Table of Contents
What is meant by a power transistor?
Power transistors are electronic components that are used to amplify or switch power in electronic circuits. They are designed to handle large currents and voltages and are commonly used in power supplies, motor control circuits, and audio amplifiers. In this article, we will explore the different types of power transistors, their applications, and their characteristics.
Types of Power Transistors:
There are two main types of power transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs).
BJTs are made up of three layers of semiconductor material: a p-type layer sandwiched between two n-type layers or an n-type layer sandwiched between two p-type layers. These layers form two PN-Junctions, and the device is controlled by varying the current or voltage applied to the base of the transistor. BJTs are used in low-frequency applications such as audio amplifiers, power supplies, and voltage regulators.
MOSFETs are made up of a metal gate separated from the semiconductor by a thin oxide layer. The device is controlled by varying the voltage applied to the gate, which creates an electric field that controls the flow of current through the transistor. MOSFETs are used in high-frequency applications such as power amplifiers, motor control circuits, and switching regulators.
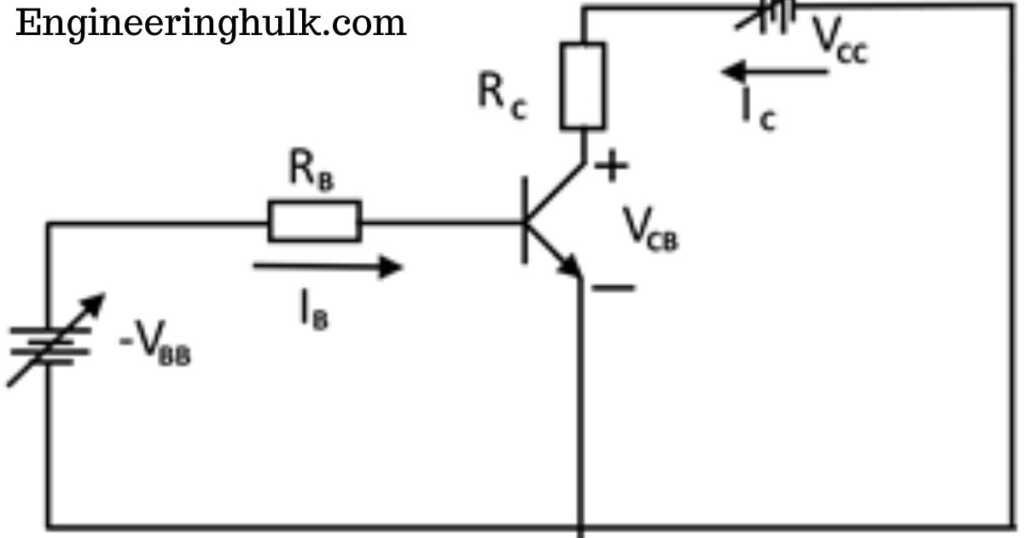
Applications of Power Transistors:
Power transistors are used in a variety of applications, including power supplies, motor control circuits, and audio amplifiers.
Power supplies use power transistors to regulate the voltage and current supplied to electronic devices. They are commonly used in switch-mode power supplies, which convert AC voltage to DC voltage. Power transistors in these circuits switch on and off rapidly to control the voltage and current output.
Motor control circuits use power transistors to control the speed and direction of motors. Power transistors are used to switch the current flowing through the motor windings, which controls the rotation of the motor. They are commonly used in industrial machines, robotics, and electric vehicles.
Audio amplifiers use power transistors to amplify the signal from a music source, such as a CD player or MP3 player. Power transistors are used to drive the speakers, which convert the electrical signal into sound. They are commonly used in home theater systems, car audio systems, and professional audio equipment.
Characteristics of Power Transistors:
Power transistors have several characteristics that must be considered when designing electronic circuits. The most important characteristics are the maximum current and voltage ratings, the gain, and the switching speed.
The maximum current and voltage ratings determine the maximum amount of current and voltage that the transistor can handle. These ratings are critical to ensure that the transistor does not overheat or break down when operating at high currents or voltages.
The gain of the transistor determines the amount of amplification or attenuation of the input signal. The gain is usually expressed as a ratio of the output current to the input current or the output voltage to the input voltage.
The switching speed of the transistor determines how quickly it can turn on and off. This is important in applications such as switch-mode power supplies and motor control circuits, where the transistor must switch on and off rapidly to control the voltage and current output.
Power transistors are essential components in electronic circuits that require high power handling capabilities. They are used in a wide range of applications, including power supplies, motor control circuits, and audio amplifiers.
The two main types of power transistors are BJTs and MOSFETs, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the characteristics of power transistors is critical to designing electronic circuits that operate reliably and efficiently.
