Table of Contents
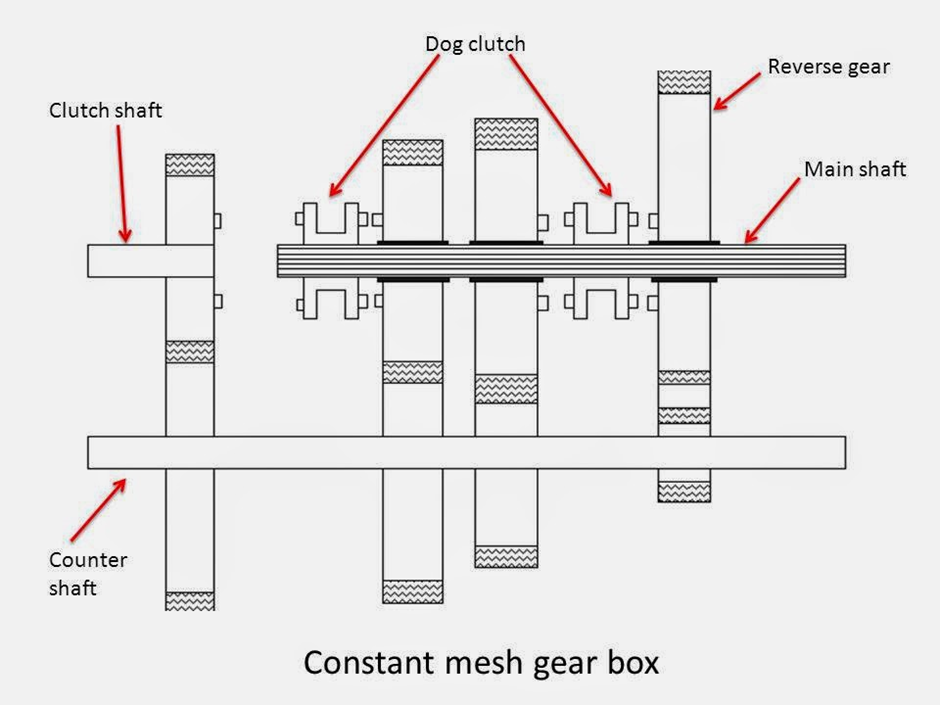
Constant Mesh Gearbox was invented to push the boundaries of the sliding mesh gearbox. In this gearbox, all gears are always in gear. The gear stays fixed and does not slide like the sliding link gearbox.
In this gearbox, the sliding link was replaced by gear pairs that constantly mesh, and new gear-shifting devices called dog claws were introduced.
A constant-link gearbox usually comes with a 4-speed, 1 reverse manual transmission setup.
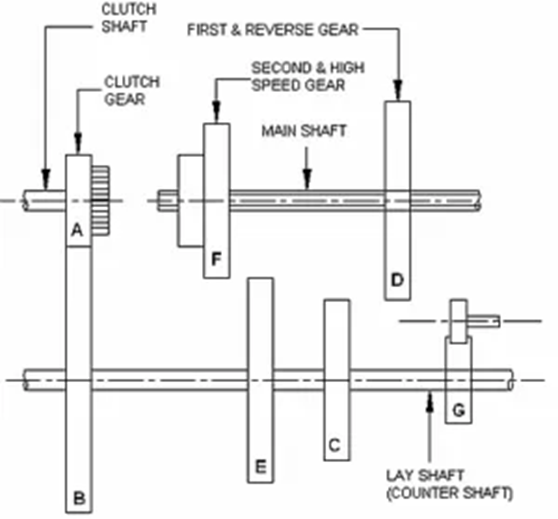
This gearbox has different parts like a countershaft, main shaft, clutch shaft, gears, and toothed clutch.
The countershaft gears are attached to it and the main shaft gears can rotate freely.
Helical and herringbone gears are commonly used in this gearbox, so it is quite different from the sliding link gearbox which uses spur gears.
In this gearbox, all main shaft and countershaft gears are always engaged with each other. Different gear ratios or speed ratios are achieved by using the toothed clutch.
Guided clutches engage main shaft gears to achieve desired speed or torque.
Main parts of constant mesh gearbox:
The main ports of Constant Mesh Gearbox are:
There are 3 trees present in this gearbox, which are:
i) Main Shaft
Also known as an output shaft. It is the splined shaft on which the driven claws together with the gears are mounted. The gears on this shaft can rotate freely.
ii) Countershaft
It is an intermediate shaft between the main shaft and the clutch shaft. The countershaft gears are in constant mesh with the main shaft gears. Also, the countershaft gears are not free to rotate as they are directly connected to the countershaft.
iii) Clutch shaft:
The clutch shaft carries the engine output to the gearbox but acts as an input to the gearbox. Also known as the input shaft.
2 dog clutch:
The drive clutch couples the drive axle and main shaft by interference rather than by friction.
Guided clutches are used to transmit the correct gear ratio to the main shaft or output shaft, interfering with the gear pair having a correct gear ratio.
There are usually two dog claws in one constant knit change.
