Table of Contents
Introduction
Sheet metal fabrication is a vital industrial process that plays a pivotal role in the creation of countless products we use daily. From automotive parts to kitchen appliances, aerospace components to architectural elements, sheet metal fabrication is the art and science of transforming flat sheets of metal into complex, functional, and aesthetically pleasing shapes.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Basics
- What is Sheet Metal?
Sheet metal refers to metal formed into thin, flat sheets, typically ranging in thickness from 0.006 inches (0.15mm) to 0.25 inches (6.35mm). Common sheet metal materials include steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and titanium.
- The Significance of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is crucial because it allows manufacturers to produce complex components and products with high precision, durability, and cost-effectiveness. It’s widely used across industries like aerospace, automotive, construction, and electronics.

Processes Involved in Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Cutting
Cutting is the first step in the sheet metal fabrication process. It involves removing excess material to create the desired shape. Common cutting methods include:
a. Shearing: Uses a straight-edged blade to make straight cuts. b. Laser Cutting: Employs a laser beam to precisely cut through the metal. c. Plasma Cutting: Uses a high-temperature, ionized gas jet to cut metal. d. Waterjet Cutting: Utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials for cutting.
- Bending
Bending involves shaping the sheet metal into the desired form. This is typically done using a press brake or other specialized machines.
- Forming
Forming is the process of manipulating the sheet metal to achieve specific contours or shapes. Techniques include deep drawing, spinning, and hydroforming.
- Welding
Welding joins two or more pieces of sheet metal together. Common welding methods include MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), and spot welding.
- Assembly and Finishing
After shaping and welding, sheet metal components often require assembly, which may involve riveting, fastening, or adhesive bonding. Finishing processes like painting, powder coating, or polishing enhance the final product’s appearance and corrosion resistance.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Automotive Industry
Sheet metal is extensively used in vehicle bodies, chassis, and interior components due to its strength-to-weight ratio and ease of fabrication.
- Aerospace
Aircraft components, such as wings, fuselages, and engine enclosures, rely heavily on sheet metal fabrication for their lightweight yet robust construction.
- Construction
Architectural elements like facades, roofing, and structural components often feature sheet metal due to its durability and aesthetic versatility.
- Electronics
Sheet metal enclosures and brackets are vital for housing and protecting sensitive electronic components.
- Appliances
Kitchen appliances, HVAC systems, and industrial machinery incorporate sheet metal for both structural support and aesthetic appeal.

Materials Used in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal can be crafted from various materials, each with its unique properties and applications:
- Steel: Renowned for its strength, durability, and affordability, steel is a common choice in sheet metal fabrication.
- Aluminum: Known for its lightweight and corrosion resistance, aluminum is favored in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Copper and Brass: These metals are prized for their electrical conductivity and attractive appearance, making them suitable for electrical components and decorative elements.
- Stainless Steel: Resistant to corrosion and staining, stainless steel is ideal for applications demanding a high level of hygiene, such as kitchen equipment and medical devices.
Advancements in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication continues to evolve with technological advancements:
- Automation: Robotics and computer numerical control (CNC) systems enhance precision and efficiency in cutting, bending, and welding processes.
- 3D Printing: Metal 3D printing allows for intricate and custom sheet metal components with reduced waste.
- Sustainable Practices: Eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes are becoming increasingly important in sheet metal fabrication, focusing on reducing waste and energy consumption.
