Table of Contents
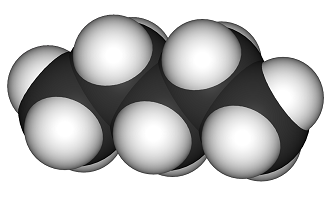
Pentane is a hydrocarbon with five carbon atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms, which makes it an alkane with the molecular formula C5H12. It is a clear, colorless liquid that is commonly used as a solvent in laboratory experiments. The structure of pentane is made up of a straight chain of five carbon atoms with each carbon atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. However, due to its straight chain structure, pentane has several isomers, which are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements.
In this article, we will discuss the different isomers of pentane, their structures, and their physical and chemical properties.
There are three types of isomers of pentane:
Chain Isomers:
Pentane has five carbon atoms in a chain. Therefore, it can exist in various forms of straight-chain isomers or n-pentane, denoted as C5H12.
Position Isomers:
Position isomers arise due to differences in the position of the functional groups or substituents. For example, 2-methyl butane and 3-methyl butane are position isomers of pentane.
Stereoisomers:
Pentane can exist as stereoisomers, where the spatial arrangement of atoms in the molecule is different. These include cis and trans isomers, as well as optical isomers (enantiomers and diastereomers). However, pentane has no chiral center, so it cannot exist as an optical isomer.
Types of Isomers of pentane:
There are three types of isomers of pentane:
Straight-Chain Isomers:
Pentane has one straight-chain isomer, n-pentane, which is also known as normal pentane. In n-pentane, the carbon atoms are arranged in a straight line, and each carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The molecular formula of n-pentane is C5H12.
Branched-Chain Isomers:
Pentane has three branched-chain isomers, which are also known as isopentane, neopentane, and dimethylpropane. In these isomers, the carbon atoms are not arranged in a straight line. Instead, they are arranged in a branched structure.
a) Isopentane:
Isopentane is also known as 2-methyl butane. In isopentane, one carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms, and the remaining carbon atoms are bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The molecular formula of isopentane is C5H12.
b) Neopentane:
Neopentane is also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane. In neopentane, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms, and the remaining carbon atoms are bonded to one hydrogen atom. The molecular formula of neopentane is C5H12.
c) Dimethylpropane:
Dimethylpropane is also known as 2,2-dimethylbutane. In dimethylpropane, two carbon atoms are bonded to three other carbon atoms, and the remaining carbon atoms are bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The molecular formula of dimethylpropane is C5H12.
Cycloalkane Isomers:
Pentane has one cycloalkane isomer, which is also known as cyclopentane. In cyclopentane, the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring structure, and each carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms.
Position Isomers of pentane
Pentane is an organic compound with a molecular formula of C5H12. It belongs to the class of alkanes, which are hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. Pentane has five carbon atoms that are arranged in a straight chain, and it exists in several different isomeric forms. One type of isomerism that is exhibited by pentane is position isomerism.
Position isomers, also known as constitutional isomers, are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures due to differences in the position of functional groups or substituents on the carbon chain. In the case of pentane, there are three possible position isomers: n-pentane, isopentane, and neopentane.
n-Pentane, also known as normal pentane, is the most straightforward and simplest of the three position isomers. It has a straight-chain structure with all five carbon atoms connected by single bonds. Each carbon atom is also bonded to two hydrogen atoms, making n-pentane a saturated hydrocarbon. Its structural formula is CH3(CH2)3CH3.
Isopentane, also known as 2-methyl butane, is another position isomer of pentane. It differs from n-pentane in that it has a branched structure. Isopentane has four carbon atoms in a straight chain, with a methyl group (CH3) attached to the second carbon atom. The remaining carbon atom is also bonded to two methyl groups, making isopentane a saturated hydrocarbon. Its structural formula is CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3.
Neopentane, also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane, is the most complex of the three position isomers of pentane. It has a highly branched structure with four carbon atoms arranged in a tetrahedral shape around a central carbon atom. Each of the four carbon atoms is bonded to three other atoms: two hydrogen atoms and one methyl group. Neopentane is also a saturated hydrocarbon. Its structural formula is (CH3)3CCH3.
The physical and chemical properties of the three position isomers of pentane differ due to differences in their structures. For example, n-pentane has a higher boiling point than isopentane and neopentane due to its straight-chain structure, which allows for stronger intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules. Isopentane and neopentane, on the other hand, have lower boiling points and are more volatile due to their branched structures, which reduce intermolecular forces of attraction.
The three-position isomers of pentane – n-pentane, isopentane, and neopentane – exhibit different structures and properties due to differences in the position of functional groups or substituents on the carbon chain. These differences in structure and properties have important implications for the applications of these compounds in various fields, such as in the petrochemical industry, where they are used as solvents and as feedstocks for the production of other chemicals.
Stereoisomers
Stereoisomers are a class of organic molecules that have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their atoms. Pentane, which has the chemical formula C5H12, is an example of a molecule that can have stereoisomers. In this article, we will explore the different types of stereoisomers of pentane.
Pentane is a straight-chain hydrocarbon that contains five carbon atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms. It has the structural formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3, and each carbon atom in the chain is bonded to two other carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms. There are three stereoisomers of pentane, which are known as the cis isomer, the trans isomer, and the axial isomer.
The cis and trans isomers of pentane are examples of geometric isomers, which differ in the orientation of their atoms around a double bond. In the case of pentane, there is no double bond, but the cis and trans isomers still differ in their spatial arrangement. The cis isomer of pentane has both of its methyl (CH3) groups on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides.
The axial isomer of pentane is a type of stereoisomer that arises from the different orientations of the carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule. In pentane, the carbon-carbon bonds can be either axial or equatorial, depending on their position in the chain. The axial isomer of pentane has all of its carbon-carbon bonds in the axial position, while the equatorial isomer has them in the equatorial position.
The axial isomer of pentane is less stable than the equatorial isomer due to steric hindrance. In the axial isomer, the methyl groups are positioned in a way that makes them too close to each other, leading to repulsive interactions. In contrast, the equatorial isomer positions the methyl groups farther apart from each other, resulting in a more stable structure.
Pentane has three stereoisomers: the cis isomer, the trans isomer, and the axial isomer. The cis and trans isomers differ in the orientation of their atoms around a double bond, while the axial isomer arises from the different orientations of the carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule. Understanding the different types of stereoisomers is important in organic chemistry, as it can help predict the properties and reactivity of molecules in different contexts.
Also, read Battery Charging Methods in Automobiles