Table of Contents
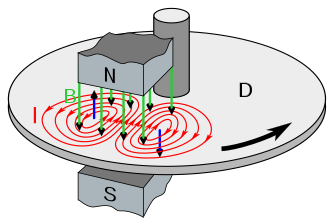
Eddy current is a type of electrical current that is induced in a conductor when there is a change in the magnetic field surrounding the conductor. It is also known as Foucault’s current or Len’s Law current. This phenomenon was first discovered by a French physicist named Leon Foucault in 1851. Eddy currents are widely used in various applications such as metal detection, induction heating, and non-destructive testing.
How Eddy Current Works:
Eddy currents are produced when a conductor is placed in a changing magnetic field. The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, which in turn generates a current. The direction of the current is such that it opposes the change in the magnetic field that produced it. This is known as Lenz’s Law.
The strength of the eddy current depends on several factors such as the strength of the magnetic field, the size and shape of the conductor, and the conductivity of the material. Materials with high electrical conductivity such as copper and aluminum tend to have stronger eddy currents.
Applications of Eddy Current:
Metal Detection:
Eddy currents are widely used in metal detection systems. Metal detectors generate a magnetic field, and when the metal object passes through the field, eddy currents are induced in the metal. The eddy currents, in turn, generate their own magnetic field, which can be detected by the metal detector.
Induction Heating:
Eddy currents are also used in induction heating systems. Induction heating is a process in which an electrically conductive material is heated by eddy currents induced by an alternating magnetic field. This process is widely used in various industrial applications such as metalworking and heat treatment.
Non-Destructive Testing:
Eddy currents are also used in non-destructive testing (NDT) applications. NDT is a technique used to detect flaws or defects in materials without damaging them. Eddy current testing is one of the most widely used NDT techniques, and it is used to detect surface and sub-surface defects in materials such as metals, plastics, and composites.
Advantages of Eddy Current:
Non-Contact Method:
Eddy current testing is a non-contact method, which means that it does not require physical contact with the material being tested. This makes it an ideal technique for testing delicate or fragile materials.
High-Speed Testing:
Eddy current testing is a high-speed testing method, which means that it can quickly detect defects in materials. This makes it an ideal technique for testing large volumes of materials in a short amount of time.
Accurate Results:
Eddy current testing provides accurate results, which means that it can detect even the smallest defects in materials. This makes it an ideal technique for detecting flaws in critical components such as aircraft parts and medical devices.
Eddy current is an amazing phenomenon that has a wide range of applications in various industries. It is a non-contact method that provides accurate results and is widely used in metal detection, induction heating, and non-destructive testing.
As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the applications of eddy currents will continue to expand, making it an essential tool for modern industries.
Also, read RTU
















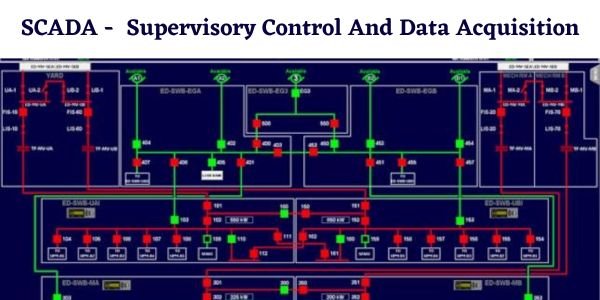

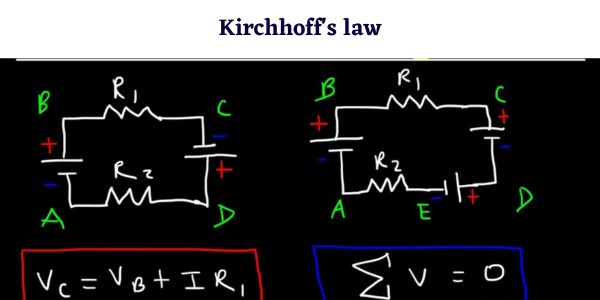
Comments on “Eddy Current – Working, Advantages, Applications”
Comments are closed.