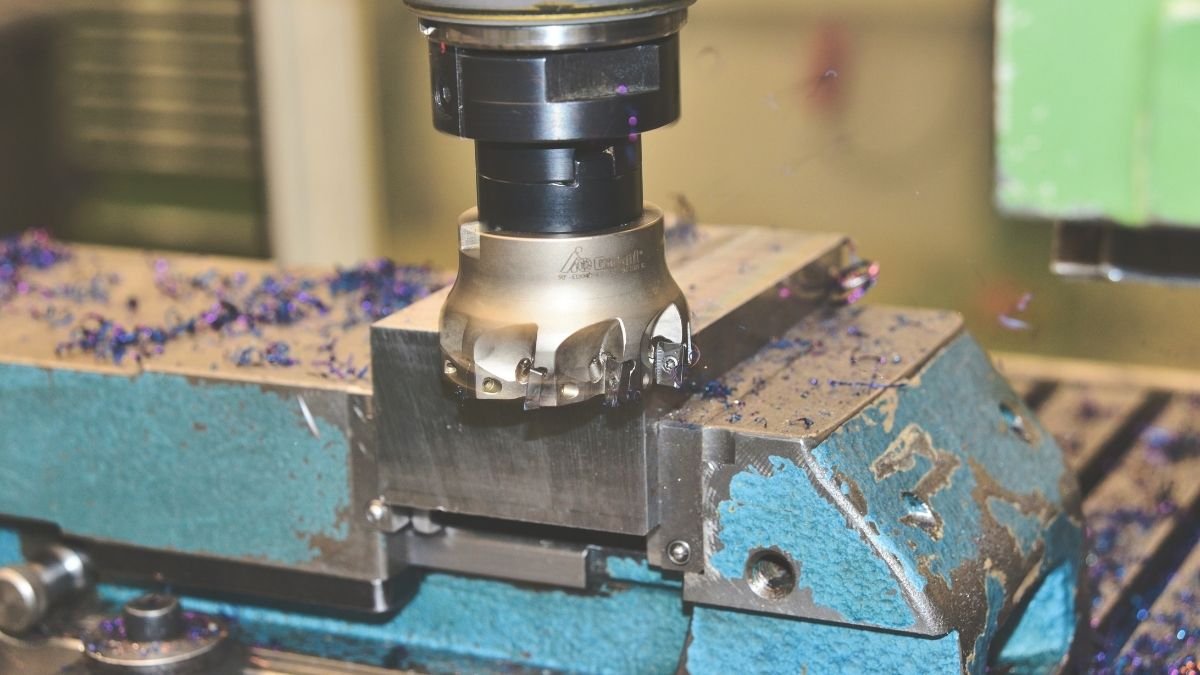
Sheet Metal Fabrication Machine

Sheet metal fabrication involves the process of creating metal parts and structures from flat sheets of metal. Machine components used in sheet metal fabrication play a crucial role in cutting, bending, shaping, and assembling these metal sheets into various products and parts. Here are some essential machine components commonly used in sheet metal fabrication:
- Shearing Machine:
- Shear Blades: These are sharp blades used for cutting sheet metal to the required size and shape.
- Punch Press:
- Punch and Die Sets: Punch presses use punch and die sets to create holes, notches, and various shapes in sheet metal.
- Bending Machine (Press Brake):
- Bending Die: This die is used to bend the sheet metal to the desired angle.
- Back Gauge: It ensures the accuracy and consistency of bends by setting the distance from the edge of the sheet metal.
- **Rolling Machine (Roller):
- Rolls: These are cylindrical rolls that shape the sheet metal into curves, cylinders, or cones.
