Table of Contents
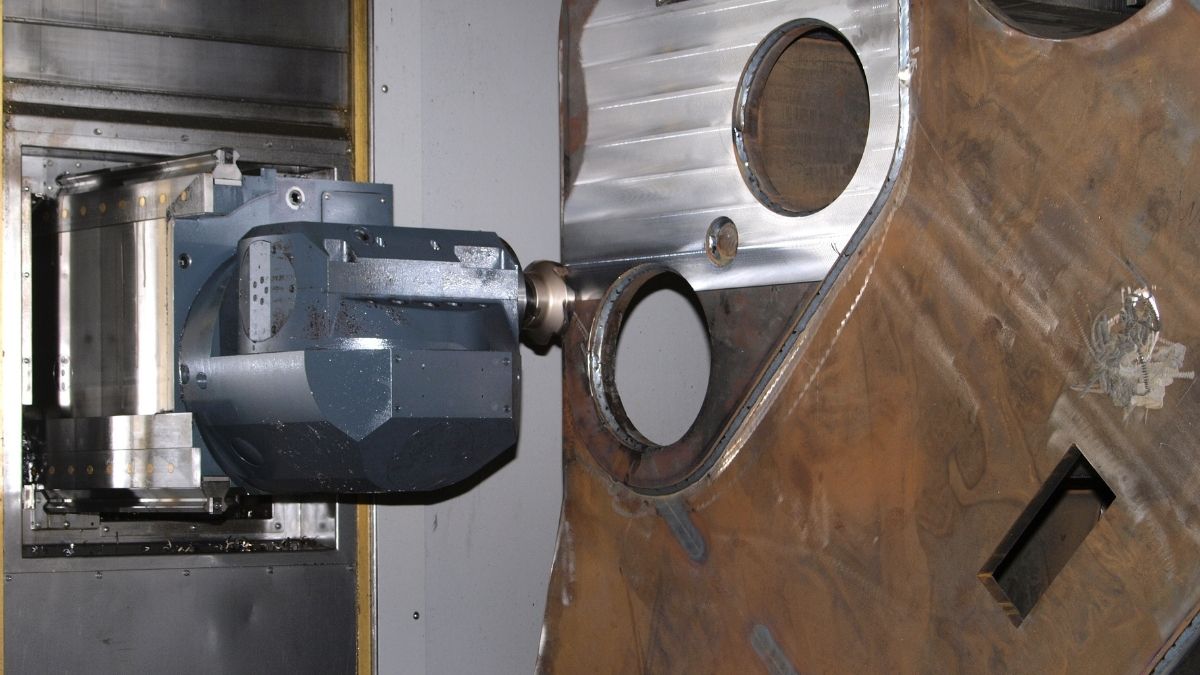
In manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. One of the most groundbreaking tools that have revolutionized the manufacturing industry is the CNC Mill. Short for Computer Numerical Control Milling Machine, CNC Mills have transformed the way products are designed, prototyped, and mass-produced.
CNC Milling:
The origins of CNC technology can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the U.S. Air Force sought a way to automate the machining of complex aircraft parts. John T. Parsons, along with his team at MIT, developed the first numerical control system in the late 1940s. It wasn’t until the 1950s that the concept matured into what we now know as CNC machining.
The first CNC milling machine, the Cincinnati Milacron Hydrotel, emerged in the 1950s. It was a far cry from the sophisticated machines used today, but it paved the way for CNC technology to evolve. As computer technology advanced, so did CNC Mills. They became more precise, faster, and versatile, making them essential in a wide range of industries.

How CNC Mills Work:
At its core, a CNC Mill is a machining tool that uses computer-controlled movements to remove material from a workpiece. The key components of a CNC Mill include:
1. Workpiece: This is the raw material or component that undergoes machining. It can be made of various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
2. Cutting Tools: These are the end mills or drills used to remove material from the workpiece. The choice of tool and its parameters (speed, feed rate, depth of cut) depends on the material and desired outcome.
3. CNC Controller: The brain of the CNC Mill, it interprets the digital design (usually in G-code) and sends signals to motors and actuators to move the cutting tool precisely.
4. Motors and Actuators: These components control the movement of the cutting tool along different axes (X, Y, and Z) with high precision.
5. Workholding Devices: These fixtures or clamps secure the workpiece in place during machining to ensure stability and accuracy.
CNC mill programming
At its core, CNC mill programming involves the creation of a set of instructions that dictate the toolpath, tool selection, cutting parameters, and other relevant actions to produce a specific part. These instructions are typically written in a language known as G-code, which consists of letters, numbers, and symbols that convey precise information to the CNC machine.

