Table of Contents
Types of Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps

Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pump used in industrial and commercial settings. They work by converting rotational energy into kinetic energy to move fluids. The fluid enters through the pump’s center and is then accelerated by the impeller, which rotates at high speeds. As the fluid moves through the impeller’s vanes, it gains momentum and exits the pump at a high velocity.
Centrifugal pumps are used for low-viscosity fluids such as water, chemicals, and oils. They are widely used in water supply systems, irrigation, HVAC systems, and wastewater treatment plants.
End-Suction Centrifugal Pump
End-suction centrifugal pumps are one of the most common types of centrifugal pumps. They have a single impeller mounted on the end of a shaft, which is driven by an electric motor. These pumps are typically used for applications that require low to moderate flow rates and low to moderate pressure.
End-suction pumps are easy to install and maintain, making them a popular choice for many industrial and commercial applications. They are also versatile, as they can handle a wide range of fluids, from water and chemicals to petroleum products and slurries.
Split-Case Centrifugal Pump
Split-case centrifugal pumps have two impellers that are mounted on opposite sides of a shaft. These pumps are designed for high flow rates and high-pressure applications. They are commonly used in water treatment plants, fire suppression systems, and HVAC systems.
Split-case pumps are highly efficient and can handle a wide range of fluids. They are also easy to maintain and repair, as the casing can be easily removed to access the impellers and other components.
Vertical Multistage Centrifugal Pump
Vertical multistage centrifugal pumps are designed for applications that require high pressure and low flow rates. They consist of multiple impellers stacked on top of each other, with each impeller increasing the pressure of the fluid as it passes through.
Vertical multistage pumps are commonly used in water supply systems, irrigation systems, and industrial processes. They are highly efficient and can handle a wide range of fluids, including chemicals and corrosive liquids.
Regenerative Turbine Centrifugal Pump
Regenerative turbine centrifugal pumps are designed for low flow rate and high head applications. They use a series of rotating discs and stationary vanes to create a regenerative action that amplifies the pressure of the fluid.
Regenerative turbine pumps are commonly used in refrigeration systems, fuel oil transfer, and boiler feed applications. They are highly efficient and can handle fluids with high viscosity and low specific gravity.
Submersible Centrifugal Pump
Submersible centrifugal pumps are designed for use in applications where the pump needs to be submerged in the fluid it is pumping. They are commonly used in sewage systems, stormwater systems, and irrigation systems.
Submersible pumps are highly efficient and can handle a wide range of fluids. They are also easy to install and maintain, as they do not require a separate motor or mounting.
Dynamic pumps
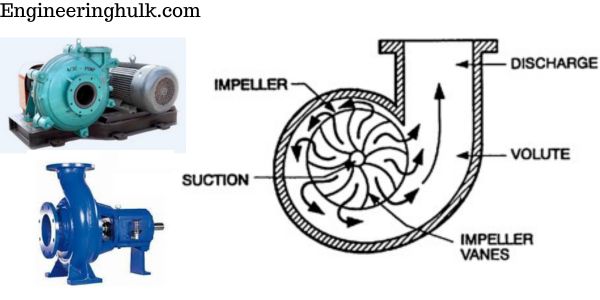
Dynamic pumps are mechanical devices used to move fluids by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. They are classified into two main categories, namely, positive displacement pumps and dynamic pumps. Unlike positive displacement pumps, dynamic pumps work by converting kinetic energy into potential energy. The two main types of dynamic pumps are centrifugal pumps and axial flow pumps. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of dynamic pumps.
Axial Flow Pumps
Axial flow pumps, also known as propeller pumps, are another type of dynamic pump. They use a propeller-like impeller to move fluid axially along the pump axis. The impeller blades are angled to create a flow of fluid along the length of the impeller. The fluid is then discharged at the end of the impeller into a diffuser, which helps to increase the pressure of the fluid before it is discharged. Axial flow pumps are commonly used in irrigation, drainage, and flood control applications, as well as in industrial processes.
Mixed Flow Pumps
Mixed flow pumps are a combination of centrifugal and axial flow pumps. They use an impeller with curved blades to create a flow of fluid that combines both radial and axial components. The fluid is drawn in radially by the impeller blades and then pushed outwards in an axial direction by the curved blades. Mixed flow pumps are commonly used in applications that require both high flow rates and moderate to high pressures, such as irrigation, cooling water systems, and water supply systems.
Regenerative Pumps
Regenerative pumps, also known as peripheral pumps or turbine pumps, are a type of dynamic pump that uses a rotating impeller with small channels or vanes on the circumference. As the impeller rotates, the vanes trap fluid between the impeller and the pump casing, and the fluid is forced out at high pressure. Regenerative pumps are commonly used in applications that require high pressures and low flow rates, such as air conditioning and refrigeration systems, as well as in some industrial processes.
Positive Displacement Pumps

