Table of Contents
The Introduction to Kranz Anatomy:
Kranz anatomy is a type of anatomy that has been used for centuries by medical professionals to identify and classify tissues in the body. It is based on the observation and study of the patterns of tissue arrangement and organization found in a variety of animals.
In Kranz’s anatomy, tissues are divided into two broad categories: the epidermis and the dermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin and contains the stratum corneum, the stratum lucidum, and the stratum granulosum.
The dermis is the innermost layer and contains connective tissues, blood vessels, glands, and muscle fibers. Kranz’s anatomy is based on the observation of the arrangement of tissues in the body.
The tissues are grouped according to their anatomical location and the degree of their structural complexity. This is done by assigning a name to each tissue based on its location and characteristics.
For example, the epidermis is divided into the stratum corneum, the stratum lucidum, and the stratum granulosum. The dermis is further divided into the dermis proper, the subcutaneous layer, the submucosal layer, and the subdermal layer.
Kranz anatomy is a useful tool for medical professionals as it provides a comprehensive structure for the study of the human body. It is used in the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of conditions, including skin diseases, infections, joint problems, and organ dysfunction.
Additionally, Kranz’s anatomy is used to study the different tissues that make up the human body and their functions. This knowledge can be used to develop treatments and therapies for a range of medical conditions.
The definition of Kranz’s Anatomy:
Kranz’s Anatomy is a branch of anatomy that specifically deals with the structures of the inner ear and associated structures. It was named after the German anatomist and physiologist, Alfred Kranz (1860-1932).
Kranz’s Anatomy focuses on the three compartments of the inner ear: the vestibule, the semi-circular canals, and the cochlea.
The vestibule is a bony chamber that contains the utricle and saccule, which are responsible for detecting linear and angular acceleration, respectively.
The semi-circular canals are three curved tubes that sense head rotation and help maintain balance. The cochlea is a spiral-shaped cavity in the temporal bone that is responsible for hearing and contains the organ of Corti, which is made up of three rows of hair cells that detect sound waves.
In addition to studying the inner ear, Kranz’s Anatomy also examines the muscles and ligaments that attach to the temporal bone and other structures of the middle ear.
The anatomy of the auditory nerve and its connections to the brain are also studied. Kranz’s Anatomy is important for understanding the structure and function of the ear, and for diagnosing and treating diseases and disorders of the ear.
It is also used in research to further our understanding of hearing and balance.
The History of Kranz’s Anatomy:
Kranz anatomy, also known as ‘crown anatomy,’ is a system of anatomy developed by German anatomist and surgeon Dr. Johann Christian Kranz in the mid-eighteenth century.
Kranz was a professor at the University of Halle and was known for his meticulous anatomical studies, including developing a unique anatomical system.
The Kranz system is based on the concept of a ‘crown’ or ‘crown-shaped’ body, which is divided into four main parts. The four parts are the head, thorax, abdomen, and pelvis.
Each part is divided into a number of segments, which are further divided into various organs. The anatomy is based on the concept of the ‘parts within a part’, and the organs are grouped together according to their location within the body.
The Kranz system is one of the earliest and most commonly used systems of anatomy and is still in use today. It was used extensively by medical students and doctors in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, and it is still used in medical schools and hospitals today.
Kranz’s anatomy is based on the concept of the body as a whole, rather than individual organs or systems. This allows for a more holistic approach to anatomy, which is useful in understanding the body as a whole, rather than simply looking at individual organs.
It also allows for a more detailed examination of the body, as each part can be examined separately and in great detail. Kranz’s anatomy is also renowned for its accuracy and detail.
Kranz was known for his meticulous studies, and his anatomical system was highly accurate, even for an anatomist of his time. His system was also useful in helping doctors and medical students visualize the body and its complex anatomy.
Kranz’s anatomy is still used today, but it is no longer the primary system of anatomy used in medical schools and hospitals. It has been supplanted by more modern systems, such as the International Anatomical Terminology (IAT), which is now the standard system used in medical schools and hospitals worldwide.
