Table of Contents
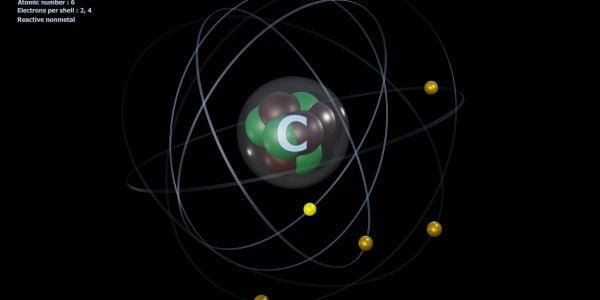
Carbon is a versatile element that plays a critical role in the chemistry of life. At the heart of carbon’s versatility lies its tetravalency – the ability of a carbon atom to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. Tetravalency is one of the fundamental concepts in chemistry, and its understanding is essential to comprehend the structure and function of biological molecules.
What is Tetravalency?
Tetravalency is the property of an atom to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. Carbon is a prime example of a tetravalent atom as it has four valence electrons that can form covalent bonds with other atoms. These covalent bonds can be either single, double, or triple bonds, allowing carbon to form a vast array of organic molecules.
Why is Carbon Tetravalent?
The reason behind carbon’s tetravalency lies in its electronic configuration. Carbon has four valence electrons in its outermost shell, and to achieve a stable configuration, it needs to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. When carbon shares its valence electrons with other atoms, it achieves a stable electronic configuration similar to that of the noble gas, Neon.
This stable configuration is responsible for the chemical reactivity of carbon, allowing it to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions.
Importance of Tetravalency in Organic Chemistry
Tetravalency is crucial to organic chemistry, which is the study of carbon-based compounds. Organic compounds are the basis of all living things, and their unique properties are determined by their molecular structure. Carbon’s ability to form four covalent bonds with other atoms enables it to form long chains, branched structures, and rings, resulting in a diverse array of organic molecules with different properties.
For example, the structure of carbohydrates is determined by the tetravalency of carbon. Carbohydrates are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and they play an essential role in energy storage and structural support in living organisms. The tetravalency of carbon allows the formation of the linear or branched structures of carbohydrates, giving them their distinct properties.
Another example of the importance of tetravalency in organic chemistry is the structure of proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules made up of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | The ability of an atom to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. |
| Key Element | Carbon (C) |
| Electronic Configuration of Carbon | 1s² 2s² 2p² |
| Reason for Tetravalency | Carbon has four electrons in its outer shell. It needs four more electrons to complete its octet. As a result, it forms four covalent bonds with other atoms. |
| Types of Hybridization Involved | sp³, sp², and sp, depending on the nature of the bonds and molecules formed. |
| Examples of Tetravalent Compounds | CH₄ (Methane), CCl₄ (Carbon Tetrachloride), C2H2 (Acetylene with a triple bond and one sigma bond) |
| Significance in Organic Chemistry | Almost all organic compounds have carbon as their backbone due to its tetravalency. This results in the vast diversity of organic compounds. |
| 3D Geometries in Tetravalency | Tetrahedral (e.g., CH₄), Trigonal Planar (e.g., C2H4, where one bond is a pi bond), Linear (e.g., C2H2 with a triple bond) |
| Bond Angles Associated with Geometries | Tetrahedral: 109.5°, Trigonal Planar: 120°, Linear: 180° |
| Notable Properties | Due to tetravalency and catenation ability (self-linking), carbon can form a vast array of compounds, from simple hydrocarbons to complex molecules like DNA. |
Tetravalency is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and carbon’s tetravalency is the cornerstone of organic chemistry. The ability of carbon to form four covalent bonds with other atoms allows for the formation of a vast array of organic molecules with different properties. Understanding tetravalency is crucial in comprehending the structure and function of biological molecules and their significance in living organisms.
Hybridization of Carbon
Hybridization of carbon refers to a process where atomic orbitals of carbon are mixed to form new hybrid orbitals that participate in the bonding of carbon atoms in molecules. Carbon has four valence electrons in its outermost shell, which can form four covalent bonds by sharing these electrons with other atoms.
During hybridization, one or more electrons from the 2s orbital are promoted to the 2p orbitals, resulting in the formation of four identical hybrid orbitals with sp3 hybridization. These hybrid orbitals are oriented towards the corners of a tetrahedron, which is the most stable arrangement for the four electrons in the outermost shell of carbon.
The sp3 hybridization of carbon is commonly found in organic molecules such as methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), and propane (C3H8), where carbon is bonded to four hydrogen atoms or to other carbon atoms via single covalent bonds.
In addition to sp3 hybridization, carbon can also undergo other hybridization schemes such as sp2 and sp hybridization. In sp2 hybridization, one s orbital and two p orbitals combine to create three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals that are arranged in a trigonal planar geometry. This hybridization is found in molecules such as ethene (C2H4) and benzene (C6H6), where carbon forms three covalent bonds via double bonds.
In sp hybridization, one s orbital and one p orbital merge to produce two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals that are aligned in a linear geometry. This hybridization is observed in molecules such as acetylene (C2H2), where carbon forms two covalent bonds through triple bonds.
Also, read the general