Positive displacement pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and then forcing it through the pump’s outlet. These pumps are ideal for handling high-viscosity fluids, such as syrups, slurries, and oils. Positive displacement pumps are further divided into two types: reciprocating and rotary.
Reciprocating Pumps
Reciprocating pumps use a piston or diaphragm to move fluid through the pump. As the piston or diaphragm moves back and forth, the fluid is forced out of the pump. These pumps are commonly used in chemical processing, oil and gas, and food and beverage industries.
Rotary Pumps
Rotary pumps use a rotating element to move fluid through the pump. The most common type of rotary pump is the gear pump, which uses two interlocking gears to move the fluid through the pump. These pumps are commonly used in the oil and gas industry, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
Diaphragm Pumps
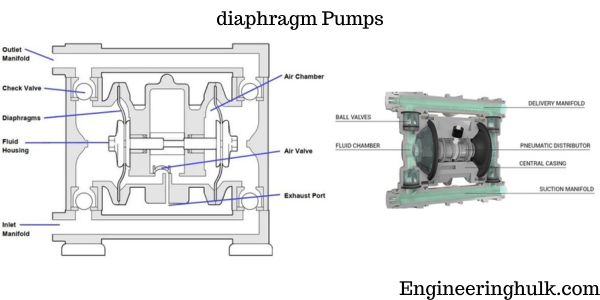
Diaphragm pumps are positive displacement pumps that use a flexible diaphragm to move fluids. These pumps are ideal for pumping a wide range of liquids, including chemicals, corrosives, and viscous fluids. They are commonly used in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and water treatment. In this article, we will discuss the different types of diaphragm pumps and their applications.
Air-Operated Double Diaphragm Pumps
Air-operated double diaphragm pumps, or AOD pumps, use compressed air to move the fluid through the pump. These pumps have two diaphragms that alternate between suction and discharge cycles. As one diaphragm fills with fluid, the other diaphragm pushes the fluid out of the pump. AODD pumps are commonly used in the chemical and petrochemical industries, as well as in food and beverage processing.
Electric Diaphragm Pumps
Electric diaphragm pumps are powered by an electric motor and are commonly used in applications where compressed air is not available or not practical. They are ideal for pumping clean fluids and are often used in the water treatment industry, as well as for chemical transfer and food and beverage processing.
Hydraulic Diaphragm Pumps
Hydraulic diaphragm pumps use hydraulic fluid to move the diaphragm. They are commonly used in applications where a constant flow rate is required, such as in chemical dosing and water treatment. Hydraulic diaphragm pumps are also used in high-pressure applications, such as in the oil and gas industry.
Double Diaphragm Pumps
Double diaphragm pumps use two diaphragms that work in unison to create a pumping action. They are often used in applications where a constant flow rate is required, and where the liquid being pumped is highly viscous or contains solids. Double diaphragm pumps are also ideal for handling abrasive or corrosive fluids.
Pneumatic Diaphragm Pumps
Pneumatic diaphragm pumps are similar to air-operated diaphragm pumps, but they use a different type of air distribution system. They are ideal for pumping fluids that contain solids, as well as for handling abrasive or corrosive liquids. Pneumatic diaphragm pumps are commonly used in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
Metal Diaphragm Pumps
Metal diaphragm pumps are designed for applications where the liquid being pumped is highly corrosive or abrasive. They are often used in the chemical and petrochemical industries, as well as in mining and oil and gas applications. Metal diaphragm pumps are also suitable for pumping high-temperature fluids.
Non-Metallic Diaphragm Pumps
Non-metallic diaphragm pumps are ideal for handling highly corrosive and abrasive liquids. They are commonly used in the chemical processing industry, as well as in the production of electronic components and semiconductors. Non-metallic diaphragm pumps are also suitable for pumping food and beverage products.
Magnetic Drive Pumps
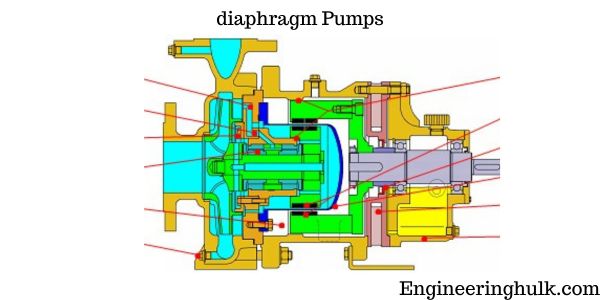
Magnetic drive pumps use a magnetic coupling to transfer power from the motor to the impeller. The magnetic coupling eliminates the need for a traditional seal, which can be a significant source of leaks and maintenance issues. These pumps are commonly used in the chemical processing industry and in applications where the fluid being pumped is hazardous or corrosive.
Also, read the Carnot cycle





















Comment on “Types of Pumps – All Types and Subtypes with Description”
Comments are closed.