Table of Contents
Construction:
The Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) process uses a jet of abrasive particles mixed with air or gas to remove material from a workpiece’s surface. It’s a subtractive manufacturing technology often used for cutting, deburring, or etching materials.
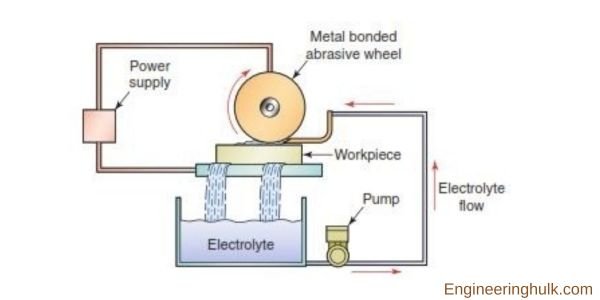
1. Gas Supply and Regulator: This usually consists of a cylinder containing compressed air or another suitable gas. A pressure regulator controls the gas’s pressure before it enters the mixing chamber.
2. Mixing Chamber: In this chamber, the compressed gas is mixed with the abrasive particles. This may be a simple venturi where the negative pressure created by the fast-moving gas draws the abrasive particles into the flow.
3. Abrasive Feeding System: This system consists of a container holding the abrasive particles and a mechanism to feed those particles into the mixing chamber. The type of abrasive varies depending on the application, but common choices include aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or glass beads.
4. Nozzle: The nozzle directs the mixed stream of gas and abrasive particles onto the workpiece. It must be made of a material that can withstand the abrasive action of the particles, so it’s often made from tungsten carbide or ceramic material.
5. Work Chamber: The work chamber contains the workpiece and allows the operator to manipulate it as needed. It’s usually equipped with a window so that the operator can see the workpiece, and it might have gloves built into the side to allow the operator to handle the workpiece without being exposed to the abrasive jet.
6. Dust Collector: The abrasive action generates a lot of dust and waste material. The dust collector removes this from the work chamber to keep the working environment clean.
7. Control System: The control system can vary in complexity from simple manual controls to sophisticated CNC systems that allow the abrasive jet to follow a pre-programmed path.
8. Cooling System: Sometimes a cooling system might be included, depending on the material and the application, to prevent any undesirable thermal effects on the workpiece.
9. Waste Removal System: Some machines will include a way to remove the used abrasive particles and other waste materials from the work chamber.

In operation, the gas is compressed and mixed with the abrasive particles, and the resulting high-speed jet of abrasive material is directed onto the workpiece. The impact of the particles erodes the surface of the workpiece, cutting it or producing the desired surface finish.
The construction of the abrasive jet machine is carefully designed to control the many variables involved in this process, such as the type and size of abrasive particles, the pressure and flow rate of the gas, and the design of the nozzle. This ensures that the machine can produce the desired results consistently and accurately.
How Abrasive Jet Machining Works:
1. Gas Source: Compressed gas (usually air or nitrogen) is mixed with abrasive particles like aluminum oxide or silicon carbide.
2. Mixing Chamber: The compressed gas and abrasive particles are mixed together in a chamber, creating a mixture ready for acceleration.
3. Acceleration Through Nozzle: The abrasive-gas mixture is forced through a nozzle, which concentrates and accelerates the jet to high velocity. The nozzle’s shape and size play a key role in determining the velocity and focus of the jet.
4. Machining the Workpiece: As the abrasive jet impacts the workpiece, the kinetic energy of the abrasive particles erodes the material on the surface. The material removal takes place due to the abrasive action of the particles against the workpiece. Softer areas are eroded more easily, leading to selective material removal.
5. Motion Control: The relative movement between the nozzle and the workpiece is controlled either manually or through automated means like CNC. This determines the shape and size of the cut, drill, or engraved pattern.
6. Standoff Distance: The distance between the nozzle and the workpiece must be maintained precisely, as it affects the focus and cutting ability of the jet.
7. Waste Management: The process generates dust and waste particles, which are typically extracted and filtered from the work area.
The essence of AJM lies in the conversion of energy: the compressed gas’s potential energy is converted into kinetic energy in the abrasive particles, which then use this energy to mechanically erode and remove material from the workpiece. This allows AJM to cut, engrave, and shape various materials, including those that are sensitive to heat or mechanical stress.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM)
Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM), also known as abrasive blasting, is a machining process where a jet of abrasive particles is propelled at high speed to impact the workpiece for material removal. It has been widely used in industries for cutting, cleaning, polishing, and etching. However, like all manufacturing methods, it has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Abrasive Jet Machining
1. Versatility
AJM can be applied to almost any material, including hard, brittle, heat-sensitive, and even soft materials, which makes it versatile in different applications.
2. No Thermal Damage
Since the process doesn’t generate significant heat, it avoids the problem of thermal distortion or hardening, preserving the material’s integrity.
3. No Mechanical Stresses
As there’s no direct contact between the tool and the workpiece, the process doesn’t create mechanical stresses, thus reducing the risk of deformations.
4. Complex Geometries
AJM allows the machining of complex shapes and intricate patterns, even on hard and brittle materials.
5. Environmentally Friendly
The process doesn’t generate hazardous by-products, and the abrasive materials can be recycled, making it more environmentally sustainable.
Disadvantages of Abrasive Jet Machining
1. Material Wastage
AJM can lead to substantial material wastage, especially if not properly controlled. This can increase the cost of operation.
2. Limited Material Thickness
While versatile, AJM might not be suitable for cutting very thick materials, as the effectiveness of the jet decreases with depth.
3. Abrasive Consumption
The continuous need for fresh abrasive particles can make AJM expensive to operate, particularly when specialized or rare abrasives are required.
4. Accuracy and Finish
The surface finish may be relatively rough, and the accuracy of the machining might not meet the standards required for some high-precision applications.
5. Health and Safety Concerns
The process generates dust and noise, which can be health hazards if not properly managed.
6. Maintenance
The machinery used in AJM can be prone to wear and tear, particularly in the nozzle area. Regular maintenance and replacements might be necessary, increasing the overall operating cost.