The Clinical Applications of Kranz Anatomy:
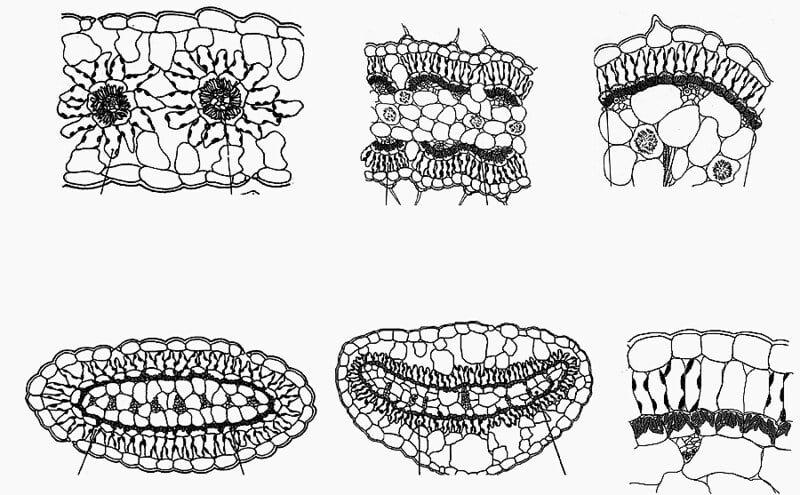
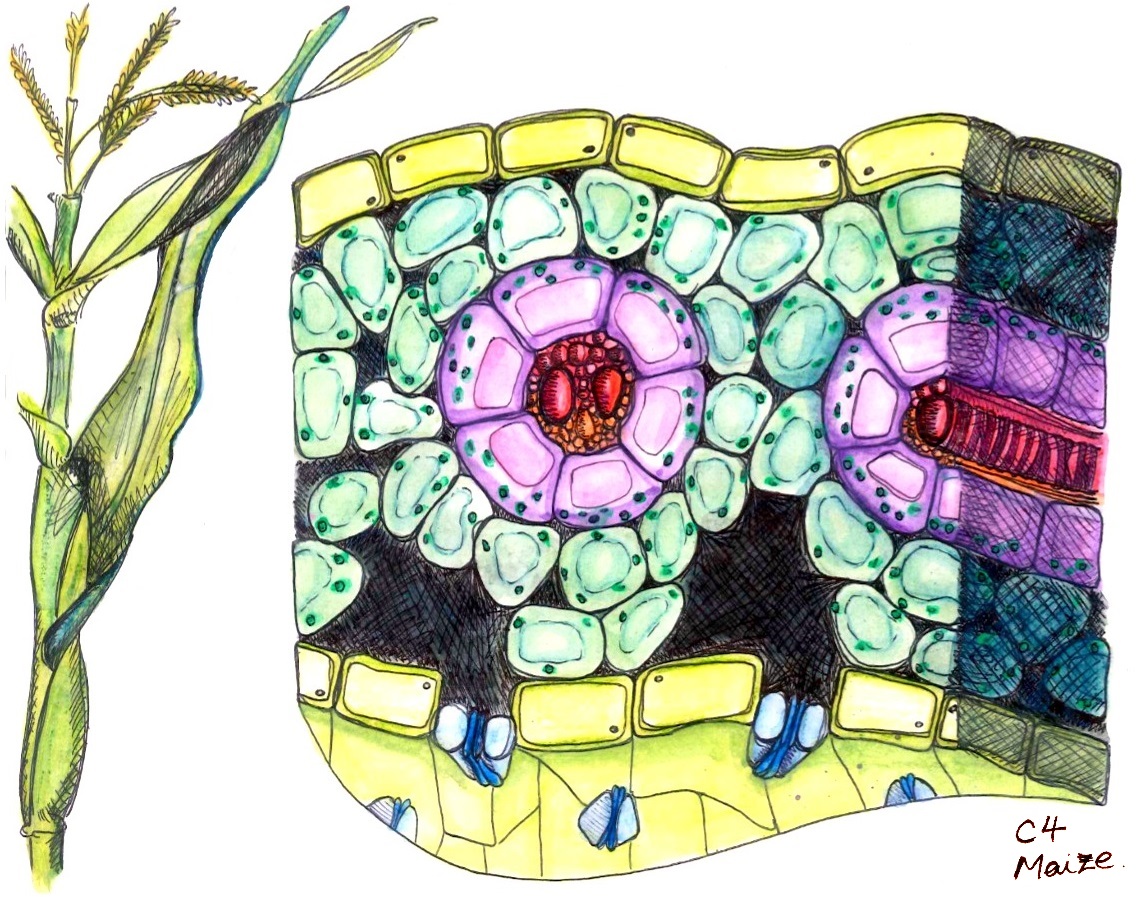
Kranz anatomy, also known as the vascular bundle anatomy, is a key concept in botany. It is a system of vascular tissue organization in plants that helps to determine the direction of water and nutrient movement within a plant.