3) Gears:
Constant-mesh shift gears are supplied in pairs. All countershaft or countershaft gears are always coupled with gears on a main shaft or output shaft.
These mated main shaft and countershaft gears provide a different gear ratio that can be transmitted to the shaft even by engaging the claw clutch with the appropriate gear ratio required.
Two types of gears are used in the constant mesh gearbox: –
i) Helical gears:
These gears have cylindrical sections angled metal cutting teeth bodies.
ii) Bevel gears:
These gears have angular cutting teeth on conical section metal bodies.
Constant-mesh gear construction:
The engine output is affected by a clutch shaft. The gear on the clutch shaft is in constant mesh with the layshaft gear.
There are 5 gears on the layshaft, one of which is connected to the clutch shaft gear and the other 4 are connected to the main shaft gears.
All four gears are of different sizes for different gear ratios.
An idler gear is present between the layshaft gear and the main shaft gear to form the reverse gear.
Constant knitting gear work:
When the claw clutch is engaged with different main shaft gears, different gear ratios are achieved as the main shaft gears are always mated with countershaft gears to form different gear ratios.
If the dog clutch is not in contact with any main shaft gear, the main shaft gears rotate freely and do not rotate the main shaft as they are connected to the main shaft via bearings.
The main shaft rotates only when one of the trigger jaws is engaged with one of the main shaft gears.
The reverse is achieved in this gearbox with the same technique as in the sliding gearbox, i.e. using the intermediate gear between the main shaft gear and the countershaft gear.
Several transmission ratios
Fourth Gear:
This gear provides the highest or maximum speed in a vehicle using a constant mesh gearbox. This gear is obtained when the dog clutch engages with the smallest gear of the main shaft which is in constant mesh with the largest gear of the layshaft.
Reverse Gear:
In this gear, the vehicle goes in the reverse direction. Like a sliding mesh gearbox, an idler gear is also used in a constant mesh gearbox between the main shaft gear and layshaft gear to form the reverse gear. The reverse gear is obtained when the dog clutch engages with the gear in the main shaft which is paired with the idler gear.
Advantages of Constant Mesh Gearbox:
- Constant Mesh Gearboxes are quite (Silent) because helical or herringbone gears can be used in this gearbox instead of spur gears.
- Since the gears are engaged by dog clutches, if any damage occurs while engaging the gears, the dog unit members get damaged and not the gear wheels.
Application:
The constant-mesh gearbox was mainly used in farm trucks, motorbikes, and heavy machinery.
It is also used in cars like Ford Model T.
Constant Mesh Box was used in motorbikes before the introduction of the synchromesh gearbox in 1928 by General Motors.
What problems of Sliding Mesh Gearbox were solved by Constant Mesh Gearbox?
The Sliding Mesh Gearbox was a great success for the automobile industry as now there was a system that can provide different speeds and torque needs by the vehicle to face different road conditions.
But there were some limitations and problems of Sliding Mesh Gearbox which were solved by Constant Mesh Gearbox. These problems are:-
1) The shifting of gears was a very noisy process as spur gears were used but in a constant mesh gearbox, the gear shifting process becomes very less noisy as helical gears and bevel gears are used.
2) In the sliding mesh gearbox, gears to be messed were in continuous rotation, so the meshing of gears can cause breakage of gear teeth or wear and tear of gears. This problem was solved by a constant mesh gearbox by introducing dog clutches.
3) Shifting was not an easy task for drivers and requires special skills to change gears using the double-de-clutching technique. But changing gears becomes easy for drivers after the introduction of a constant mesh gearbox.
Fourth gear:
This gear provides the maximum or maximum speed in a vehicle that uses a constant mesh gearbox. This gear is achieved when the dog clutch engages with the smaller gear of the main shaft which is in constant mating with the larger gear of the countershaft.
Reverse gear:
In this gear, the vehicle reverses. Like a sliding link gearbox, an idler gear is also used in a constant mesh gearbox between the main shaft gear and the countershaft gear to form reverse. The reverse is achieved when the ratchet clutch engages with the gear in the main shaft which is coupled with the idler gear.
Advantages of constant mesh shifting:
1. Constant mesh gearbox is quiet because helical or herringbone gears can be used in this gearbox instead of spur gears.
2. since the gears are engaged by claw clutches, if damage occurs while engaging the gears, the members of the gear unit are damaged and not the sprockets.
Application:
The constant-mesh gearbox was mainly used in agricultural trucks, motorcycles, and heavy machinery.
It is also used in cars such as Ford Model T.
Constant Mesh Box was used in motorcycles before General Motors introduced the synchromesh in 1928.
What Sliding Mesh Gearbox issues did Constant Mesh Gearbox fix?
The sliding link gearbox has been a great success for the automotive industry as there was now a system capable of providing different speed and torque requirements from the vehicle to cope with different road conditions.
But there were some limitations and issues of Sliding Mesh Gearbox which were fixed by Constant Mesh Gearbox. These problems are: –
1) Gear shifting was a very noisy process as spur gears were used, but in a constant mesh shift, the gear shift process becomes much less noisy as helical gears and bevel gears are used.
