Table of Contents
An overview of dicot embryo:
Development of dicot embryo: After fertilization, the fertilized egg is called a zygote or oospore, which develops into an embryo. Before it has fully germinated, the oospore enters a period of rest that can vary from a few hours to a few months. Usually, the zygote (oospore) divides immediately after the first division of the first nucleus of the endosperm.
Unlike gymnosperms, where the early stages of development show free nuclear division, the initial division of the zygote is always followed by wall formation, resulting in a bicellular pro embryo. There are no significant differences in the early developmental stages of monocot and dicot embryos.
But in the final stages, there is a clear difference between the embryos of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. Therefore, their embryogenesis was considered here separately.
The Structure of dicot embryo:
Dicotyledonous or dicotyledonous seeds are similar to peas, almonds, and cashews.
Dicots is the name for dicots. In the past, all flowering plants, or angiosperms, were divided into these groups. The seed has embryonic cotyledons, hence the name dicotyledons.
The embryo of a dicotyledonous seed consists of an embryonic axis and some cotyledons. The high visibility of the cotyledons is due to the creation of space as a food storage area for the growing seed. The embryo axis is divided into reports. The plumule is the plan that examines the last thing you did but don’t pause at the bottom of the last vase mouth. A seed coat is a protective shell that envelops everything. The regions that make up the integument testa on the outside and the tegmen on the inside.
Apples, peaches, and plums are instances of dicot seeds.
Development of dicotyledonous embryo:
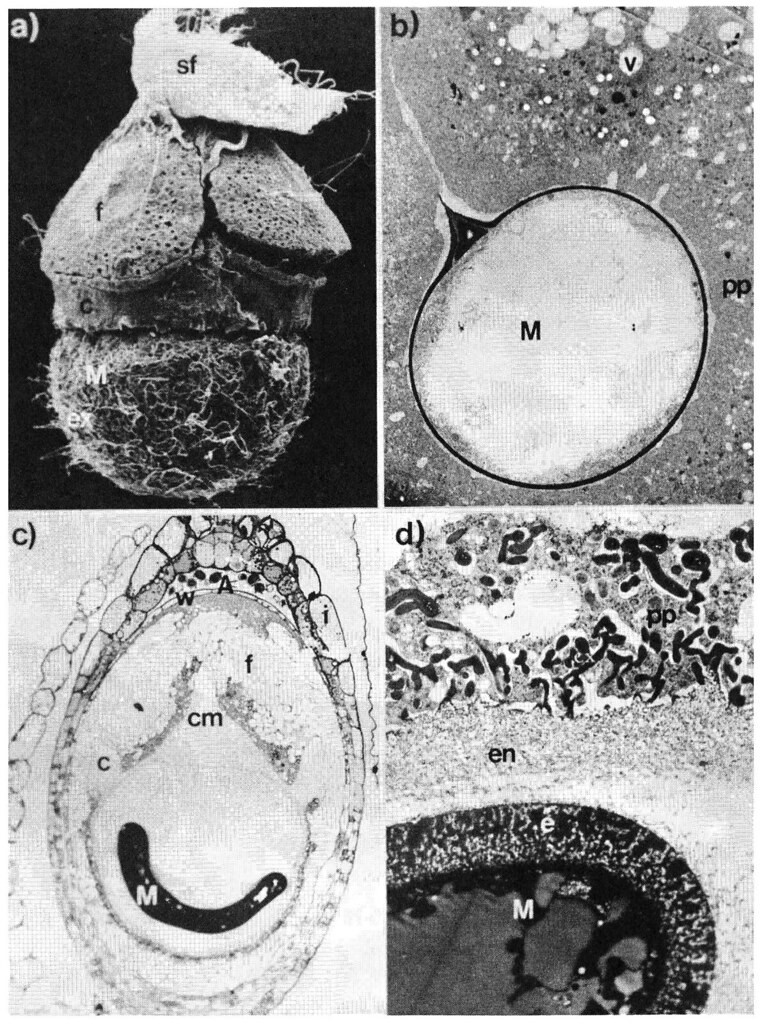
The zygote divides and forms a bicellular proembryo. The cell towards the micropyle is known as the basal cell, and the other is known as the terminal cell.