What is the use of a power transistor?
One of the primary uses of a power transistor is to control the flow of electrical power in a circuit. By adjusting the voltage applied to the transistor’s base, the amount of current flowing through the transistor can be controlled, allowing for precise regulation of the output power.
Another use of power transistors is in switching applications, where they can rapidly turn on and off to control the flow of electrical power. This is particularly useful in applications such as motor control, where the speed and direction of a motor can be controlled by rapidly switching the power supplied to it.
Overall, power transistors are essential components in a wide range of electrical and electronic systems, and their high power handling capabilities make them indispensable in many industrial, automotive, and consumer applications.
What is the difference between a transistor and a power transistor?
A transistor is an electronic device that is used to amplify or switch electronic signals. It is made up of three layers of semiconductor material, with each layer having a different type of electrical charge.
A power transistor, on the other hand, is a type of transistor that is designed to handle high power levels. It is typically larger and more robust than a regular transistor and is capable of handling higher currents and voltages. Power transistors are commonly used in applications such as power supplies, motor control, and audio amplifiers.
One key difference between a regular transistor and a power transistor is its power handling capabilities. Regular transistors are typically designed for low-power applications and have limited current and voltage ratings. Power transistors, on the other hand, are designed to handle much higher power levels and have much higher current and voltage ratings.
Another difference is their construction. Power transistors are typically larger and have a more robust construction to handle the higher power levels they are designed for. They also often have additional features such as built-in heat sinks to dissipate the heat generated by the high power levels.
while both regular transistors and power transistors operate on the same basic principles, power transistors are specifically designed for high-power applications and are built to handle higher current and voltage levels.
Is the power transistor and Mosfet the same?
No, power transistors and MOSFETs are not the same, although they both belong to the family of transistor devices.
Power transistors are bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), which are made up of a p-type and an n-type semiconductor material sandwiched together. Power transistors are designed to handle high current and power levels, making them suitable for use in power amplifiers, motor control circuits, and voltage regulators.
On the other hand, MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors) are a type of field-effect transistor (FET). They have a metal gate electrode separated from the semiconductor material by a thin layer of oxide. MOSFETs are known for their high input impedance, low output impedance, and fast switching speed, making them suitable for use in power electronics, such as switching regulators, motor control circuits, and inverters.
While both power transistors and MOSFETs can handle high power levels, their internal construction and behavior differ significantly. Power transistors are current-controlled devices, whereas MOSFETs are voltage-controlled devices. MOSFETs have a lower on-resistance than power transistors, which makes them more efficient and generates less heat. In summary, power transistors and MOSFETs have different characteristics and are chosen based on specific application requirements.
Advantages of power transistors
Power transistors have several advantages that make them useful for a variety of applications. Here are some of the key advantages:
- High power handling capacity: Power transistors are designed to handle high power levels, which makes them useful in applications that require high output power, such as power amplifiers.
2. Fast switching speed: Power transistors can switch on and off very quickly, which is important in applications that require high-speed switchings, such as power converters and motor control circuits.
3. Low ON resistance: Power transistors have a low ON resistance, which means that they can conduct high currents with low voltage drops. This makes them more efficient than other types of transistors.
4. High voltage capability: Power transistors can handle high voltage levels, which makes them useful in applications that require high voltage switchings, such as high voltage power supplies and motor control circuits.
5. Thermal stability: Power transistors are designed to dissipate heat efficiently, which makes them more thermally stable than other types of transistors. This is important in high-power applications where heat dissipation can be a significant issue.
6. Low cost: Power transistors are relatively inexpensive, which makes them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
In short, the advantages of power transistors make them a versatile and useful component in a wide range of electronic circuits and systems.
Limitations of power transistors
- Power transistors, like any electronic component, have their limitations. Some of the common limitations of power transistors are:
2. Voltage and Current Ratings: Power transistors have maximum voltage and current ratings beyond which they can fail or get damaged. This limits their application in high voltage and high current circuits.
3. Thermal Limitations: Power transistors generate heat when they operate, and excessive heat can damage the transistor. Therefore, they have thermal limitations that must be taken into account during their design and usage.
4. Switching Speed: Power transistors may have a slower switching speed compared to other types of transistors. This limits their use in circuits that require fast switching speeds.
5. Cost: Power transistors are typically more expensive than other types of transistors due to their larger size and higher power handling capabilities.
6. Size and Weight: Power transistors are larger and heavier than other types of transistors, which limits their use in portable electronic devices.
7. Efficiency: Power transistors may have lower efficiency compared to other types of transistors, which results in more energy loss during operation.
8. Complexity: Power transistors may require more complex drive and control circuits compared to other types of transistors, which can add to the overall complexity and cost of a circuit.