Table of Contents
Introduction:
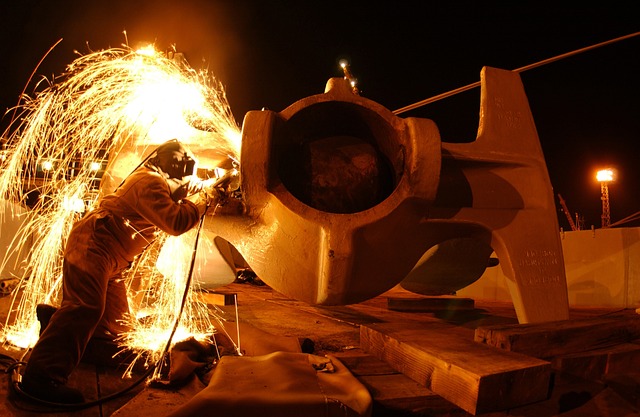
Casting is a fascinating and intricate process that plays a crucial role in the creation of various objects, from intricate sculptures to industrial components. This age-old technique involves the pouring of molten material into a mold, which then solidifies to form the desired shape.
Understanding Casting:
Casting is a manufacturing process that dates back thousands of years and is still widely used today. It involves pouring a liquid or molten material into a mold and allowing it to solidify, resulting in the creation of a three-dimensional object. The process of casting provides the ability to produce complex shapes with excellent precision, making it a preferred method for creating a wide range of objects.
Types of Casting Processes:
There are various casting processes available, each suited to different materials and applications. Some of the most commonly used casting processes include:
Sand Casting:
Sand casting is one of the most widely used casting processes due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It involves creating a mold by compacting a mixture of sand and a binder material around a pattern. Once the mold is prepared, molten metal is poured into the cavity, allowing it to solidify. Sand casting is ideal for producing large and complex shapes, making it a popular choice in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Investment Casting:
Also known as lost-wax casting, investment casting is a precise and intricate casting process. It begins with the creation of a wax pattern that replicates the desired shape. The wax pattern is then coated with a ceramic material to form a mold. The mold is heated to melt and remove the wax, leaving a cavity.
Molten metal is then poured into the cavity, filling the mold and solidifying it to create the final product. Investment casting is often used to produce highly detailed and intricate components in the jewelry, aerospace, and art industries.
Die Casting:
Die casting is a high-pressure casting process that is well-suited for the mass production of complex-shaped objects with excellent dimensional accuracy. It involves injecting molten metal, typically aluminum or zinc-based alloys, into a reusable steel mold or die under high pressure. The metal quickly solidifies, and the mold is opened to reveal the finished product.
Die casting is widely used in industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, and appliances due to its efficiency and high production rates.
Centrifugal Casting:
Centrifugal casting is a casting process that utilizes centrifugal force to distribute molten material evenly within a mold. The mold is rotated at high speeds while the molten material is poured into it. Centrifugal force ensures that the denser material is pushed toward the outer edges of the mold, resulting in a uniform and defect-free casting. This process is commonly used for producing cylindrical shapes such as pipes, tubes, and rings.
Continuous Casting:
Continuous casting is a method used to produce long and continuous metal sections with a constant cross-section. The process involves pouring molten metal into a water-cooled mold, which solidifies the outer layer of the material.
As the metal continues to harden, it is continuously drawn out from the bottom of the mold, resulting in a continuous length of metal. Continuous casting is primarily used in the steel industry for producing slabs, billets, and wire rods.
Shell Molding:
Shell molding, also known as shell mold casting, is a precision casting process that utilizes resin-coated sand to create the mold. The sand mixture is heated and applied onto a pattern, creating a shell-like mold. Once the mold is prepared, molten metal is poured into it, and the metal solidifies within the shell. Shell molding offers excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish, making it suitable for producing small to medium-sized components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and machinery.

