Table of Contents
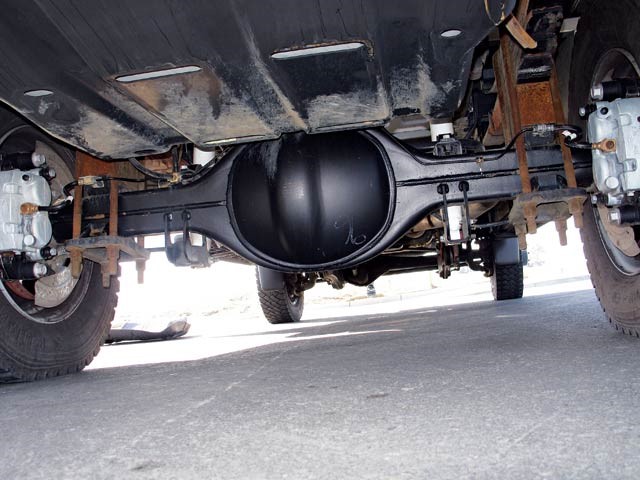
Differential used in Cars & Trucks
A differential is an essential component of a car’s drivetrain that enables the wheels to rotate at varying speeds while receiving power from the engine. It can be found in the front or rear axle or both, situated between the drive wheels.
The differential comprises a set of gears that distributes the engine’s power to the wheels while compensating for the varying distances they travel during turns. Without a differential, the wheels would lock up or slip when a car turns since the outside wheels would travel a greater distance than the inside wheels.

By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, the differential ensures that the faster rotating wheel receives less torque while the slower one receives more torque. This enables the wheels to turn smoothly, promoting better handling and stability for the vehicle.
In a differential, A smaller bevel gear called a differential side gear is mounted on the inner ends of each shaft. Two bevel gears are mounted to mesh the driven and driven shafts at a 90 ° angle. The differential case here is mounted with two-wheel axles and differential side gears.
The differential case has bearings that rotate on two drive shafts. Then the two pinions and their supporting shaft, called pinion shafts, are inserted into the differential case. The pinion shaft then meshes with the two differential side gears attached to the inner ends of the drive shafts.
The ring gear is bolted to a flange on the differential case.
The ring gear rotates the differential case. Finally, the drive pinion is mounted. The drive pinion is assembled with the differential case called the differential case or bracket. The driveshaft is connected to the drive pinion by a universal joint and meshes with the ring gear. Then the drive pinion is turned when the drive.
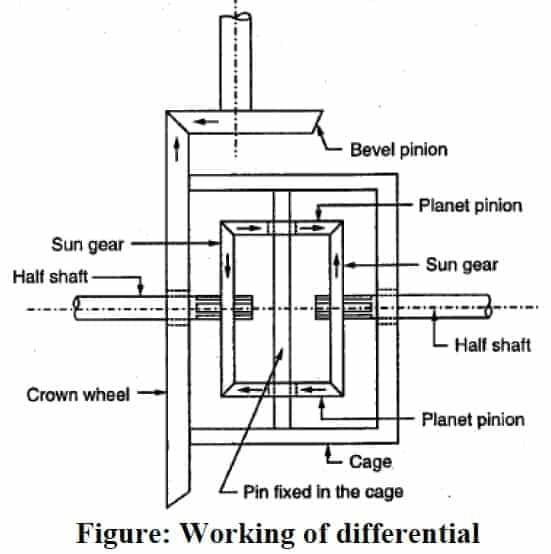
Differential Gear Operation in Automobiles:
When Running Straight:
When the vehicle is moving in a straight line, the power comes from the driveshaft to the bevel pinion that drives the crown. It is then taken to the differential case where a series of planet pinions and sun gears are located. From the sun gear, it is transmitted to the road wheels through the axle shafts.
In this case, the ring gear, differential case, planet pinions, and sun gears rotate as a single unit and there is no relative motion between the sun gear and the sun gear. The planet’s opinions do not rotate around their own axis. Road wheels, drive shafts, and solar wheels offer the same resistance to steering and therefore the differential does not work. Both wheels rotate at the same speed.
TYPES OF DIFFERENTIAL:
There are three types of spreads:
(a) Conventional type,
(b) non-slip or self-locking type, and
(c) double reduction
1) conventional type
Same torque for each rear wheel. If one of the wheels slips for any reason, the wheel will not turn and the vehicle will not move.