The basal cell undergoes several horizontal divisions to form a long suspensor. The last cell divides twice into four cells. This four-cell terminal cell stage is called the quadrant stage. The four quadrant cells are then divided horizontally into an octant level of eight, arranged in two quadrants of four. The lower part gives the edge of the stem and the cotyledons, while the upper part gives the formation of the hypocotyl.
This is followed by periclinal division into octant cells to give eight outer and eight inner cells.
The outer eight cells form the dermatome, which divides the anticlinal and develops into the epidermis. The inner cells form the periblem and plerome. The cortex develops from the periblem and the rock of the plerome. The basal cell divides several times into a long suspensor of six to ten cells. A small cell in the bone near the developing embryo is known as the pituitary gland. The pituitary, by repeated divisions, gives rise to the cover, epidermis, and cortex.
Further expansion of the hypocotyl and cotyledon results in the folding of the cotyledons. At this point, the “embryo” looks like a horse. In the mature embryo, the tip of the stem is the tip, and the two cotyledons sit in opposite positions.
Germination of dicot seed:
(Parthenogenesis and parthenocarpy)
Parthenogenesis:
If the egg remains unfertilized and forms an “embryo”, it is called parthenogenesis. Parthenogenesis has two types.
(A) haploid parthenogenesis
In haploid parthenogenesis, a haploid female gamete or even a haploid male gamete develops into an “embryo.”
(B) diploid parthenogenesis
In most plants, the megaspore mother cell does not undergo meiotic division and forms a diploid embryo sac. As a result, the egg remains diploid. An unfertilized diploid egg divides parthenogenetically and produces a normal diploid embryo. This “embryo” lacks a set of genes from the male father. This type of parthenogenesis is known as diploid parthenogenesis.
Induced parthenogenesis:
Parthenogenesis can be caused in the following ways:
(1) Show flowers that have matured at high or low temperatures when pollinated.
(2) Exposing flowers to X-rays during meiosis.
(3) Injecting other chemicals into the eggs.
Parthenocarpy:
The phenomenon of producing seedless fruits without fertilization is known as parthenocarpy.
induced parthenocarpy
Parthenocarpy can be created in several ways. In some cases, mutation or hybridization causes parthenocarpy. Using auxin and gibberellin, cutting pieces containing foreign pollen, and treating pollen with collected pollen are other methods used for parthenocarpy. Indolebutyric acid is the most suitable chemical to produce ripe parthenocarpic fruits.
Parthenocarpy helps in the production of seedless fruits and helps in nutrient enrichment.
Germination of seeds:
Most seeds germinate when they receive water and oxygen, and their dormancy ends. The main stages of seed germination are described below.
Drowning:
The first step in germination is the absorption or absorption of water by the dry seed. When planted in moist soil, the seed absorbs water through the micropyle. slow inhibition
under pressure, Dried seeds placed in a water bottle can burst when the bottle absorbs water and swells.
- Breathing:
Desire awakens the cells of the embryo and restarts the metabolic process. Primary respiration is anaerobic. Cells have too few polysaccharides to function as part of respiration. When anaerobic digestion reaches its peak, mitochondria divide into embryonic cells. Respiration now becomes aerobic as oxygen begins to enter the seed pods. - Collection of stored food:
Frozen embryonic cells stimulate the production of hormones and the digestion of stored food. Depending on the type of seed, the source can be stored mainly in the endosperm (for example, corn, cereal grains, and other monocotyledons) or in the cotyledons (for example, many dicotyledons, such as peas, grass,
Beans, etc.). in proteins that produce and release hydrolyzing enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the digestion of food. The latter is converted into sugar, amino acids, and other soluble substances. They are transferred to the embryo. - Development of the “embryo.”
Upon receiving soluble nutrients, the cells on the axis of the embryo divide and multiply. The end of the radicle of the axis of the embryo is the first to develop. It grows from pods and goes down into the soil to establish itself as a root system. Plumule also leaves seeds and soil to germinate.
For more articles, please visit the Home page