Table of Contents
What is a wheel?
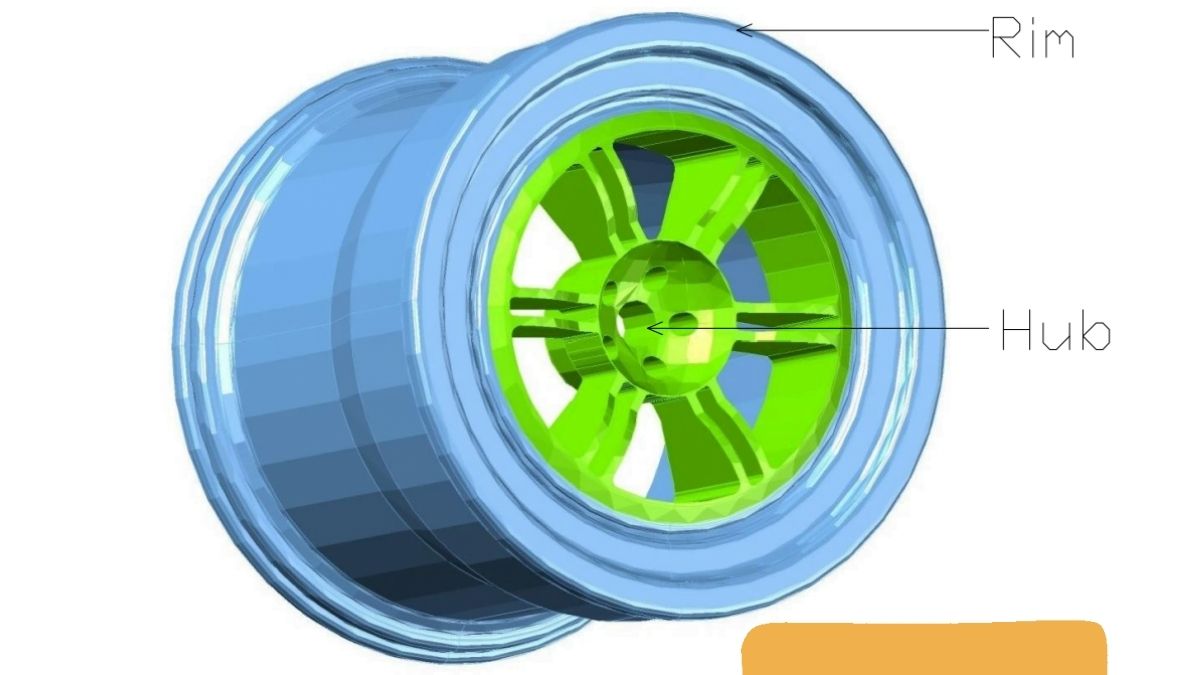
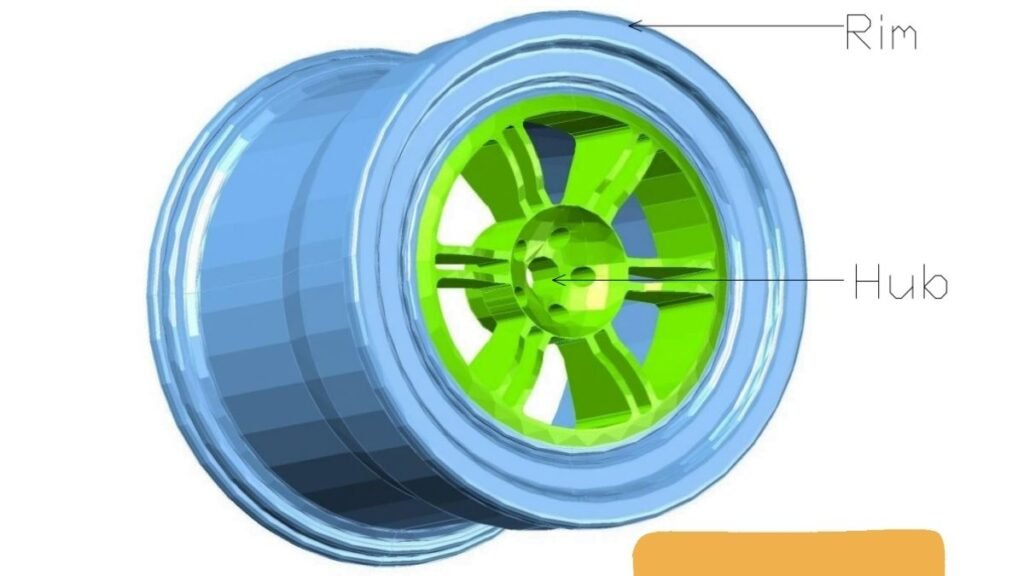
A wheel is a circular object with a rim and hub, as the main parts rotate around an axis to allow it to move easily on the ground.
Types of wheels
There are the following types of wheels, as follows:
- Pressed Steel Disc Wheel
- wire wheel
- Alloy wheels
- Light Alloy Wheel
- Divided Rims Wheel
Pressed steel disc wheel
This type of disc wheel will be used by most manufacturers around the world.