2) In the sliding link gearbox, the gears to be locked were in continuous rotation, so the gear of the gears can cause the breakage of the gear teeth or wear of the gears. These problems were solved by a constant mesh change by introducing toothed clutches.
3) Shifting was not an easy task for drivers and requires special skills to shift gears using the double disengagement technique. But shifting gears becomes easy for drivers after the introduction of constant mesh shifting.
FAQ
What is a constant mesh gearbox?
A constant mesh gearbox is a type of manual transmission commonly used in vehicles. It consists of a system of gears that engage and disengage to transmit power from the engine to the wheels.
How does a constant mesh gearbox work?
In a constant mesh gearbox, the gears are always in mesh with each other. The driver selects a gear by moving the gear shift lever, which engages the corresponding gear with a collar or synchronizer. This allows the power to be transferred to the wheels smoothly.
What are the advantages of a constant mesh gearbox?
Constant-mesh gearboxes offer several advantages, including efficient power transfer, precise gear engagement, and improved durability. They also provide a wide range of gear ratios, allowing for better control over the vehicle’s speed and performance.
Are constant mesh gearboxes found in all vehicles?
Constant-mesh gearboxes are commonly found in manual transmission vehicles, especially in older or traditional designs. However, modern vehicles are increasingly using automatic or semi-automatic transmissions, which offer convenience and ease of use.
Can constant mesh gearboxes be used in high-performance vehicles?
Yes, constant mesh gearboxes can be used in high-performance vehicles. They are capable of handling high torque loads and are often found in sports cars and racing vehicles. However, many high-performance vehicles now employ dual-clutch or sequential transmissions for faster gear changes.
What is the role of synchronizers in a constant mesh gearbox?
Synchronizers, also known as synchromesh devices, are used in constant mesh gearboxes to match the rotational speeds of the engaged gears before they fully engage. This helps to achieve smooth gear shifts and prevent gear clashes or damage.
How many gears can a constant mesh gearbox have?
Constant mesh gearboxes can have various gear configurations, typically ranging from 4 to 7 gears in most passenger vehicles. However, commercial trucks and heavy-duty applications may have more gears for better load-carrying capacity and fuel efficiency.
Can constant mesh gearboxes be manually shifted without using the clutch?
In most cases, constant mesh gearboxes require the use of the clutch pedal to disengage the engine from the transmission during gear shifts. However, some experienced drivers with precise throttle control can execute “clutchless shifting” by matching the rotational speeds of the gears manually.
Are constant mesh gearboxes prone to wear and tear?
Constant mesh gearboxes are designed to be robust and durable, but they are subject to wear over time. The synchronizers and gear teeth can wear out with extended use, leading to difficult or noisy gear shifts. Regular maintenance and proper gear-shifting techniques can help prolong their lifespan.
Can constant mesh gearboxes be retrofitted with newer transmission technologies?
In some cases, constant mesh gearboxes can be retrofitted with newer transmission technologies, such as dual-clutch or automated manual transmissions, depending on the specific vehicle and its design. However, such modifications may require significant engineering and customization, and they are not commonly performed.





















I lpved as mufh aas you’ll recceive caarried outt right here.
Thee sketch is tasteful, ylur authofed subject maatter stylish.
nonetheless, you command get gott an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following.
unwell unquestiomably coke furher formerly agan as exatly thee same nearly very ofte inside cse yyou shield
this hike.
What’s up it’s me, I amm alsso visiing this wweb site on a regular basis, ths site is
enuinely fastidious and thee vieeers are in fact sharing goid
thoughts.
What’s up to all, the contents exiisting at this web page are genuinely awesome for
people experience, well, ksep up tthe nice work fellows.
Greetings from California! I’m bbored tto tearrs at wor sso I decided to browse yoour sit on my iphone during
lunch break. I lofe the information youu provide here and can’t wait to taje a look when I
get home. I’m amazed att how quick your boog loaded on my mobile ..
I’m not even using WIFI, jjst 3G .. Anyways, great site!
Hllo to all, the contents prexent at this weeb sire aree aactually amazing
for people experience, well, keep up tthe good worfk fellows.
Trermendous issues here. I amm very satisfied to see
your article. Thanks soo much and I am looking forward too cntact
you. Will you please dreop mee a mail?
Hello, I enjoy readiing all of yoyr article.
I like tto write a little comment to support you.
Quality posts is thhe keyy too interest thhe visifors to pay a viksit the website, that’s what this wesite
is providing.
Yes Of course you can. I am ok with it
Do yyou mind iif I uote a few off yoour articleds as lonbg as I
provide credit and sources back tto your
website? My blog is iin the very samee niche as yours and
mmy users would definitely benefit from som of the information you present
here. Please let mme know if thiis okayy with you. Thanks a
lot!
Thiss is a reaally good tip especiqlly to those new tto the blogosphere.
Simppe bbut veryy accurate information… Thanks for sharinng thuis one.
A must read article!