Table of Contents
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid Prototyping (RP) refers to a set of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. The primary advantage of RP is its ability to provide designers and engineers with a physical sample or prototype in a short time frame, often within days or even hours.
This prototype can then be used for visualization, testing, and further refinement. Common techniques used in rapid prototyping include 3D printing, stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS), among others.
Evolution of Rapid Prototyping
The journey of rapid prototyping began in the 1980s. The rise of computer technology and 3D modeling software laid the foundation for RP’s emergence. The key objective was to hasten the product development process by bridging the gap between the digital model and the physical prototype.
In the late 80s, technologies like Stereolithography (SLA) were introduced, which enabled the transformation of CAD models into tangible parts. The subsequent years saw the evolution of various rapid prototyping technologies, like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), further expanding the RP landscape.

The Need for Rapid Prototyping
Before rapid prototyping, creating prototypes was time-consuming, costly, and often required manual crafting. This not only slowed down the development cycle but also made iterative changes challenging. Rapid prototyping emerged as a solution to:
- Reduce time to market.
- Facilitate multiple iterations at a minimal cost.
- Enhance collaboration and communication among design teams and stakeholders.
- Validate and test design concepts before mass production.
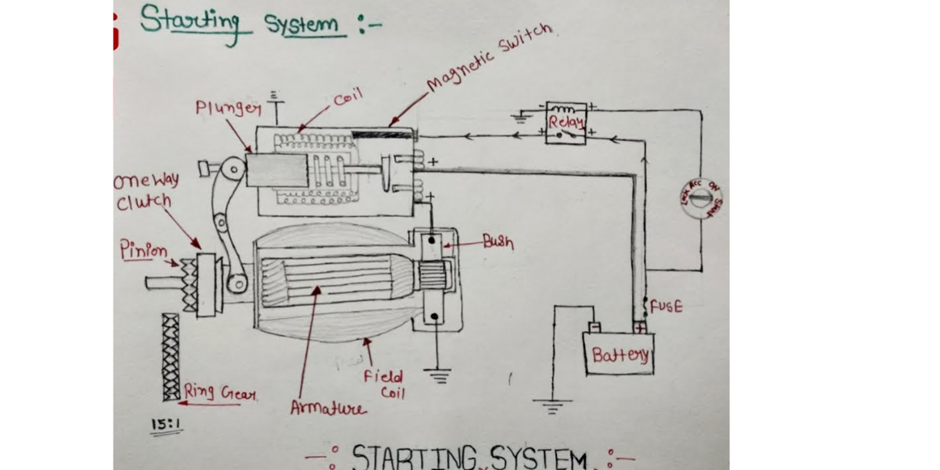
Rapid Prototyping Steps
Rapid prototyping is a systematic approach that follows specific steps to ensure a smooth transition from idea to physical model. Here are the general steps involved in the rapid prototyping process:
- Conceptualization:
- Understand the problem or need.
- Draft initial design ideas and concepts using brainstorming or other ideation techniques.
- Design and Development:
- Develop detailed 3D models using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
- Refine the design based on the intended function, aesthetics, and other factors.
- Data Conversion:
- Convert the CAD design into STL (stereolithography) format or any other format that the chosen prototyping machine understands.
- This file divides the object into layers and generates paths for the machine to follow.
- Machine Setup:
- Choose the appropriate prototyping method (e.g., SLA, FDM, SLS).
- Prepare the materials and set up the machine. This might involve adding resin, polymer, or powder, and calibrating the machine for the best results.
- Prototype Build:
- Initiate the prototyping machine. The prototype will be built layer by layer.
- Monitor the process for any errors or issues.
- Post-Processing:
- Remove the prototype from the machine.
- Clean the prototype by removing supports, excess materials, or powders.
- Further refinements like sanding, painting, or assembly might be needed to achieve the desired finish and functionality.
- Testing and Validation:
- Check the prototype for fit, form, and function.
- Depending on its purpose, the prototype might undergo stress tests, user testing, or other evaluations.
- Iteration:
- Based on the results from testing and validation, changes might be necessary.
- Repeat the design, prototyping, and testing processes as many times as needed to achieve the desired outcome.
- Final Design:
- Once the prototype meets all requirements and expectations, finalize the design.
- If the prototype is a precursor to full-scale production, use it to guide mold creation, production setups, and other manufacturing processes.
- Documentation:
- Document all design changes, testing results, and iterations.
- This step ensures that knowledge is preserved and can guide future projects.
Throughout the rapid prototyping process, communication and collaboration among stakeholders, including designers, engineers, and end-users, are vital. Regular feedback helps in refining the design, thus ensuring that the final product aligns closely with the user needs and project objectives.