This type of wheel consists of two parts. One is the steel rim and the other is the stamped steel disc.
In the figure below, the pressed steel disc is welded to the rim.

It is possible to mount or remove the tire from the wheel only with the help of a well, otherwise, it is not possible.
It is possible to pass the tire over the opposite edges of the rim when the tire bead is resting in the pit.
The steel disc is used for the operation of spokes. The wheel is installed together with the tire on the axle by tightening the nuts on the mounting studs that are secured to the flange.
Some holes or grooves are usually provided in the wheel disc to allow air to enter the inner side of the disc for better cooling of the brake drum.
Especially for heavier vehicles such as trucks, buses, etc. which are bulkier and do not fit in the good region. Therefore, the pit hoops are not used for them.
Instead, flat base hoops are generally used, which can be 2 pieces/3 pieces/4 pieces, or 5 pieces in construction.
Advantages of Pressed steel disc wheel:
- Robust construction
- • Simplicity
- • Ease of cleaning
- • Lower manufacturing cost
- • Less maintenance
- • High production
Applications of Pressed steel disc wheel:
These wheels are used in heavy engines such as buses and trucks.
It is lighter and heat dissipation will be high.
The wire wheel
The wire wheel consists of the following parts:
• Steel rim
• Spokes
• Hub
Steel rim:
This type of wheel is generally used to receive the tire.
Spokes:
The wire wheel has a separate hub that is attached to the rim and several spokes of wire are attached to it inside the wheel.
Hub:
Each spoke is fitted to one end of the hub, while the other end is pushed through a hole in the wheel rim.
Advantages of the wire wheel:
• This type of wheel can only be used for tube tires.
• Heat dissipation into the environment through rays installed in the rim.
Disadvantages of the wire wheel:
• Tubeless tires cannot be mounted on wire wheels.
• These wire wheels are difficult to clean.
Wire Wheel Applications:
• This type of wheel was used in the past, but its use is limited to racing cars and vintage cars.
• Before 5 years from today, the wire wheel will also be used on bicycles.
• Traditionally, it is also widely used on bicycles.
Light Alloy Cast Wheel or Forged Wheel:
Alloy wheels are better conductors of heat, which helps the wheels dissipate heat generated by tires or brakes.
Forged wheels and cast wheels have to be machined to produce a better look.
Advantages of alloy wheels:
• The main advantage of alloy wheels is that they weigh about 50% of steel wheels and 70% of aluminum alloy wheels for similar strength.
• Wider rims are possible in this case of alloy wheels to improve cornering stability.
• Magnesium alloys have properties of high impact and fatigue resistance, so they can withstand vibrations and shocks during charging.
Disadvantages of alloy wheels:
Magnesium alloys are prone to corrosion and therefore some protective coating must be applied to them.
The higher cost is the biggest disadvantage of alloy wheels compared to other wheels mentioned above.
Alloy Wheel Applications:
Aluminum alloys are used in the wheels of cars and commercial vehicles, while magnesium alloy wheels are used in sports and racing cars.
This is a detailed explanation of the different types of wheels. Therefore, let us discuss the types of tires in detail and their advantages.
- Split rim wheel:
As the name implies, the wheels are divided into two halves and joined by means of screws.
As long as the tire is inflated the rims must not be separated. The only advantage of split hoops is that they are very easy to assemble and disassemble. - Split rims:
Split rims are used in larger vehicles such as trucks, buses, forklifts, etc., but not in cars or light vehicles.
They are usually multi-piece wheels, in which with the help of a locking ring the tire is adjusted in one place.
This is a detailed explanation of various types of wheels. Now, let’s discuss tires and their properties, functions, etc.
What is a tire?
A tire is a cushion provided inside the wheel of an automobile.
Tire functions:
• To support the vehicle load.
• To transmit braking and driving forces to the road.
• For smooth steering, cornering power is provided.
Tire properties:
Damping effect:
The tire must be in a position to absorb the vibrations created by the uneven road surface, providing a cushioning effect to make the ride smoother.
Non-slip:
This is one of the important properties of the tire which makes the vehicle not skid even on wet roads and this may be possible by designing a suitable tread pattern on the tire.
Battery capacity:
When the vehicle is running on uneven or smooth roads, the tires experience alternating stresses during each revolution of the wheel. The tire design and material must be good enough to support the load properly.
Uniform wear:
The non-skid property is maintained by evenly distributing wear on each wheel. To achieve this, ribbed floor patterns will be used.
Tyre parts:
- Tire belts
- Tire Tread
- Tire sidewall
- Tire shoulder
- Tire grooves
- Tire bead
- Tire plies
Tire Chemical Compounds:
In the current era, tires are made from rubber mixed with other constituents to impact the tire surface. strength, durability, and temperature resistance.
