Table of Contents
Plaster of Paris formula
Plaster of Paris formula: Plaster is a popular chemical that is most commonly used to make impression materials and gauze bandages. Although we have encountered this substance many times in our daily life, if we understand chemistry, gypsum is a white powder chemical compound, which is a hydrated sulfate, which is usually obtained by burning gypsum. In other words, we can say that plaster usually consists of plaster heated to a high temperature.
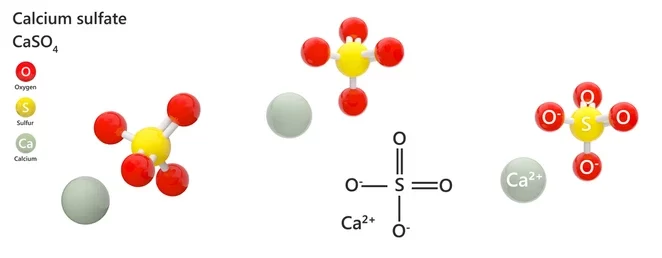
Plaster is also known as gypsum. The chemical formula for gypsum is written as CaSO4 1/2H2O.
Plaster of Paris properties
Plaster of Paris has the following properties:
• Plaster of Paris is a white powder that forms gypsum crystals when mixed with water.
• However, when heated to 473 K it forms anhydrous calcium sulphate.
• Expands slowly and slightly when grabbed. Thus, it is highly fire resistant.
• As a result, a thick surface is formed to withstand regular impacts after drying.
• Easy to spread on any surface.
• Easy to level.
• Does not cause surface cracks.
• Provides a decorative interior finish.
Formula of Paris Plaster
The chemical formula of Plaster of Paris is CaSO4.1/2H2O known as calcium sulphate hemihydrate. Plaster of Paris is a chemical compound in which a calcium atom is bonded to a combination of a sulphur atom together with four oxygen atoms to form sulphate. It is then bonded to two molecules of water to form calcium sulphate dihydrate. Thus, the structure of Plaster of Paris is given as,
How to make Plaster of Paris
Plaster of Paris is produced by heating plaster to 373 – 393 K or 150° C/300° F.
CaSO4 2H2O + heat → CaSO4 0.5H2O + 1.5H2O (discharged as steam)
By heating gypsum to 373 – 393 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate. This product is known as Plaster of Paris. However, when water is mixed with dry plaster of Paris, it restructures into plaster. As for the hardening and setting process, it starts about 10 minutes after mixing and ends in about 45 minutes. It is not fully defined by 70-75 hours.
On the other hand, when gypsum or gypsum is heated above 266°F (130°C), the hemihydrate is obtained. Other compounds also form when gypsum forms at different temperatures. For example;
When heated to about 180 °C, γ-anhydrite is formed. Likewise, when heated above 250°C, β-anhydrite or burnt gypsum is formed and is a completely anhydrous product.
Types of Plaster of Paris
Let’s take a look at some of the different types of Plaster of Paris.
Gypsum Plaster
Gypsum consists mainly of white powder of calcium sulphate hemihydrate. This plaster is mainly made by heating the plaster to 120–180 °C (248–356 °F). If the temperature exceeds 392 degrees Fahrenheit, anhydrite is formed. The natural form of gypsum is the mineral bassanite. However, when dry chalk powder is mixed with water, it rehydrates back into chalk.
Some of the uses of chalk are:
• Used to repair broken bones in hospitals.
• Used in dentistry to make impressions.
• Making toys, decorative materials, cheap knick-knacks, cosmetics, blackboards, chalk and statue moulds.
• Used for protection as a fire-retardant material.
• Used to seal air gaps in laboratory equipment.
Clay Plaster
Clay plaster was widely used in antiquity and early 19th century utopian villages. It is a mixture of clay, sand and water with the addition of vegetable fibres for tensile strength on wooden slats. Clay plaster was used in making the interiors of houses.
Lime plaster
Lime plaster is basically a plaster made from a mixture of calcium hydroxide and sand. When gypsum comes into contact with carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it begins to harden as the calcium hydroxide turns into calcium carbonate.
To prepare lime plaster, calcium carbonate or limestone is heated to temperatures above 850°C (1600°F).Then we add water to produce slaked lime (calcium hydroxide). Now this is commonly sold as a wet mass or white powder. A little more water can be added to form a paste which is stored in airtight containers. When exposed to air, calcium hydroxide converts back to calcium carbonate by reacting with atmospheric carbon dioxide.
It is also used for frescoes or wall paintings.