Techniques in Rapid Prototyping
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA employs ultraviolet (UV) lasers to harden layers of a photosensitive resin. The laser traces the CAD design onto the resin, solidifying it layer by layer until the part is complete.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM works by melting a thermoplastic filament, which is then extruded through a nozzle. The nozzle moves in a pre-defined path, depositing the material layer by layer.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Unlike SLA which uses liquid resin, SLS uses powdered materials, typically nylon. A laser fuses these particles together based on the CAD design. As there’s no support required, complex geometries can be easily achieved.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SLA, DLP uses light to cure liquid resin. However, DLP cures a whole layer in a single flash, making it faster than SLA.
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
In LOM, layers of adhesive-coated paper, plastic, or metal laminates are successively glued together and cut to shape using a knife or laser cutter.
Below is a simplified table outlining various rapid prototyping processes along with some essential parameters for each:
| Process | Material Used | Technology Base | Layer Creation Method | Post-Processing |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Photopolymer Resin | Laser-based | UV Laser Curing | Cleaning, UV post-curing |
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | Thermoplastic Filaments | Extrusion-based | Material Extrusion | Support removal, sanding |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Powdered Polymers/Metals | Laser-based | Laser sintering | Powder removal, sometimes dyeing or infiltration |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Photopolymer Resin | Light projector-based | Light Curing | Cleaning, UV post-curing |
| Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) | Paper, Plastic laminates | Lamination | Material cutting & lamination | Excess material removal |
| PolyJet Printing | Photopolymer Resin | Jetting | Material jetting & curing | Support removal |
This table provides a quick glance at some of the popular rapid prototyping processes. Each method has its unique advantages, material requirements, and post-processing needs. The choice of a particular method usually depends on the design requirements, desired material properties, the purpose of the prototype, and budget constraints.
Applications of Rapid Prototyping
Conceptualization
RP allows designers to transform their ideas into tangible objects quickly. This aids in understanding the look and feel of a design, facilitating early feedback and iterations.
Design Validation
Physical prototypes help validate design accuracy, fit, and function, ensuring they meet the desired specifications and requirements.
Functional Testing
With RP, functional prototypes can be created to test the actual performance of the design under real-world conditions, be it mechanical stress, thermal conditions, or user interaction.
Customization
In fields like medicine and dentistry, rapid prototyping plays a vital role in creating customized implants or prostheses tailored to individual patients.
End-use Production
Advancements in rapid prototyping technologies have expanded their applications from mere prototyping to actual production, especially for small batches or custom products.

Advantages of Rapid Prototyping
Speed
One of the most significant advantages of RP is the speed at which physical models can be produced, reducing the development cycle.
Cost-efficiency
Traditional prototyping methods, particularly for intricate designs, can be expensive. RP provides a cost-effective alternative.
Risk Reduction
Having a physical model before final production helps in identifying design flaws, thereby reducing the risk of costly design errors.
Enhanced Creativity
Since designers know they can see their designs in a tangible form quickly, it encourages exploration and innovation.
Stakeholder Communication
Physical models can be an excellent tool for communicating ideas to stakeholders, be it clients, investors, or team members.
The Future of Rapid Prototyping
The future of RP is promising. With the rise of Industry 4.0 and the convergence of technologies like Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), the possibilities are endless. We can expect:
- Faster and more efficient prototyping methods.
- Enhanced material variety, including smart and self-healing materials.
- Seamless integration of electronics into prototypes.
- Expansion of rapid prototyping into sectors like biotechnology, where we might see the printing of organic tissues or even organs.
Rapid prototyping has revolutionized the design and manufacturing landscape. By providing a bridge between the digital and physical worlds, it has not only streamlined the product development process but has also opened doors to innovation, exploration, and boundless possibilities.
As technology continues to evolve, so will the capabilities and applications of rapid prototyping, further blurring the lines between imagination and reality.
Also, read about Maryland Lacrosse