Table of Contents
The Antilock Braking System (ABS) is a type of active safety system in a vehicle. It is also known as a non-slip braking system. This system kicks in when the driver suddenly applies the brakes during an emergency. The use of the antilock braking system in cars and motorcycles is now mandatory in most of the world.
Need for antilock brakes:
Whenever the driver suddenly brakes a vehicle at high speed, there is always the possibility that the wheels will lock up. Locking the wheel means that the respective wheel comes to a sudden stop instead of slowing to a stop. Due to the locking of the wheels, the driver loses control of the vehicle and the vehicle goes off the road. This is how a fatal accident occurs. To avoid such situations, manufacturers use ABS.
Components of antilock braking system (ABS):
The ABS has the following components:
- Wheel speed sensors
- ABS control module
- Brake control unit
- Valves
- Pump
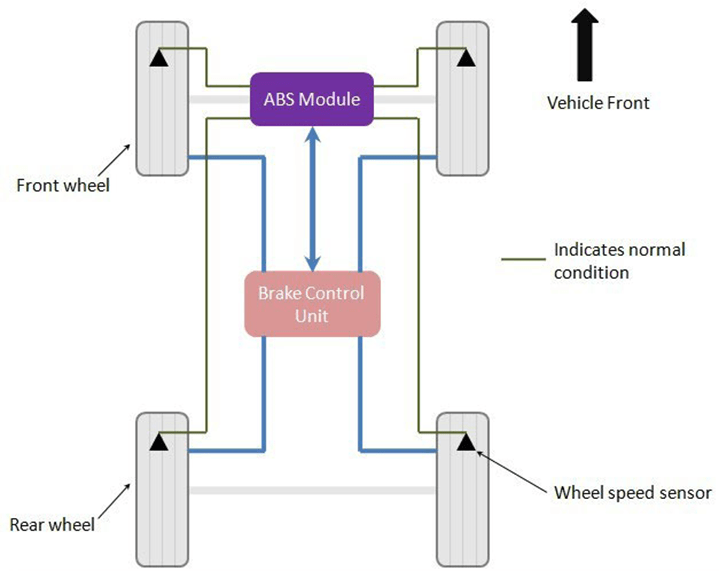
Wheel speed sensors continuously monitor the speed of each wheel. As long as all the wheels have comparable speeds, the system does not interfere with their operation. However, if the speed sensors find that the speed of any of the wheels is reducing drastically, then it means that the particular wheel is going to lock.
However, the locked wheel hampers vehicle stability. Thus, the vehicle stops responding to the steering input given by the driver. At this moment, the vehicle also starts to skid, thereby causing a fatal accident. To avoid such a mishap, the ABS comes into action.
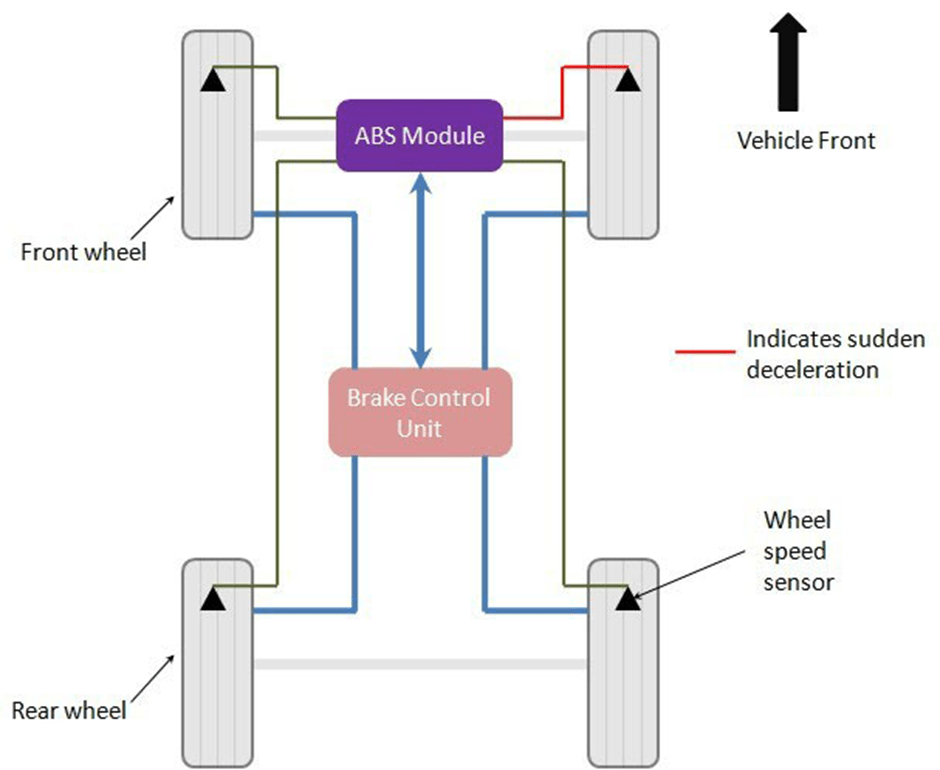
How does the Antilock braking system (ABS) work?