Kranz’s anatomy is a three-dimensional arrangement of vascular bundles within a plant. It is composed of a central cylinder of xylem (water-conducting tissue) surrounded by a peripheral cylinder of phloem (food-conducting tissue).
The arrangement of the xylem and phloem in the vascular bundle is called the Kranz anatomy. Kranz’s anatomy has many clinical applications in the field of medicine.
In the diagnosis of cancer, vascular bundles can be used to look for abnormal patterns in the tissue’s structure and examine the tumor’s blood supply. This can help to determine the stage of the disease, as well as its potential for spread.
In treating cardiovascular diseases, vascular bundles can be used to help identify sites for stent placement and assess the health of the patient’s vasculature.
Kranz’s anatomy can also be used to study the development of plants and their responses to environmental changes. It can help researchers understand how plants adjust their vascular bundles in response to changing temperature, light, and other environmental cues.
This knowledge can be applied to developing new crop varieties that are more resistant to disease and environmental stressors. Finally, Kranz’s anatomy can be used to study the structure of complex organs such as the heart, lungs, and brain.
By studying the vascular bundles in these organs, researchers can gain insight into the structure and function of the organ, as well as the potential for disease.
This information can then be used to develop new treatments for diseases of these organs.
The Conclusion:
In conclusion, Kranz’s Anatomy is a comprehensive and detailed anatomy book that covers the basic principles of human anatomy. It is an excellent resource for anyone studying anatomy and related topics.
It provides a clear overview of the structure and function of the human body, as well as its development and evolution. The book is well-written and organized and includes detailed illustrations and diagrams.
It is also a great resource for medical professionals and students alike. Overall, Kranz’s Anatomy is an invaluable resource for anyone interested in the structure and function of the human body.
The references:
Kranz’s Anatomy is a comprehensive guide to anatomy and physiology written by Dr. George Kranz. This book is a comprehensive guide to the anatomy of the human body, including its organs, systems, cells, and tissues.
It is written in an easy-to-understand manner, making it suitable for both medical students and professionals. The book is divided into four main sections:
Anatomy and Physiology, Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. The Anatomy and Physiology section covers the basics of the body’s structure, including the major organ systems, the major body parts, and the major body functions.
It also covers the anatomy of the ear, eye, and nervous system. The Pathology section covers the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and disorders.
It includes information on common medical conditions, such as diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. It also includes information on the diagnosis of genetic disorders.
The Diagnosis section covers the diagnostic tests and procedures used to detect and diagnose diseases and disorders. It includes information on tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans.
The Treatment section covers the treatment of diseases and disorders, including surgical and non-surgical treatments. It includes information on medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
Kranz’s Anatomy is a valuable tool for medical students and professionals alike. It provides an in-depth look at the anatomy and physiology of the human body and is a great resource for those studying anatomy and physiology.
Also, read Two nation theory

























Comments on “Kranz Anatomy”
Comments are closed.