Table of Contents
S.I unit of conductivity Introduction:
Electrical conductivity is a precise property of the material. Electric current is the number of electric charges that flow through a specific area in a unit of time.
Definition of electric conductivity:
Electrical conductivity is defined as the ratio between current viscosity and electric field strength. Its SI unit is Siemens per meter ( s/ m), denoted by e.
Electrical resistance:
Current and electrical conductivity are electrical currents. It’s an estimate of a subject’s capability to alter current inflow. The resistivity of a conduit is a measure of darkness.
Ωm is the SI unit of electrical resistivity.
Electrical resisters:
• Material resistance and temperature inflexibility.
• blends are used to stabilize the essence’s capability to toast sword.
• Essence have a high resistivity, which makes them operators of modified heat.
• Insulators also like graphite, plastic, glass, rubber, group. Operators are stronger when they’re made of essence.
• Semiconductor is a type of semiconductor whose resistance varies with temperature. It’ll act as current negative resistivity of the micro conductor.
What’s Conductivity?
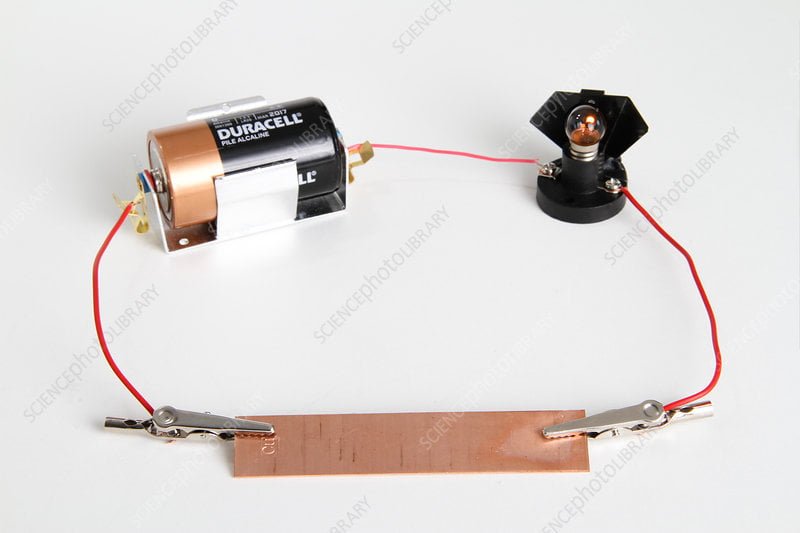

Conductivity is a measure of how fluently an electrical charge moves through a conduit. Operators are used to give resistance to the inflow of electric current through an electrical medium. The copper is a great conductor of electricity.
Specific Conductivity:
Specific conductance is one of the electrolyte functions in which electricity is measured. There’s another one, the electrolyte companion that can be digested by the electricity force now as a resistor. A conductance is inversely proportional to
electrical resistance.
S( Siemens) is an SI unit of dimension like S/m.
G = 1/ R
R = pi/ A
G = 1/ p x A/ I
G = kA/ I
Then, a specific resistivity is denoted as P,
The specific conductivity is denoted as k
It’s as repetitious as the repetitious resistive. Both can have a relationship with someone differently.
K 1/ p = C/ R
Types of Conductivity:
Conductivity is vastly divided into three types:
1.Electrical conductivity – ( further divided into two types)
• Electrolytic conductivity.
• Ionic conductivity.
2.Hydraulic conductivity.
3.Thermal conductivity.
SI Units and Conductivity:
When you’re talking about electric current, the SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter( S/ m) or ,mho and is represented by the Greek letter sigma, σ, and its formula is given as;
As for the SI unit of heat, it’s measured in watts per cadence- kelvin( W/( m K)) or watts per centimetre- kelvin( W/( cm K)). It’s represented by the formula;
K = QLAΔT
Where,
K_ thermal conductivity. In W/ m K,
Q is the energy used in J/ s or W,
A is the base of the body in m2
ΔT is the contrast temperature parameter in K.
Other Conductivity Units:
Some other conductivity units also include ohmmeter, BTU, tog, clo, R value, U_value, ppm, EC, TDS and CF.
I hope you learned the SI unit of conductivity and other units of conductivity. Keep an eye on BYJU’S to stop using blessed wisdom and calculation generalities.
Siemens (unit):
The Siemens, shortened S, is the SI unit of electrical conductance. It’s a conductance that allows a current of one ampere to write with a implicit drop of one volt. The Siemens is the reciprocal of the ohm.
Siemens is named after Ernst Werner von Siemens( 1816- 1892), one of the authors of electrical engineering and author of what latterly became Siemens AG, a major electrical and electronic company.
The Siemen unit of the SI member is equal to 1 A/ V, or Ω- 1; or in SI base units V = s3 · A2 · m- 2 · kg- 1.
Simons and mho:
Before BIPM saw Siemens as a set taken in 1971, the unit of conduct was the mho( reversed ohm), shortened ℧. Mho is still
used, by a man who didn’t beget it as a complaint, as an reversed omega isn’t to be confused with the lower case of seconds, not which occurs in formulas.