Table of Contents
In the fast-paced world of business, understanding the product life cycle is crucial for effective marketing and product management. The concept of the product life cycle (PLC) is a fundamental framework that helps businesses comprehend the various stages a product goes through from its inception to eventual decline. This knowledge empowers companies to make informed decisions, allocate resources wisely, and adapt their strategies accordingly.
What is the Product Life Cycle Theory?
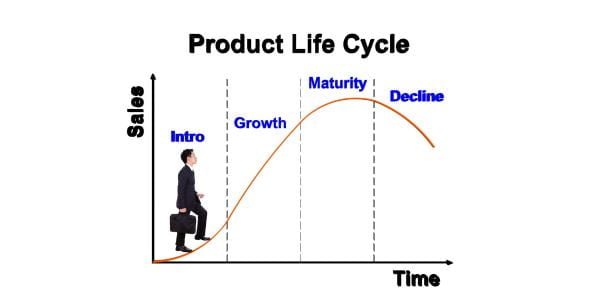
The product life cycle is a concept that illustrates the progression of a product through four distinct stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Each stage has its own characteristics, challenges, and opportunities, and understanding these can help businesses devise tailored strategies to maximize a product’s success.

Product Life Cycle Stages
1. Introduction Stage:
At the outset, a new product is introduced to the market. This stage is characterized by slow growth and often substantial investments in research, development, and marketing. Consumers are typically not aware of the product, and businesses may experience initial losses due to high production and promotion costs. Strategies at this stage include building brand awareness and targeting early adopters.
2. Growth Stage:
Once a product gains traction, it enters the growth stage. Sales begin to surge, and the product becomes more profitable. Competitors may enter the market, increasing competition. Businesses focus on expanding market share, improving product quality, and meeting consumer demand. Price stability or even reductions may be necessary to fend off competitors.
3. Maturity Stage:
In the maturity stage, sales growth levels off. Market saturation occurs as most potential customers have already adopted the product. Competition intensifies, and companies need to differentiate their offerings to maintain market share. Price competition often becomes prominent, and cost control becomes essential to maintain profitability. Companies may also explore diversification or product enhancements to extend this stage.
4. Decline Stage:
The decline stage signals a decline in sales and profitability. Factors like changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, or the emergence of superior alternatives can contribute to a product’s decline. Businesses must decide whether to discontinue the product, maintain it for a niche market, or revitalize it through rebranding or product innovations.

Strategies at Each Stage:
Understanding the product life cycle enables businesses to formulate effective strategies for each stage:
– Introduction:
- Investment in Promotion: Heavily promote the product to build awareness.
- Limited Product Variations: Focus on a few core product variations.
- Premium Pricing: Charge a premium price to recover development costs.
– Growth:
- Expand Distribution: Widen the product’s availability.
- Improve Product: Enhance product features and quality.
- Stabilize Pricing: Maintain competitive prices.
– Maturity:
- Diversify Offerings: Offer variations or complementary products.
- Cost Control: Manage costs to maximize profits.
- Promotional Strategies: Focus on promotions and loyalty programs.
– Decline:
- Decide on Product’s Fate: Determine whether to discontinue or rejuvenate.
- Liquidate Inventory: Clear remaining stock.
- Focus on Profit Margins: Aim for profitability rather than market share.
What is Product Life Cycle Management (PLM)?
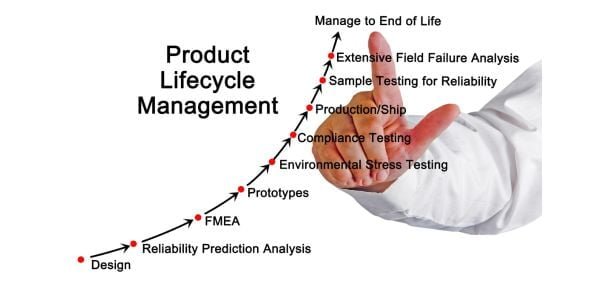
Product Life Cycle Management, commonly referred to as PLM, is a strategic process that enables companies to oversee the entire life cycle of a product, from its inception to its eventual obsolescence. PLM involves the integration of people, processes, business systems, and information to efficiently manage all aspects of a product’s journey.
PLM encompasses several key components and activities:
1. Product Data Management (PDM):
PDM is the foundation of PLM, focusing on the organization and centralization of product-related data. This includes design specifications, bills of materials, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files, and other critical information. PDM ensures that the right data is accessible to the right people at the right time, promoting collaboration and reducing errors.
2. Product Design and Development:
PLM aids in streamlining the product design and development processes. It facilitates collaboration among design teams, helps manage design iterations, and ensures that products meet quality and compliance standards.
3. Manufacturing and Production:
Efficient manufacturing and production processes are essential for cost-effectiveness and product quality. PLM supports these aspects by providing accurate manufacturing instructions, optimizing production workflows, and managing changes smoothly.
4. Supply Chain Integration:
PLM extends into the supply chain, allowing businesses to manage suppliers, track materials, and ensure on-time delivery of components. This integration enhances supply chain visibility and resilience.
5. Lifecycle Analysis:
PLM enables companies to assess the environmental and sustainability impacts of their products. This is becoming increasingly important as businesses strive to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations.
6. Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is crucial, especially in sectors like healthcare, aerospace, and automotive. PLM systems help ensure that products adhere to all relevant standards and requirements.
7. Maintenance and Support:
Even after a product is in the market, PLM continues to play a role in managing maintenance, updates, and customer support. This ensures that products remain competitive and customer satisfaction is maintained.
The Benefits of PLM
Implementing a robust PLM strategy offers numerous advantages for businesses:
- Enhanced Collaboration: PLM promotes collaboration across departments and with external partners, leading to more efficient product development and faster time-to-market.
- Reduced Costs: By optimizing processes and minimizing errors, PLM helps lower production and development costs.
- Improved Quality: Better control over product data and design processes results in higher product quality and reliability.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Streamlined workflows and better communication speed up product development, allowing companies to respond to market demands more quickly.
- Compliance and Risk Management: PLM systems assist in tracking regulatory compliance and mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
- Sustainability: PLM enables companies to incorporate sustainability considerations into product design and manufacturing, aligning with environmental and social responsibility goals.
- Market Adaptation: By tracking product performance and customer feedback, PLM facilitates adjustments to product strategies and updates to meet evolving market demands.
PLM Implementation
Implementing PLM is a complex undertaking that involves selecting the right PLM software and tailoring it to a company’s specific needs. It requires strong leadership, change management strategies, and a commitment to ongoing improvement.
The Importance of the Product Life Cycle:
Understanding the PLC offers several benefits to businesses:
- Strategic Planning: Helps in long-term planning, resource allocation, and decision-making.
- Resource Management: Ensures efficient allocation of resources based on a product’s stage.
- Competitive Advantage: Allows companies to anticipate and respond to market changes, giving them a competitive edge.
- Marketing Adaptation: Tailor’s marketing efforts to suit the product’s stage, optimizing ROI.
- Innovation: Encourages innovation and product development to extend the life cycle.
- Profitability: Maximizes profitability by focusing on the right strategies at each stage.
Product life cycle is a fundamental concept in business that provides a roadmap for product management and marketing. By understanding the distinct stages and implementing appropriate strategies, companies can navigate the dynamic market landscape effectively, ultimately achieving sustainable success for their products.
Also, read Lean Manufacturing