Table of Contents
SOURCE OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY: Geothermal energy is heat within the earth. The word “geothermal” basically comes from Greek words which are broken into 2 parts geo means (earth) and thermal means (heat). Geothermal energy is a source of renewable energy because heat is continuously produced inside the world. People are using geothermal energy for different purposes.
| Category | Description | Examples/Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrothermal Reservoirs | These are the most common sources and involve naturally occurring pockets of steam or hot water beneath the Earth’s surface. | – Geysers | – Most explored and developed | – Limited to certain geographic areas |
| – Hot springs | – Predictable and consistent energy source | – Can be depleted if managed improperly | ||
| – Steam and flash steam power plants | ||||
| Geopressurized Zones | Deep underground areas where both hydrothermal resources and pressurized brine (salty water) coexist. | – Mostly experimental extraction methods | – Potential for dual energy extraction: heat and gas | – Technologically challenging |
| – High energy density | – Limited locations | |||
| Hot Dry Rock (HDR) | This involves regions where rocks are hot but have little water or steam. Water can be injected to produce steam for energy generation. | – Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) | – Widespread resource availability | – High costs for drilling and water injection |
| – Can be established in many locations | – Risk of induced seismicity | |||
| Magma Resources | Magma is molten rock. Tapping directly into magma can provide significant heat. | – Mostly theoretical or experimental for direct use | – Extremely high energy potential | – Technologically challenging |
| – Safety concerns | ||||
| Ocean Thermal Energy | Difference in temperature between surface seawater and deep seawater can be used to produce power. | – Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) systems | – Renewable and consistent | – Low efficiency due to small temperature difference |
| – Potential co-benefits: desalination | – Large infrastructural needs |
Geothermal energy is a renewable source of energy that originates from the heat generated within the Earth’s core. It’s an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels that has gained popularity in the United States in recent years. In this article, we’ll explore the source of geothermal energy and how it can be utilized to generate clean, renewable energy.
The core of the Earth is a hot, molten mixture of rock and metal that generates a tremendous amount of heat, estimated to be around 7,200 degrees Fahrenheit. This heat is created by the radioactive decay of elements like uranium and thorium in the Earth’s mantle and core.
The heat from the core is transferred to the Earth’s surface through the crust, which is a layer of rock that varies in thickness from a few kilometers to several tens of kilometers. This process is known as geothermal energy.
How to harness geothermal energy?
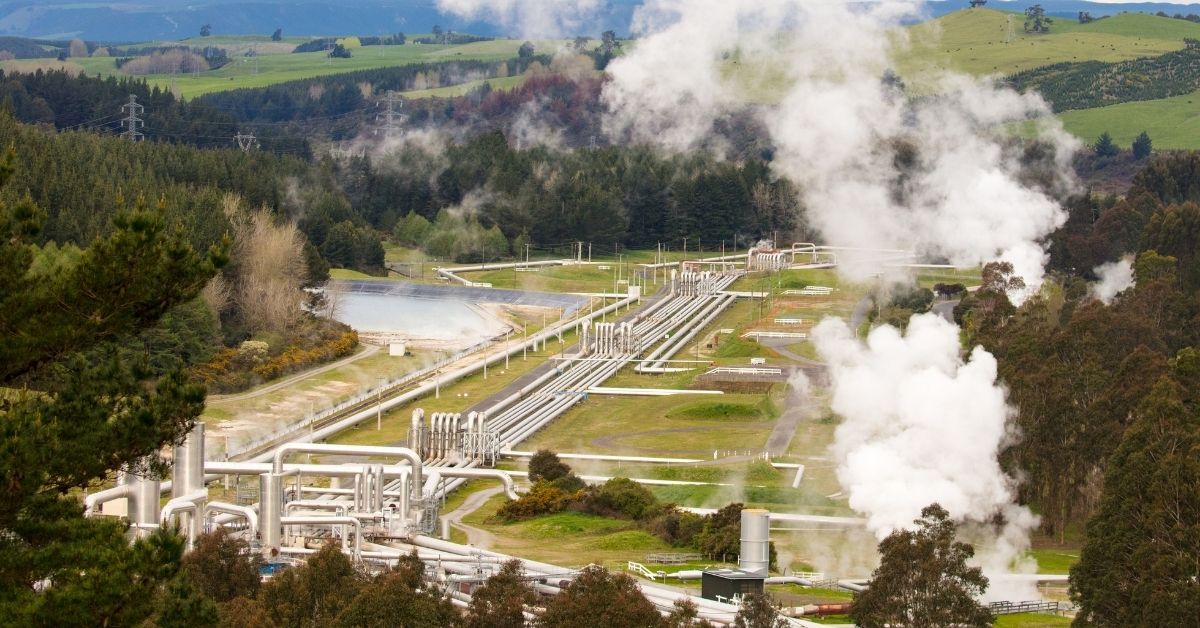
There are several methods to harness geothermal energy, the most common of which is through geothermal power plants. These power plants extract hot water and steam from underground reservoirs using geothermal wells.