Key Elements of CNC Mill Programming:
- Toolpath Generation: The first step in CNC mill programming is defining the toolpath. This entails determining the route the cutting tool will follow to shape the workpiece. Toolpath generation can be done using specialized software, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files, or Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, which generates G-code automatically based on the 3D CAD model.
- Tool Selection: Choosing the right cutting tool is crucial. Factors such as material type, cutting speed, and the desired finish determine which tool is appropriate for the job. Tools come in various shapes and sizes, including end mills, drills, and specialty tools.
- Speed and Feed Rates: CNC mill programming involves specifying the rotational speed (RPM) of the cutting tool and the rate at which it advances through the material, known as the feed rate. These parameters are selected to optimize material removal while maintaining tool life and part quality.
- Depth of Cut: The depth at which the cutting tool engages with the material is referred to as the depth of cut. This parameter affects machining time, tool wear, and the final surface finish. It must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired results.
- Toolpath Compensation: Toolpath compensation ensures that the tool’s physical characteristics, such as its diameter, are accounted for in the programming. This helps achieve precise cuts and avoids collisions between the tool and the workpiece.
- Safety Precautions: Programming should incorporate safety measures, including tool retraction to clear obstacles and prevent damage to the machine or workpiece.
The Role of G-code in CNC Mill Programming:
G-code is the language spoken by CNC machines. It consists of commands and coordinates that instruct the machine on how to move and operate. Some common G-code commands include:
- G00: Rapid positioning, moving the tool quickly without cutting.
- G01: Linear interpolation, used for straight-line movements.
- G02/G03: Circular interpolation, for creating arcs and curves.
- M-codes: Control auxiliary functions such as coolant, spindle speed, or tool changes.
Programmers write or generate G-code based on the desired toolpath and cutting parameters. The G-code is then loaded into the CNC controller, which interprets the instructions and translates them into precise movements of the machine’s axes.
Challenges and Future Developments:
CNC mill programming requires a high level of skill and attention to detail. Mistakes in programming can lead to costly errors and rework. However, ongoing advancements in software and automation are making CNC programming more accessible and user-friendly. Machine learning and artificial intelligence also play a role in optimizing toolpaths and cutting parameters for improved efficiency and quality.

Applications of CNC Mills:
CNC Mills are incredibly versatile and find applications in a wide range of industries, including:
1. Aerospace: CNC Mills are used to create intricate aircraft components with precision, ensuring safety and reliability.
2. Automotive: From engine parts to chassis components, CNC machining is essential in the automotive industry for both prototyping and mass production.
3. Medical: Medical devices and implants require high precision, and CNC Mills deliver on these exacting standards.
4. Electronics: The manufacturing of circuit boards and small electronic components benefits from the precision and repeatability of CNC machining.
5. Prototyping: CNC Mills are invaluable for rapidly creating prototypes, allowing engineers to test and refine designs before full-scale production.
6. Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors use CNC Mills to transform digital designs into tangible art forms, pushing the boundaries of creativity.
Advantages of CNC Milling:
CNC Milling offers numerous advantages:
1. Precision: CNC Mills can achieve tolerances in the range of micrometers, ensuring high-quality and accurate parts.
2. Efficiency: Automation reduces the need for manual labor and increases production speed.
3. Versatility: CNC Mills can work with a variety of materials, from metals to plastics and even ceramics.
4. Repetition: They can produce identical parts repeatedly, crucial for mass production.
5. Complex Shapes: CNC Mills can create intricate and complex geometries that would be impossible or highly labor-intensive through manual machining.
Challenges and Future Developments:
While CNC Mills have come a long way, there are still challenges to overcome, such as the high cost of equipment and the need for skilled operators. The industry is continually evolving, with developments in automation, integration with AI and machine learning, and improvements in material handling capabilities.
As we look to the future, CNC Mills will likely continue to play a pivotal role in manufacturing, becoming even more accessible and versatile. The ongoing fusion of digital technology and manufacturing promises to open new horizons, enabling the creation of previously unimaginable products with unprecedented precision.

Disadvantages of CNC Mills:
- High Initial Costs: Acquiring and setting up a CNC Milling machine can be expensive. The cost includes not only the machine itself but also the necessary software, tooling, and infrastructure. This initial investment can be a significant barrier for small businesses or startups.
- Skilled Labor Requirement: Operating and programming CNC Mills requires a high level of technical expertise. Skilled operators and programmers are needed to create the toolpaths, set up the machine, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Finding and retaining qualified personnel can be challenging and costly.
- Programming Complexity: Creating G-code programs for CNC Mills can be complex, especially for intricate parts or designs. Even small errors in programming can result in costly mistakes, including material waste and machine damage.
- Maintenance and Downtime: CNC Mills require regular maintenance to ensure their accuracy and reliability. Downtime for maintenance and repairs can disrupt production schedules and lead to increased costs.
- Limited Flexibility: CNC Mills excel at producing precise parts with known geometries, but they may struggle with rapid changes in design or frequent setups for different parts. This limitation can make them less suitable for job shops that require frequent adjustments.
- Material and Size Constraints: While CNC Mills can work with various materials, some extremely hard or brittle materials may pose challenges. Additionally, the size of the workpiece is limited by the machine’s travel distance and table size, restricting the production of large components.
- Environmental Impact: CNC machining generates waste in the form of chips and coolant. Proper disposal and recycling of these materials can add to the operational costs and environmental concerns.
- Risk of Tool Wear: The cutting tools used in CNC Mills wear out over time, affecting the quality of the machined parts. Regular tool replacement and tool wear monitoring are necessary to maintain consistent quality.
- Complex Setup: Setting up a CNC Mill for a new job can be time-consuming and require careful calibration. This setup time may not be suitable for small-batch or one-off production runs.
- Dependence on Electricity: CNC Mills rely on a stable electrical supply. Power outages or fluctuations can disrupt production and potentially damage the machine or workpiece.
- Lack of Creativity: While CNC Mills are exceptional for precision and repeatability, they may not be well-suited for creative or artistic endeavors where imperfections or variations are desired.
CNC Mills represents a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility across various industries. As technology continues to advance, these remarkable machines will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of innovation, shaping the future of manufacturing in ways we can only begin to imagine.