What is the abrasive jet application?
Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) is a manufacturing process that uses a high-speed stream of abrasive particles carried in a gas or air stream to erode material from the workpiece. Common applications include cutting, drilling, engraving, and deburring various materials, especially hard and brittle substances like glass, ceramics, and metals.
What is the principle of AJM?
The principle of AJM is based on the use of a focused stream of abrasive particles accelerated through a nozzle. These particles strike the workpiece with significant kinetic energy, removing material through a continuous erosion process. The particles and carrier gas are mixed in a mixing chamber, then expelled through the nozzle to achieve the desired material removal.
What are the 5 uses of abrasives?
1. Material Cutting: Abrasives can cut through hard materials with precision.
2. Grinding and Polishing: They are used to smooth and finish surfaces by removing small amounts of material.
3. Cleaning and Deburring: Abrasives remove burrs and other imperfections from metal parts.
4. Surface Texturing: They can be used to create specific surface textures for aesthetic or functional purposes.
5. Drilling: In AJM, abrasives are used for drilling holes in hard and brittle materials.

What material is used in AJM?
In AJM, the abrasive materials typically used include aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, glass beads, and other hard, granular materials that can erode the workpiece material.
What are the parameters of AJM?
Key parameters in AJM include:
– Abrasive type and size
– Nozzle size and shape
– Carrier gas pressure and type
– Standoff distance (distance between nozzle and workpiece)
– Traverse speed of the nozzle
What is the velocity of AJM?
The velocity of the abrasive particles in AJM can vary widely based on the equipment and settings, ranging from 150 to 300 meters per second or even higher.
Which carrier gas is used in AJM?
Typically, dry and clean air is used as the carrier gas, although other gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide can also be used depending on the specific application.
What is the removal rate of AJM metal?
The removal rate in AJM depends on several factors, including abrasive type, velocity, workpiece material, and machining parameters. It can range from a few millimeters per minute to several centimeters per minute.
What is the abrasive grain size in AJM?
The abrasive grain size in AJM can vary, typically ranging from 10 to 50 micrometers. The choice depends on the specific requirements of the task, such as the desired surface finish and material removal rate.
What is the stand of distance in AJM?
The standoff distance in AJM refers to the distance between the nozzle and the workpiece. It is a crucial parameter that affects the focusing of the abrasive jet and consequently the quality and efficiency of the machining process. Typical standoff distances range from 0.5 to 2 mm.
Also, read Site selection for hydroelectric power plant
























Comment on “Abrasive jet machining – Detailed Information 2023”
Comments are closed.