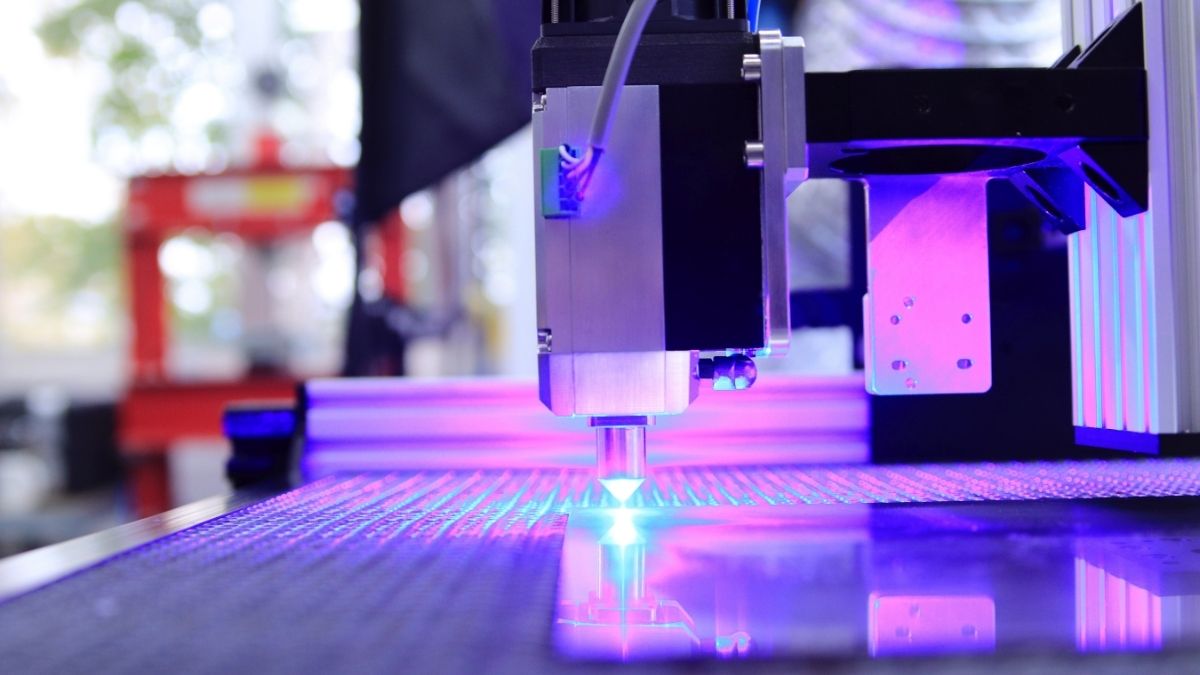
- Laser Cutting Machine:
- Laser Beam: The laser beam is used for precision cutting of sheet metal.
- Focusing Lens: It helps to concentrate the laser beam and achieve precise cuts.
- Plasma Cutting Machine:
- Plasma Torch: The plasma torch generates a high-temperature plasma stream for cutting through the sheet metal.
- Welding Machine:
- Welding Torch or Gun: This is used to join pieces of sheet metal together by melting and fusing them.
- Electrode or Wire: The material used to create the weld, such as a welding electrode or wire.
- Spot Welding Machine:
- Electrodes: The electrodes apply pressure and electrical current to create spot welds, joining metal pieces at specific points.
- Riveting Machine:
- Rivet Gun: It is used to insert and secure rivets, and fasten sheet metal parts together.
- Grinding Machine:
- Grinding Wheel: Used to smooth and polish the edges of cut or welded sheet metal.
- Deburring Tools:
- Deburring Bits or Brushes: These tools remove sharp edges and burrs from the edges of sheet metal.
- Forming Dies:
- Various dies and tooling: Different dies are used to create specific shapes and forms in the sheet metal.
- Feeding and Conveying Systems:
- Feeder mechanisms: These systems help to advance and position the sheet metal for processing.
- Control Panels and CNC Systems:
- Control panels: These allow operators to set and control the machine’s parameters.
- CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Systems: They enable automated and precise control of machine operations.
- Safety Features:
- Emergency Stop Buttons: These ensure the safety of operators in case of emergencies.
- Guards and Safety Sensors: To protect operators from moving parts and hazards.
- Worktable or Bed:
- The surface on which the sheet metal is placed and processed.
Sheet metal fabrication is a versatile and indispensable industry that impacts virtually every aspect of modern life. From the cars we drive to the buildings we inhabit, sheet metal plays a crucial role in creating the structures and products that define our world.
With ongoing technological advancements and a commitment to sustainability, the future of sheet metal fabrication promises to be even more innovative and environmentally responsible, further cementing its place in manufacturing and engineering.
Also, read CNC Mill


























Comment on “Sheet Metal Fabrication: A Comprehensive Guide in 2024”
Comments are closed.