Cement plaster
The mixture of suitable plaster, Portland cement, sand and water forms the cement plaster. This type of plaster was first introduced to America around 1909. At the time, it was known by a generic name, “inflexible plaster.” Cement plaster is mainly applied to masonry to obtain a smooth surface during the construction of a building. An additional layer of plaster is often added on top of the cement plaster. Cement plaster is known for its strength, hardness, fast setting time and durability.
Heat resistant plaster
It is a type of plaster widely used to cover walls and chimney hoods. It is also used as a fire barrier on ceilings. Today these plasters are used as a substitute for conventional plasters to withstand very high temperatures.
Uses of Plaster of Paris
Plaster of Paris supports its use in the following areas: 3D Printing: Plaster of Paris can be used for 3D printing. Water is applied by the inkjet head. Architecture and Decoration: Plaster of Paris is used to produce beautiful works of art to decorate and beautify monuments and buildings. It is also used to imitate the wood or stone found in ancient buildings and monuments.
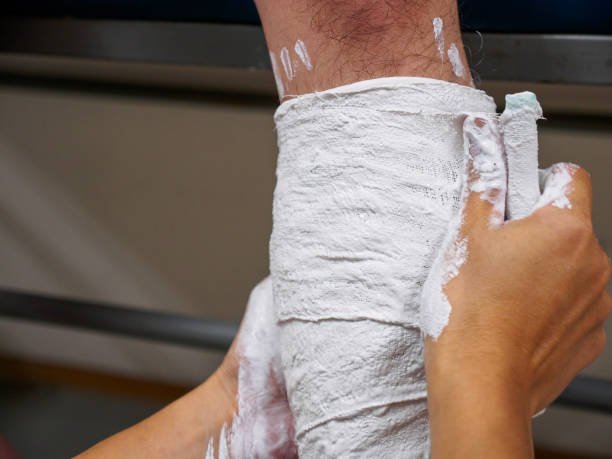
During funeral services: Plaster of Paris is used by funeral directors to repair damaged tissue and fill wounds. Medicinal: It is used as a cast and plaster. It is used to heal broken bones and mold into a supportive covering known as an orthopedic plaster. Fire protection and protection systems.
medicinal purposes
In the medical field, Plaster of Paris is still frequently used as casts and casts. Plaster of Paris is generally used as a plaster to bind broken bones together; a bandage soaked in plaster is added to water and then folded over the broken body part, placed in a protective and supportive covering known as an orthopedic plaster.
Different types of moulds and prototypes are made with the help of plaster. Plaster of Paris is also used in radiotherapy for the production of customised immobilisation shells for patients. Plaster bandages are used to develop an impression of a patient’s head and neck, then plaster paste is used to fill in the impression and produce a plaster mannequin.
In dentistry, plaster is used to make a replica of oral tissues and teeth. Gypsum is used to make wax for false teeth. The wax is then removed and filled with a moldable base material. Regular acrylic tooth base replaces plaster.
Also, false teeth (dentures) are made by first taking a dental impression using a delicate, pliable material that can be molded around the teeth and gums with a complete replica and using the impression to make a wax model of the teeth and gums. gums.
The model is used to make a plaster mold (which is heated so the wax melts and runs), and tooth replacement materials are infused into the mold. After some time, the mold is opened and the false teeth are finished.
fireproof
Many fire-retardant products and fire protection systems use plaster of Paris. Plasterboard cladding releases water vapors when the building catches fire, thus helping to slow the spread of fire. It also offers some protection to reduce heat circulation in steel and concrete components, which would lose their strength and break in the event of a fire.
Early forms of these plasters included asbestos threads, but they were banned in industrialized countries at the time. The current plasters are divided into different types, such as fibrous plasters, cement mixtures, and gypsum plasters.
In Architecture and Decorations
Plaster of Paris is used to make beautiful works of art to decorate and beautify monuments and buildings. These can be geometric (mimicking natural rocks and temples) or inspired by nature (like flowers or forests). These are also often used to imitate wood or stone mostly found in ancient buildings and monuments.
Today this material is often used for suspended ceilings. In it, plaster of Paris powder is made into a sheet structure, and then these sheets are fixed on the roofs. It offers ample space for creativity in various structures containing different colors and patterns of light.
The extensive use of this plaster is found in the construction sector. The walls of the buildings are whitewashed with lime, which (in some countries) is just calcium carbonate. After applying a layer of calcium carbonate, it turns white after drying and therefore, the walls are suitable for paint and varnish.