The chemical compounds used for the preparation of rubber are
Sulfur
carbon black
Synthetic rubber
Silica
Tire Types:
In general, tires are classified into two categories, namely:
Conventional Tube Tire
Tubeless Tire
- Conventional Tube Tire:
As the name implies, it has an inner tube inside the tire and rim assembly.
Rim
Tube
Tire
Rim:
It is the steel material that is used to hold the inner tube and tire so that it can support the load of the vehicle. It has a hole in its circumference to allow the passage of the tubular valve.
Tube:
It is a material made of rubber and consists of a valve that is pressurized by means of air so that it can inflate as needed and fit properly into the tire.
It has the disadvantage that whenever there is a puncture, air will be suddenly lost from the inner tube, the tire, and also from the valve region.
Tyre:
It is a composite rubber material and acts like most automobiles. Engine power must be transmitted to the wheels through the axles so that the vehicle can move smoothly.
It consists of steps separated by grooves in their circumference so that they can act as friction between the road and the tire.
Conventional Tube Tire Work:
• The inner tube is placed correctly between the tire and the rim so that the inner tube valve can pass through the hole in the rim.
• Then the air is pressurized in the tube to the desired value so that it can run on the road properly.
• Make sure the air in the tube is at the desired value as described by the manufacturer. If the air is less, the vehicle moves slowly.
| Feature/Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Wheels | |
| Material | Common materials include steel, alloy (magnesium or aluminum), and in some high-end cars, carbon-fiber. |
| Diameter | Measured in inches, this determines the size of the tire that fits onto the wheel. |
| Width | Indicates the breadth of the wheel, which can influence the width of the tire that can be mounted. |
| Offset | The distance from the wheel’s mounting surface to its centerline. Affects wheel fitment in the wheel well. |
| Bolt Pattern | Defines the number and arrangement of bolts. E.g., 5×114.3 means 5 bolts in a 114.3mm diameter circle. |
| Center Bore | The hole in the center of the wheel that locates it on the hub. Needs to match the vehicle’s hub size. |
| Weight | Affects unsprung mass, which can influence vehicle dynamics and fuel efficiency. |
| Design/Style | Various styles such as multi-spoke, split-spoke, mesh, etc., primarily for aesthetics. |
| Finish | Chrome, painted, polished, matte, etc. |
| Tires | |
| Tire Type | Summer, winter, all-season, performance, off-road, etc. |
| Width | The width of the tire’s tread in millimeters. |
| Aspect Ratio | The height of the tire’s sidewall as a percentage of its width. E.g., in 225/45 R17, 45 is the ratio. |
| Construction | R for radial, which means the tire’s ply cords are arranged at 90 degrees to the direction of travel. |
| Diameter | The height of the tire’s sidewall is a percentage of its width. E.g., in 225/45 R17, 45 is the ratio. |
| Load Index | A numerical code that corresponds to the maximum weight a tire can support. |
| Speed Rating | Indicates the maximum speed the tire can handle (e.g., H for up to 130 mph, V for up to 149 mph). |
| Tread Pattern | Design of the tread, which can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, directional, etc. |
| Tread Depth | The wheel size the tire is designed to fit, is measured in inches. |
| Sidewall Markings | Contains important information such as tire specifications, manufacturing details, and safety warnings. |
| Wear Indicator | Raised sections at the bottom of tread grooves, which show when a tire is approaching its wear limit. |
| UTQG Rating | Uniform Tire Quality Grade: Measures treadwear, temperature resistance, and traction. |
Also, read Suspension System
FAQ
How do I choose the right tyre size for my car?
Check your vehicle’s manual or the sidewall of your current tyres for the recommended size, which includes information on width, aspect ratio, and diameter.
What is the importance of tyre maintenance?
Proper tyre maintenance ensures safety, better fuel efficiency, longer tyre life, and improved handling. Regularly check tyre pressure, tread depth, and alignment.
How often should I replace my tyres?
Tyre lifespan varies, but generally, they should be replaced every 4-6 years or when the tread depth reaches 2/32 inches (1.6 mm).
Can I mix different tyre brands on my car?
It’s best to avoid mixing tyre brands, as it can affect handling and performance. Stick to a set of tyres from the same brand and model for optimal results.
What is the purpose of tyre rotation?
Tyre rotation involves swapping tyres’ positions to promote even wear, extending their lifespan, and maintaining balanced performance.
When should I use winter tyres?
Winter tyres are designed for cold temperatures and icy/snowy conditions. Use them during winter months for better traction and safety.
How does tyre pressure affect my car’s performance?
Proper tyre pressure ensures even wear, better fuel efficiency, and optimal handling. Low pressure can lead to increased wear and reduced performance, while high pressure can cause a harsh ride and uneven wear.
What are run-flat tyres?
Run-flat tyres are designed to be driven on for a limited distance even after a puncture, allowing you to reach a safe location without needing to change the tyre immediately.
How does the wheel size affect my vehicle?
Larger wheels can enhance the appearance of your car but may sacrifice ride comfort and increase the risk of damage on rough roads. Smaller wheels often provide a smoother ride and better fuel efficiency.