The hot water and steam are used to drive turbines, which generate electricity. Geothermal energy can also be used to heat and cool buildings directly through ground-source heat pumps. These systems use underground pipes to circulate fluid that absorbs heat from the Earth in the winter and releases heat back into the Earth in the summer.
The United States is one of the leading producers of geothermal energy in the world. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the country had a total installed geothermal capacity of 3.7 gigawatts in 2020. California is the largest producer of geothermal energy in the United States, followed by Nevada, Utah, and Oregon.
Geothermal energy is a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy source that has the potential to meet a significant portion of the United States’ energy needs. It does not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants associated with fossil fuels. Moreover, geothermal power plants have a relatively low environmental impact since the land used for these plants can often be restored and used for other purposes.
Geothermal energy is a renewable and sustainable source of energy derived from the Earth’s core’s heat. It can be harnessed through geothermal power plants and ground source heat pumps and has the potential to meet a significant portion of the United States’ energy needs.
As the United States continues to explore ways to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, geothermal energy is likely to play an increasingly vital role in the country’s energy mix.
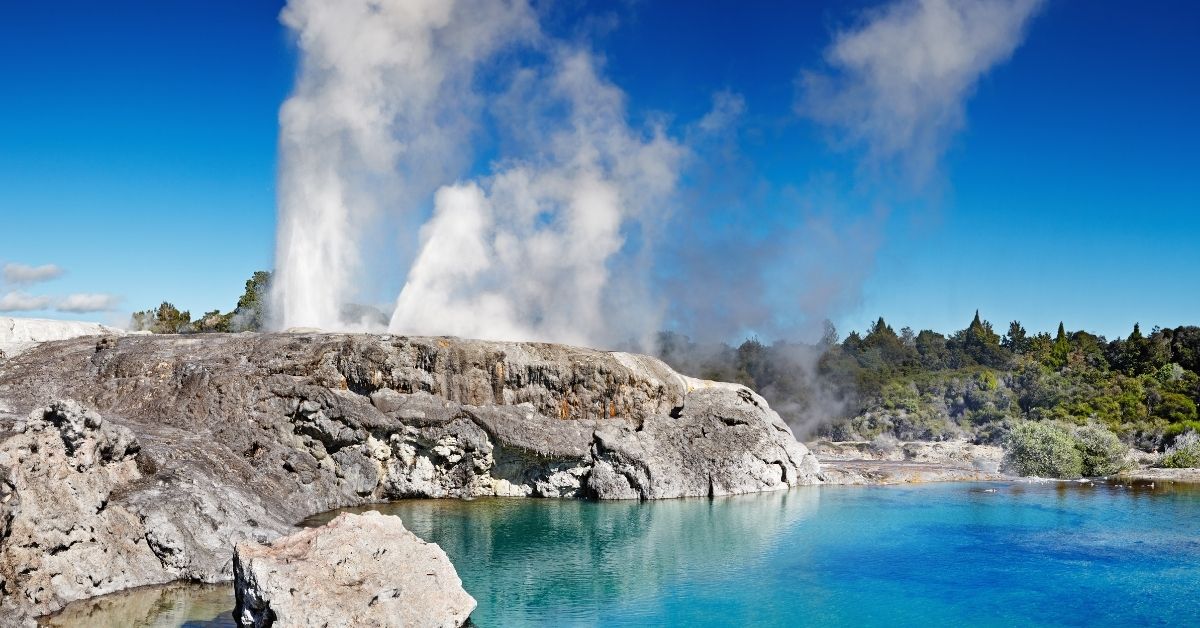
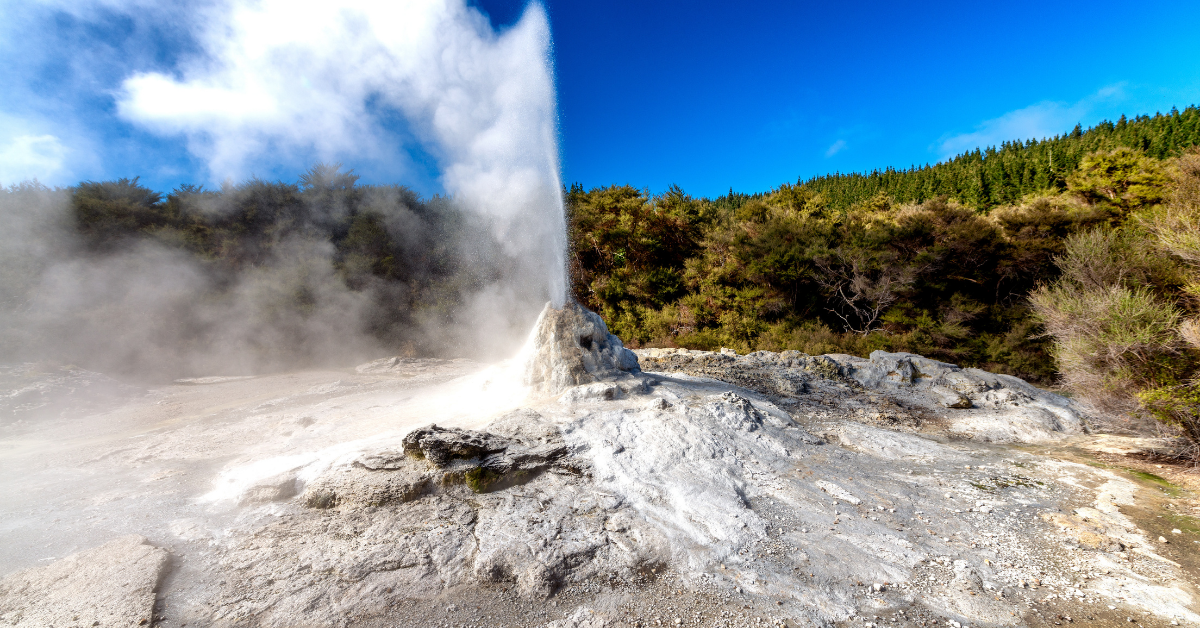
Magma heats nearby rocks and underground aquifers. Hot water is often released through geysers, hot springs, steam vents, underwater hydrothermal vents, and dirt pots. These are all sources of geothermal energy. Their heat is often captured and used directly for warmth, or their steam is often wont to generate electricity.