2) Non-slip or self-locking type
The slip-resistant or self-locking differential solves this problem. Its construction is similar to that of the conventional type differential. However, two sets of clutch discs are also supplied. In addition, the ends of the satellite shafts are free in the notches provided in the differential case.
3) Double reduction type
The double reduction type differential provides further reduction in speed with additional gear. This type of differential is used in heavy vehicles that require a greater downshift between the engine and the wheels.
Advantages of the differential gearbox:
1) Both drive wheels can turn in the same direction at the same speed.
2) Both drive wheels can turn in the same direction at different speeds.
3) Both drive wheels can rotate in opposite directions at the same speed.
4) Both driving wheels can rotate in the opposite direction at a different speed
The function of differential gears:
- Transmit torque at right angles in equal proportion when the vehicle is traveling in a straight line.
- Differentiate the speed of the wheels when turning.
- Equitable distribution of torque in all driving situations.
FAQ
What is a rear differential?
A rear differential is a mechanical device that transfers power from the engine to the rear wheels of a vehicle, allowing them to rotate at different speeds when turning.
How does a rear differential work?
It uses gears to split the engine’s torque into two outputs, sending power to each rear wheel independently, enabling smooth turns and preventing wheel slippage.
What happens if a rear differential fails?
A failed rear differential can lead to loss of power to the rear wheels, difficulty in turning, strange noises, and potential damage to other drivetrain components.
How often should the rear differential fluid be changed?
It’s typically recommended to change the rear differential fluid every 30,000 to 50,000 miles (48,000 to 80,000 kilometers) or as specified in the vehicle’s manual.
What causes rear differential noise?
Common causes of rear differential noise include worn gears, low or contaminated fluid, improper meshing of gears, or damaged bearings.
Can you drive with a bad rear differential?
Driving with a faulty rear differential is not recommended as it can lead to further damage and unsafe driving conditions. Seek professional help if issues arise.
How can I prevent rear differential problems?
Regular maintenance, such as fluid changes and inspections, is crucial to prevent rear differential issues. Avoid aggressive driving to reduce stress on the differential.