Materials Used in Casting:
Casting can be performed using a wide range of materials, depending on the desired properties of the final product. Some common casting materials include:
a. Metals:
Metals like aluminum, iron, steel, bronze, and brass are frequently used in casting due to their excellent strength, durability, and heat resistance.
b. Alloys:
Various alloy compositions are employed to achieve specific characteristics, such as increased strength, corrosion resistance, or improved casting properties.
c. Plastics:
Casting processes are not limited to metals; plastics such as polyurethane, epoxy, and polyester can also be used to create intricate shapes for industrial, artistic, and prototyping purposes.
The Casting Process in Detail:
The casting process involves several key steps:
a. Pattern Making:
A pattern is created, either by carving it out of wood, machining it from metal, or using 3D printing techniques. The pattern replicates the final shape of the desired object.
b. Mold Preparation:
The pattern creates a mold, usually made of sand, plaster, or other refractory materials. The mold is designed to withstand the high temperatures of the molten material.
c. Melting and Pouring:
The casting material is melted in a furnace and brought to the desired temperature. Once molten, it is carefully poured into the mold through a gating system.
d. Solidification:
The molten material cools and solidifies inside the mold, taking the shape of the pattern.
e. Cooling and Removal:
After solidification, the mold is allowed to cool, and the casting is removed. In some cases, secondary processes like sandblasting, machining, or polishing are performed to achieve the desired finish.

Applications of Casting:
Casting finds applications in various industries and sectors, including:
a. Automotive:
Casting is used to produce engine blocks, transmission components, and other intricate parts.
b. Aerospace:
Complex aerospace components like turbine blades, engine casings, and structural parts are often manufactured using casting techniques.
c. Art and Sculpture:
Casting offers artists the ability to create intricate and detailed sculptures in various materials.
d. Jewelry:
Precious metals like gold and silver are cast to create stunning jewelry pieces with intricate designs.
e. Industrial Components:
Many industrial sectors rely on casting for the production of valves, pumps, gears, and other essential components.
FAQS
What are the advantages of the casting process?
Some advantages of the casting process include the ability to produce complex shapes, high production rates, good dimensional accuracy, and the ability to use a wide range of materials.
What types of materials can be used in the casting process?
Various materials can be used for casting, including metals (such as iron, steel, aluminum, and copper alloys), as well as non-metallic materials like plastics and composites.
What are the different casting methods?
There are several casting methods, including sand casting, investment casting, die casting, permanent mold casting, and centrifugal casting. Each method has its own unique characteristics and applications.
How does sand casting work?
In sand casting, a pattern of the desired object is created using a mold made of sand. Molten metal is then poured into the mold, which solidifies and forms the final shape once it cools. After solidification, the mold is removed, and the casting is cleaned and finished.
What is investment casting?
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, involves creating a wax pattern of the desired object. The wax pattern is then coated with a ceramic material, which hardens to form the mold. The wax is melted out, and molten metal is poured into the cavity. Once solidified, the ceramic mold is broken to reveal the final casting.
What is die casting?
Die casting is a process where molten metal is forced into a mold cavity under high pressure. The mold called a die, is typically made of steel and consists of two halves. Once the metal solidifies, the die is opened, and the casting is ejected.
What is permanent mold casting?
Permanent mold casting involves the use of reusable molds, typically made of metal, to create castings. The molten metal is poured into the mold, where it solidifies and takes the shape of the mold cavity. After solidification, the mold is opened, and the casting is removed.
What factors affect the quality of castings?
Several factors influence the quality of castings, including mold design, material selection, pouring temperature, cooling rate, and post-casting processes like heat treatment and surface finishing.
References
- “Metal Casting: A Sand Casting Manual for the Small Foundry, Vol. 1” by Steve Chastain
- This book provides detailed information and practical guidance on sand casting, making it suitable for small foundries and hobbyists.
- “Investment Casting Handbook” by Douglas C. Heaton
- This comprehensive handbook covers the investment casting process, including patterns, molds, wax and shell materials, and quality control.
- “Die Casting Engineering: A Hydraulic, Thermal, and Mechanical Process” by William Andresen
- This book focuses on die casting and covers topics such as die design, alloys, process optimization, and defects in die castings.
- “ASM Handbook, Volume 15: Casting” published by ASM International
- ASM International is a well-respected organization in materials science and engineering. This handbook provides an in-depth overview of various casting processes, materials, and related technologies.
- “Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials, Processes, and Systems” by Mikell P. Groover
- This textbook covers a wide range of manufacturing processes, including casting. It offers a comprehensive introduction to casting methods and principles.
- “Metal Casting Principles and Techniques” by Trevor L. Jones and Richard J. Talbert
- This book provides a comprehensive understanding of metal casting processes, including sand casting, investment casting, and permanent mold casting.
- “Foundry Technology” by Peter Beeley
- This book covers the principles and practices of foundry technology, including casting processes, materials, and equipment.
Also, read Chasis frame

























Comment on “The Casting Process: A Comprehensive 2023 Guide”
Comments are closed.