced. If there is no damage, immediately lubricate the unit.
• The ball joint of the shift lever may be binding
3. Gears collide when changing:
• The clutch adjustment may be incorrect, which can be checked and corrected if necessary.
• The clutch connection can be constrained, which can be repaired or lubricated as needed.
• Clutch housing misalignment can be another reason, which can be checked on the rear side and corrected if necessary.
• Components of the shifting mechanism or synchronizer assemblies can be worn or damaged. To correct this, the gear must be removed and disassembled. During the inspection, defective components can be identified and replaced.
• The lubricant may be of the wrong specification or its level may be lower. To remedy this, empty and refill the gearbox with suitable oil. Also, check for any source of the leak if the level was low and repair if necessary.
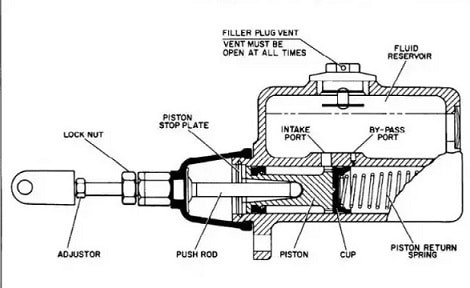
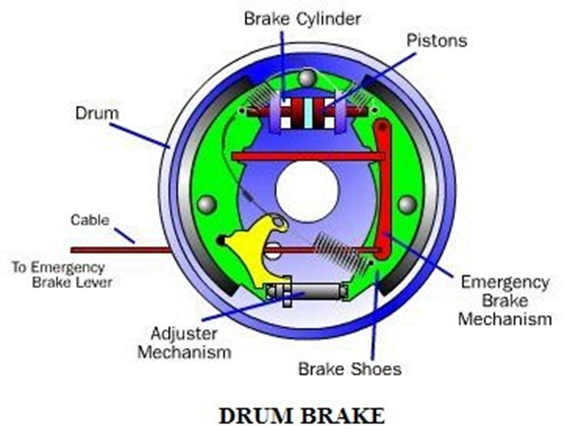
4. Transmission oil leak:
• Damaged oil seals, which should be replaced.
• Seals damaged or even missing. The only alternative is a replacement.
• The bolts on the shift cover may be loose, which should be properly tightened.
• The oil used may be more diluted than specified. In this case, the entire oil must be drained and replaced with new oil of suitable characteristics.
• The vent (vent) hole in the top of the gearbox may be blocked, which could open.
• The oil level in the gearbox may be higher than required; excess oil must be drained.
• The drain plug may be loose or damaged, which can be tightened or replaced as needed.
• The gearbox may be cracked. If the cracks do not extend to the bearing seats, the bearing can be welded, otherwise, it must be replaced.
FAQ
What are the common signs of transmission system problems?
Common signs of transmission system problems include slipping gears, delayed engagement, rough shifting, grinding noises, fluid leaks, and a burning smell.
How can I determine if my transmission fluid needs to be changed?
Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended maintenance schedule. In general, transmission fluid should be changed every 30,000 to 60,000 miles or as specified by the manufacturer. Additionally, if the fluid appears dark, smells burnt, or has a gritty texture, it’s likely time for a change.
What should I do if my transmission is slipping?
If your transmission is slipping, it may be due to low fluid levels, a worn-out clutch, or internal damage. Start by checking the transmission fluid level and condition. If it’s low, top it up to the appropriate level. If the problem persists, it’s best to consult a professional technician for a thorough diagnosis.
Why does my transmission make a grinding noise when shifting?
A grinding noise during shifting can indicate a worn-out clutch, damaged synchronizers, or low transmission fluid. If the noise occurs while shifting gears, it’s crucial to have the transmission inspected by a qualified mechanic to identify the exact cause and perform necessary repairs.
How can I prevent overheating of the transmission?
To prevent transmission overheating, ensure that the transmission fluid is at the correct level and in good condition. Additionally, avoid towing heavy loads beyond the recommended capacity, and if you frequently drive in hot climates or engage in intense driving conditions, consider installing an auxiliary transmission cooler.
What are some common causes of transmission fluid leaks?
Transmission fluid leaks can be caused by a damaged seal or gasket, a loose drain plug, a cracked transmission pan, or a faulty transmission cooler line. It’s important to identify and repair the source of the leak promptly to prevent further damage to the transmission.
Can I tow a vehicle with a damaged transmission?
It is generally not recommended to tow a vehicle with a damaged transmission. Towing can put additional stress on the transmission and exacerbate the existing issues. It’s best to consult a professional technician who can assess the extent of the damage and provide guidance on the safest course of action.
What should I do if my vehicle’s transmission is stuck in one gear?
If your vehicle’s transmission is stuck in one gear, it may be due to a malfunctioning shift solenoid, a faulty valve body, or a computer system issue. First, check if there are any error codes stored in the vehicle’s onboard computer system. If there are, have the codes read and diagnosed by a professional to pinpoint the cause of the problem.
How can I extend the lifespan of my transmission?
To extend the lifespan of your transmission, follow the recommended maintenance schedule, including regular fluid changes. Avoid aggressive driving, excessive towing, and overloading your vehicle. Additionally, allow the transmission to warm up before driving in cold weather and use the correct transmission fluid specified by the manufacturer.
When should I seek professional help for transmission problems?
It’s advisable to seek professional help for transmission problems as soon as you notice any signs of trouble. Ignoring or delaying the diagnosis and repair of transmission issues can lead to more extensive damage and higher repair costs. A qualified technician can accurately diagnose the problem and provide the necessary remedies to get your transmission back in proper working order.



















Comments on “Troubleshooting and Remedies of the Transmission system”