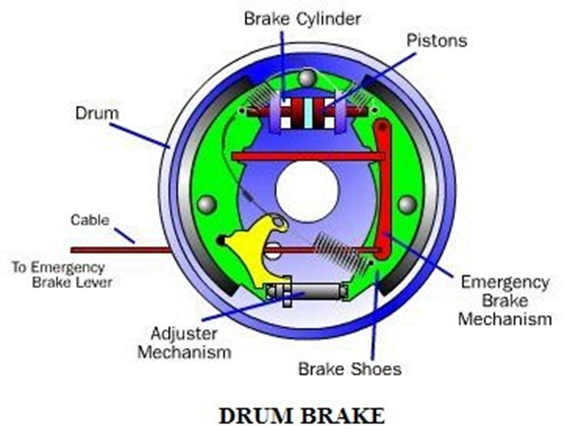
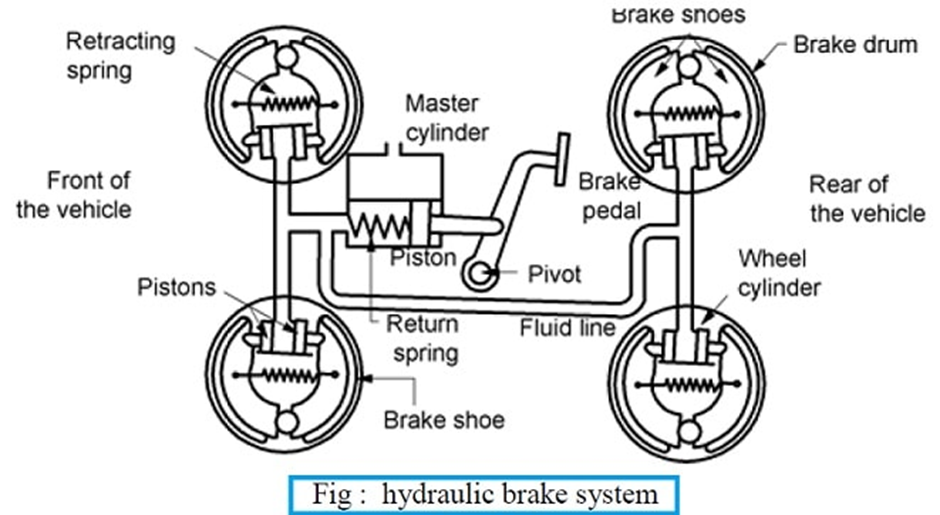
After receiving the very low-speed signal from the wheel speed sensor, the ABS module instructs the brake control unit to reduce the braking force of that wheel. Reducing the braking force means reducing the hydraulic pressure in the brake line acting on that wheel.
The brake control unit reduces the line pressure with the help of the system valves. When the braking force is reduced, the wheel starts to turn faster, thus preventing the wheel from locking. Since the wheel does not lock, the drivability of the vehicle remains intact.
This means that the vehicle moves according to the driver’s input without skidding. Once the normal condition is restored, the Brake Control Unit restores the hydraulic pressure in the brake line with the help of a pump.
Advantages of Antilock braking system (ABS) :
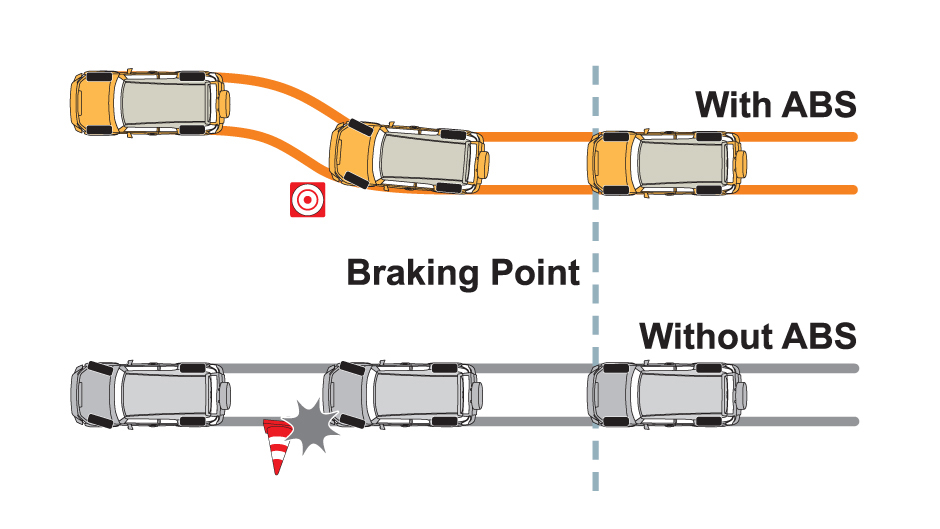
1. ABS maintains the drivability and stability of the vehicle during emergency braking.
2. Reduces stopping distance by up to 10% or more, especially on wet surfaces.
Disadvantages of antilock braking system (ABS):
The only downside to the anti-lock braking system is its higher cost. The purchase of an anti-lock braking system installed on a bicycle or car costs the customer significantly. However, this higher cost is fully offset by the increased security provided by this system. In addition, the automotive industry is working to develop a low-cost version of the anti-lock braking system.
FAQ
How does ABS work?
ABS uses wheel speed sensors to monitor the rotational speed of each wheel. When a wheel is about to lock up, indicating imminent skidding, the ABS control module reduces the brake pressure on that wheel through electronic valves. This modulation of brake pressure occurs rapidly and repeatedly to maintain traction and prevent wheel lock-up.
What are the benefits of ABS?
ABS offers several benefits, including:
Enhanced vehicle stability and steering control during emergency braking.
Reduced stopping distances on slippery surfaces.
Preventing wheel lock-up and skidding.
Improved overall vehicle safety, especially in adverse weather conditions.Can ABS prevent accidents?
While ABS is a valuable safety feature, it cannot entirely prevent accidents on its own. It helps maintain control and stability during emergency braking, reducing the risk of skidding and maintaining steering control. However, other factors such as road conditions, driver reaction time, and vehicle speed also play significant roles in accident prevention.
Can ABS stop a vehicle faster?
ABS is primarily designed to maintain control and stability during braking, rather than improving stopping distances. In certain conditions, ABS may reduce stopping distances, especially on slippery surfaces, by allowing the driver to maintain steering control. However, the primary goal of ABS is to prevent wheel lock-up and skidding.
Can ABS be retrofitted to older vehicles?
ABS is typically installed during the manufacturing process, and retrofitting ABS to older vehicles can be challenging and expensive. It often requires significant modifications to the braking system, including the addition of wheel speed sensors, electronic control modules, and hydraulic valves. Retrofitting ABS is not a common practice, and it’s generally more feasible to purchase a vehicle equipped with ABS.
Does ABS work in all driving conditions?
ABS performs well in most driving conditions, especially during emergency braking situations. However, it may not be as effective on loose surfaces, such as gravel or sand, where tire traction is limited. In such cases, the wheels may still lock up, and the vehicle’s stopping distance may increase.
Can ABS malfunction or fail?
Like any mechanical or electronic system, ABS can experience malfunctions or failures. Common issues include faulty wheel speed sensors, malfunctioning electronic control modules, or problems with the hydraulic valves. Regular maintenance and inspections can help detect and resolve ABS-related issues.
Can ABS be turned off?
ABS is a standard safety feature that is always active. However, some advanced systems may offer a way to temporarily disable ABS, such as for specific off-road driving scenarios. It’s important to consult the vehicle’s owner’s manual to understand if and how ABS can be turned off in a specific vehicle.
Is ABS a substitute for safe driving practices?
No, ABS is not a substitute for safe driving practices. While ABS enhances vehicle control during emergency braking, it does not eliminate the need for safe driving habits, such as maintaining a safe distance, driving at a reasonable speed, and being alert to road conditions. Safe driving practices, along with ABS, work together to enhance overall safety on the road.