What is limited-slip differential (LSD)?
A limited-slip differential is a variation that provides more traction by limiting the speed difference between the two rear wheels during turns.
How do I know if my vehicle has a rear differential problem?
Signs of rear differential problems include noise during turns, vibrations, difficulty in steering, or a noticeable decrease in performance.
Can a rear differential be repaired, or does it need replacement?
Minor issues can often be repaired, but severe damage may require a complete replacement of the rear differential.
Can I change the rear differential fluid myself?
If you have the necessary tools and experience, you can change the rear differential fluid yourself. Otherwise, it’s best to have it done by a professional.
Is rear differential maintenance expensive?
Routine maintenance, such as fluid changes, is relatively affordable. However, major repairs or replacements can be costly, so timely maintenance is essential to avoid expensive issues.















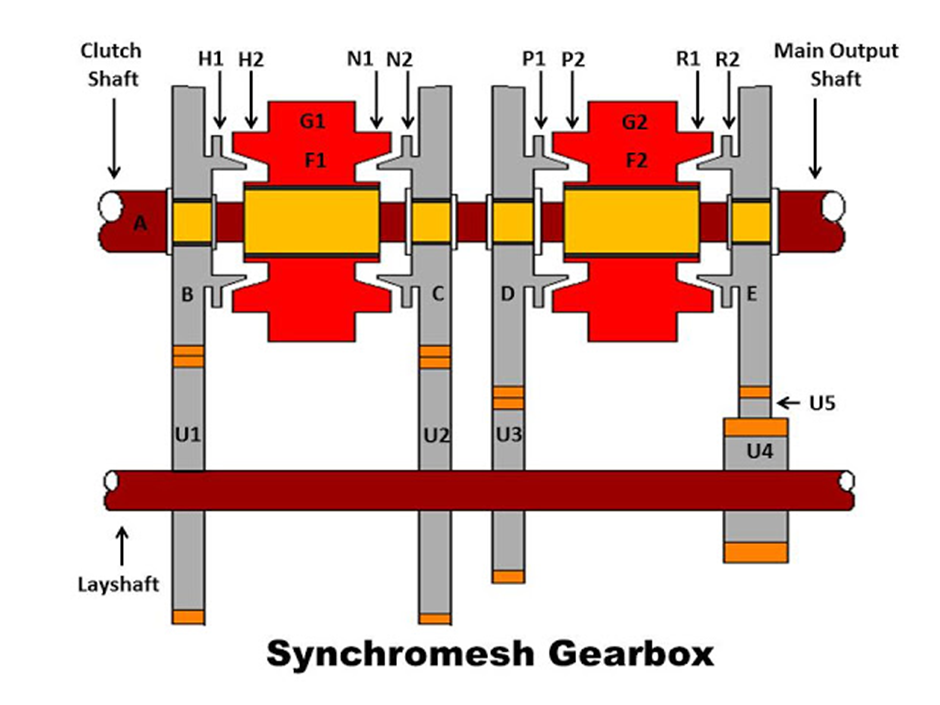
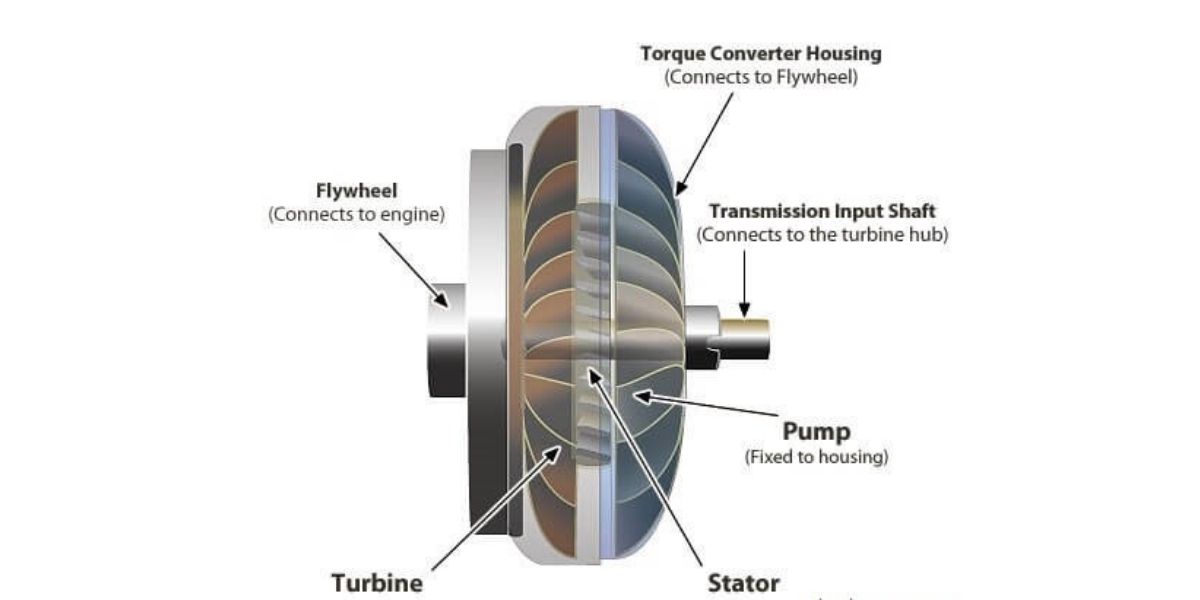



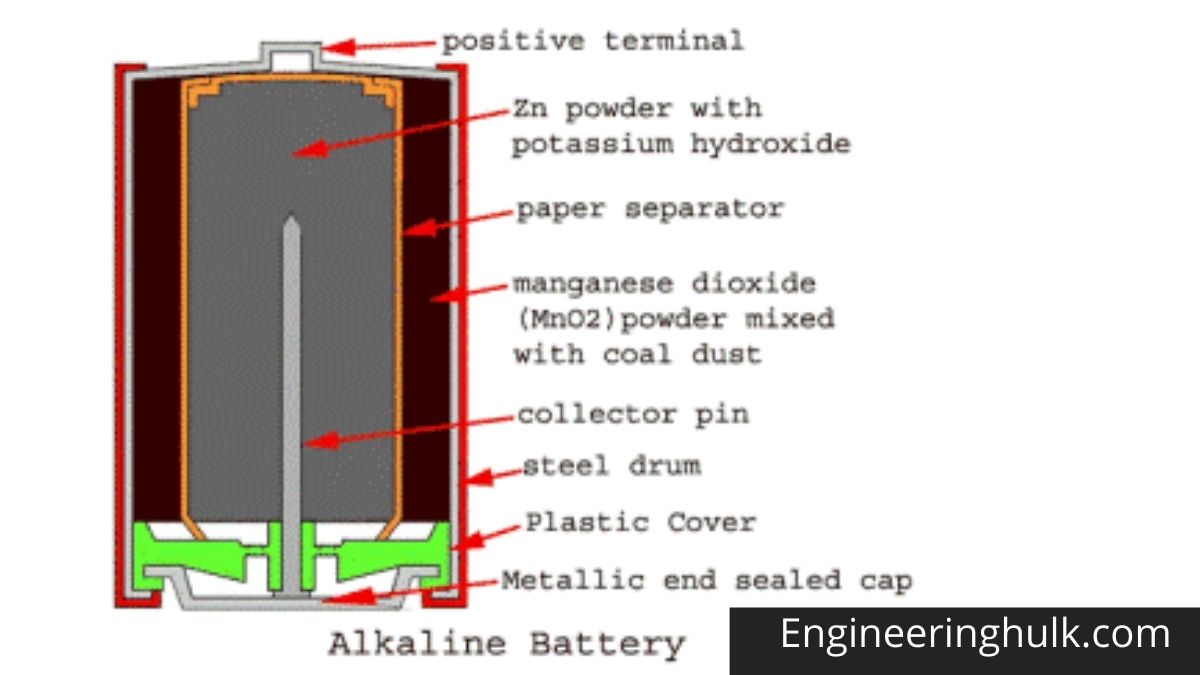
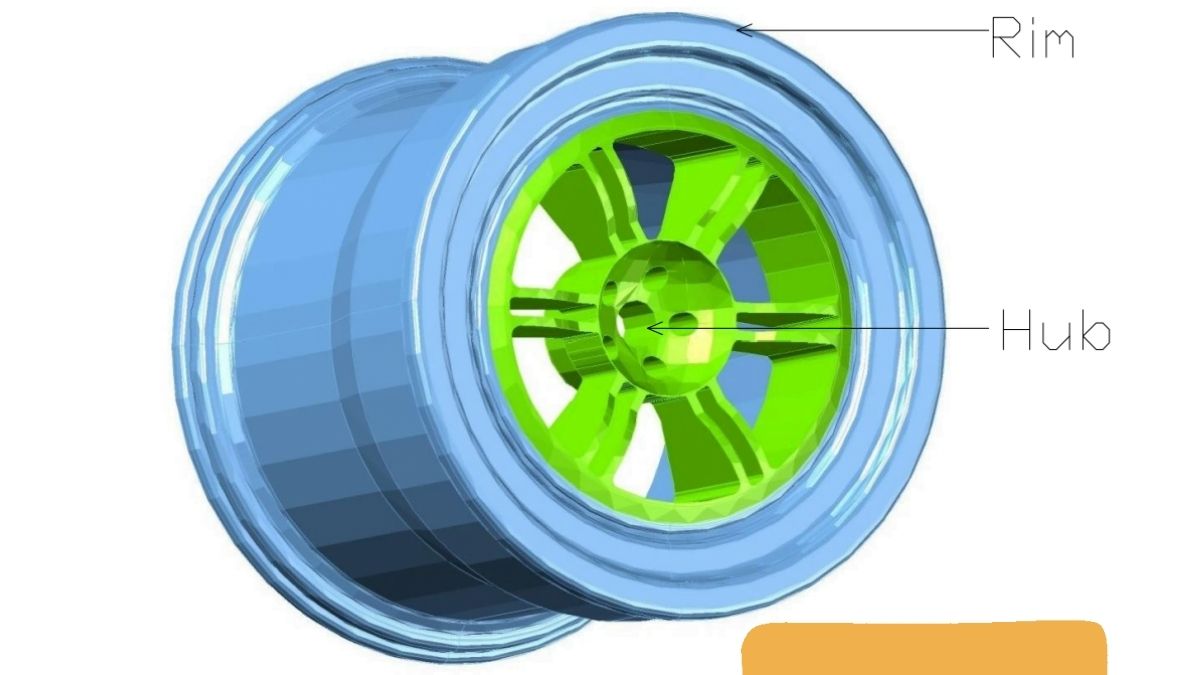

Comment on “Rear Differential – Construction, Working, Types & Features”