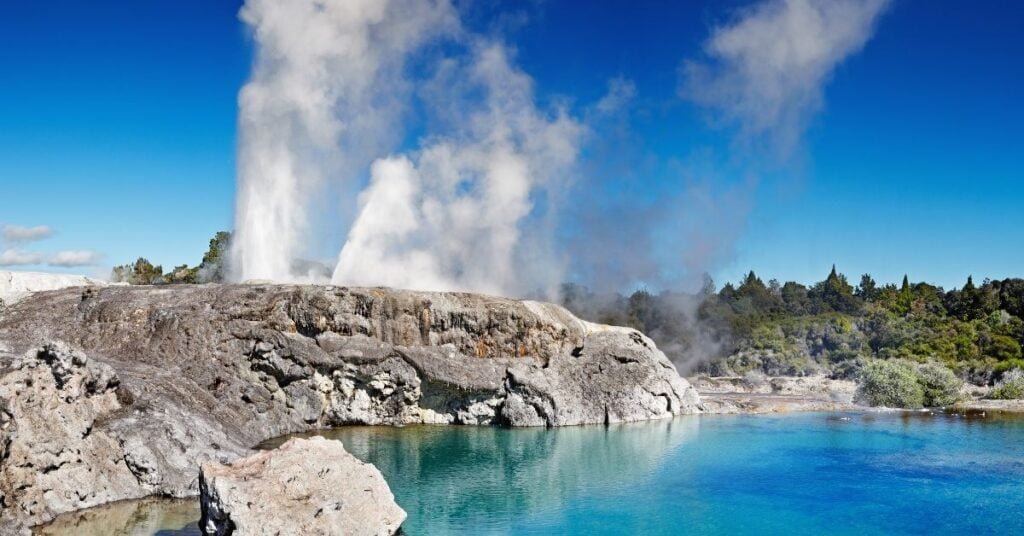

Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy refers to the assembly of energy using the interior heat of the Earth’s crust. This heat comes from continual heat loss from the earth’s original formation.
In the different Sources of Geothermal Energy, The production of heat involves drilling wells into the Earth’s crust at approximately a depth of 7-10 km. The heat is extracted with a spread of methods but in most cases is drawn from the world using water and steam. Hot water from the world could also be extracted to heat homes and buildings.
This is done either by directly circulating the recent water through buildings or by pumping it through a device that transfers the warmth to the building. Geothermal heat also can be wont to produce electricity during a geothermal power station. When geothermal heat produces steam that spins turbines on a generator due to the cause of Electricity is generated.
Earth’s internal thermal energy
The Earth’s internal thermal energy flows to the surface by conduction at a rate of 44.2 terawatts (TW) and is replenished by the decay of minerals at a rate of 30 TW. In addition to the interior heat flows, the highest layer of the surface to a depth of 10 m (33 ft) is heated by solar power during the summer and cools during the winter due to releases of that energy.
Outside of the differences due to the season, the geothermal gradient of temperatures through the crust is 25–30 °C (77–86 °F) per km of depth in most of the planet. The conductive heat flux averages 0.1 MW/km2. These values are much higher where the crust is thinner. They may be further augmented by fluid circulation, either through magma conduits, hot springs, hydrothermal circulation, or a mixture of those.
In the different Sources of Geothermal Energy, A geothermal apparatus can extract enough heat from shallow ground anywhere in the world to supply home heating, but industrial applications need the upper temperatures of deep resources. The most demanding applications receive the best enjoy a high natural heat flux, ideally from employing a thermal spring.
The next best choice is to drill a well into a hot aquifer. If no adequate aquifer is out there, a man-made one could also be built by injecting water to hydraulically fracture the bedrock. This last approach is named hot dry rock heat in Europe, or enhanced geothermal systems in North America. A much greater potential could also be available from this approach than from the conventional tapping of natural aquifers.
Also, read Hydrothermal Energy



























Comment on “SOURCE OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY”