Table of Contents
Introduction:
In the realm of power generation and steam production, boilers play a crucial role. One such type of boiler that has gained prominence is the Loeffler boiler. Developed by the German engineer, Sebastian Loeffler, this boiler exhibits unique features that make it a preferred choice in various industrial applications.
Definition of Loeffler Boiler
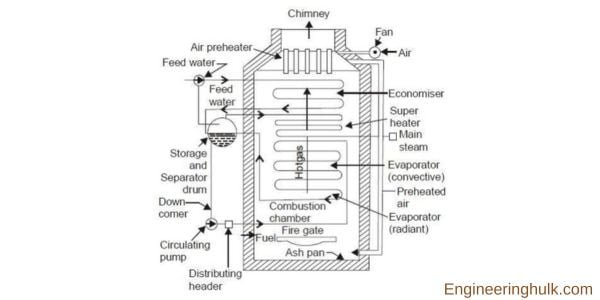
A Loeffler boiler is a type of water tube boiler that operates on the principle of forced circulation. It falls under the category of high-pressure boilers and finds extensive use in power plants where large quantities of steam are required. This boiler is renowned for its ability to burn a wide range of fuels efficiently, making it adaptable to different industrial settings.
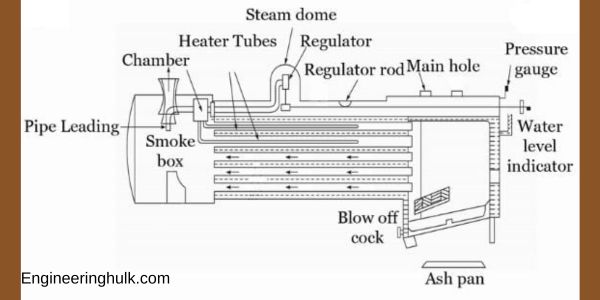
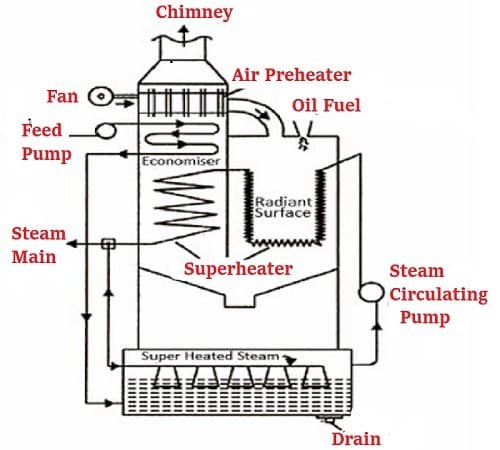
Parts of Loeffler Boiler
1. Furnace:
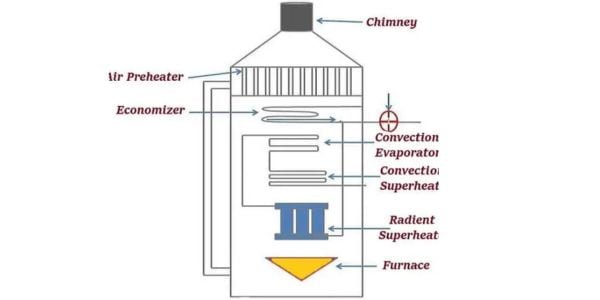
The furnace is the primary chamber where the combustion of fuel takes place. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and houses the burner mechanism responsible for igniting the fuel. In a Loeffler boiler, the furnace is typically cylindrical in shape and lined with refractory materials to ensure heat retention and prevent heat loss.
2. Water Tubes:
Water tubes form a significant part of the Loeffler boiler. These tubes are arranged in a specific pattern to maximize heat transfer from the hot gases to the water circulating inside them. The hot gases pass through these tubes, while water circulates around them. This arrangement promotes efficient heat exchange, resulting in the production of high-quality steam.
3. Economizer:
The economizer is an essential component of the Loeffler boiler that utilizes the waste heat from the flue gases to preheat the feedwater before it enters the boiler system. This preheating process increases the overall thermal efficiency of the boiler, minimizing fuel consumption and energy wastage. The economizer also helps in reducing the environmental impact by lowering the emissions from the boiler.
4. Superheater:
The superheater is responsible for further increasing the temperature of the steam produced by the Loeffler boiler. It is placed in the path of the hot gases, allowing the steam to absorb additional heat and reach a higher temperature. Superheated steam is desirable in many industrial processes as it carries more energy and enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of steam-based applications.
5. Feedwater Pump:
The feedwater pump plays a crucial role in maintaining the forced circulation of water within the Loeffler boiler. It is responsible for supplying water from the economizer to the water tubes and other components of the boiler. The pump ensures a constant flow of water, preventing any disruptions or overheating issues. It also helps in maintaining the desired pressure and water level in the boiler.
6. Steam Separator:
The steam separator is a critical part of the Loeffler boiler, located between the superheater and the steam turbine. It separates any remaining moisture or water droplets from the steam, ensuring that only dry and superheated steam enters the turbine. This process is vital to protect the turbine from potential damage caused by the presence of water.
Working Principle of Loeffler Boiler
The Loeffler boiler operates on the principle of forced circulation. It is a high-pressure, water tube boiler that employs a closed-loop system to generate steam. The working process of the Loeffler boiler is as follows:
1. Feedwater Preheating:
The feedwater enters the economizer, where it gets preheated using the waste heat from the flue gases. This preheating process improves the overall thermal efficiency of the boiler.
2. Water Circulation:
The preheated feedwater then enters the evaporating drum or drum separator, where it is mixed with a small fraction of the superheated steam. This mixture ensures the prevention of superheater tubes’ overheating.
3. Forced Circulation:
The feedwater and steam mixture is pumped by a feedwater pump into the radiant evaporator tubes. These tubes are exposed to the hot gases produced by the furnace. The forced circulation of water through the tubes ensures efficient heat transfer and avoids any steam bubble formation, ensuring the production of high-quality steam.
4. Superheating:
The partially evaporated water in the radiant evaporator tubes enters the superheater, where it absorbs additional heat from the hot gases. This process increases the temperature of the steam and produces superheated steam, which is desirable for various industrial applications.
5. Steam Separation:
The superheated steam then passes through the steam separator, where any remaining moisture or water droplets are separated from the steam. This ensures that only dry and superheated steam enters the downstream steam turbine or other applications.
Advantages of Loeffler Boiler
1. High Efficiency:
The Loeffler boiler exhibits high thermal efficiency due to its forced circulation system, economizer for feedwater preheating, and superheater for producing superheated steam.
2. Fuel Flexibility:
This boiler can burn a wide range of fuels efficiently, making it adaptable to different industrial settings and fuel availability.
3. High Steam Quality:
The forced circulation mechanism and steam separation process result in the production of high-quality dry and superheated steam, which is essential for various industrial processes.
4. Improved Energy Utilization:
The economizer and superheater in the Loeffler boiler enhance energy utilization by utilizing waste heat from flue gases for feedwater preheating and increasing the temperature of steam, respectively.
Disadvantages of Loeffler Boiler
1. Complex Design:
The Loeffler boiler has a relatively complex design compared to other boiler types, requiring skilled engineers and technicians for proper operation and maintenance.
2. High Initial Cost:
The initial cost of installing a Loeffler boiler is higher than conventional boilers due to its complex design and additional components such as the economizer and superheater.
3. Space Requirement:
The Loeffler boiler typically occupies more space compared to other boiler types due to its forced circulation system and additional components.
Applications of Loeffler Boiler
1. Power Generation:
Loeffler boilers find extensive use in power plants, particularly in applications where high-pressure and high-temperature steam is required for electricity generation.
2. Petrochemical Industry:
These boilers are suitable for petrochemical plants that require superheated steam for various processes like distillation, hydrogenation, and drying.
3. Textile Industry:
Loeffler boilers are utilized in the textile industry for steam generation required in processes such as dyeing, drying, and printing.
4. Food Processing:
The Loeffler boiler’s ability to produce high-quality steam makes it ideal for applications in food processing industries like sterilization, cooking, and canning.
Also, read Gate Valve















Comment on “What is the construction and working of the Loeffler boiler?”
Comments are closed.