Table of Contents
Thermochemical conversion technologies
Biomass conversion technologies: Thermochemical conversion is an efficient method of converting biomass into biofuels. It includes two different categories: dry (non-aqueous) techniques and hydrothermal techniques. In a dry thermochemical biomass conversion technologies process, with increasing temperature, the biomass mainly undergoes structural destruction, degrading into condensable vapours and finally decomposing into gaseous molecules.
Dry thermochemical biomass conversion technologies processes have sequence connections; taking as an example a splinter of wood just burning, the toasting takes place in the lower part of the splinter in the region below 300 ° C, where volatile substances are released.
Process in Biomass conversion technologies
Carbonization and pyrolysis occur in the region between 300 ° C and 700 ° C, near the surface of the wood chips, where the wood material is converted into pyrolyzed vapours and the vapours are further gasifier to become combustible gases at 700 ° C Region of –900 ° C and are burned on the surface of the wood above 900 ° C. It is the combustion of the gas that gives rise to the flame. That is why we can always see the flame above the burning wood, but we rarely see it above the burning coal. In a hydrothermal chemical biomass conversion technologies process, mainly coal (solid product) is produced under mild conditions (below 280 ° C, self-generated pressure) and the process is known as hydrothermal carbonization (HTC).
In the range of medium temperatures (280 ° C to 370 ° C) and high pressures (up to 22 MPa), mainly tar (liquid) would be formed, and the process is called hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL). When the temperature and pressure rise to exceed the supercritical state of the water (above 370 ° C and 22 MPa), the dominant products are the gaseous substances, and the process is commonly called HTG. Temperature is often crucial for the thermochemical biomass conversion technologies to reactant and catalyst reactivity and directly determines product distribution. The residence time of the raw material in the reactor also plays an important role in the production of biofuels; a longer residence time can result in higher gas and coal yields, but less liquid products.
History
Particle size has a large impact on heat and mass transfer within biomass particles. The task of the reactors is to transmit good heat and mass transfer to the raw material during the thermochemical biomass conversion technologies process with the least energy consumption. Most of the current thermochemical biomass conversion technologies to produce biofuels have been adapted by fossil fuel industries since the 1970s so that they lack industry standards dedicated to biomass processing.
Furthermore, due to the complex composition of biomass and its degradation products, knowledge of biomass conversion technologies still inadequate for the production and application of biofuels. A better understanding, from the mechanism of decomposition of a single compound to the technical-economic evaluation of the biofuels industry, is necessary to reach the industrial production of biofuels on a large scale through thermochemical biomass conversion technologies.
Pyrolysis in Biomass conversion technologies
Pyrolysis biomass conversion technologies have recently received attention for the production of liquid fuels from cellulosic raw materials by “rapid” and “flash” pyrolysis in which the biomass has a short residence time in the reactor. A more detailed understanding of the physical and chemical properties governing pyrolytic reactions allowed us to optimize the reactor conditions required for these types of pyrolysis. Further work is now focusing on the use of high-pressure reactor conditions to produce hydrogen and on low-pressure catalytic techniques (requiring zeolites) for the production of alcohol from pyrolytic oil are the biomass conversion technologies.
Carbonization
It is an ancient pyrolytic process optimized for coal production. Traditional methods of coal production are based on the use of mounds of earth or covered ditches in which the wood is stacked. Control of reaction conditions is often rudimentary and heavily dependent on experience. The biomass conversion technologies efficiency using these traditional techniques is considered to be very low; Based on weight, Openshaw estimates that the wood-to-coal conversion rate for such techniques ranges from 6 to 12 tons of wood per ton of coal.
Carbon accumulates primarily due to the reduction of hydrogen and oxygen levels in wood. Wood undergoes a series of physicochemical changes with increasing temperature. These condensable vapours (long-chain carbon molecules) form the pyrolysis oil, which can be used for the production of chemicals or as fuel after cooling and washing. Between 270°C and 280°C, an exothermic reaction develops which can be detected by spontaneous heat generation.
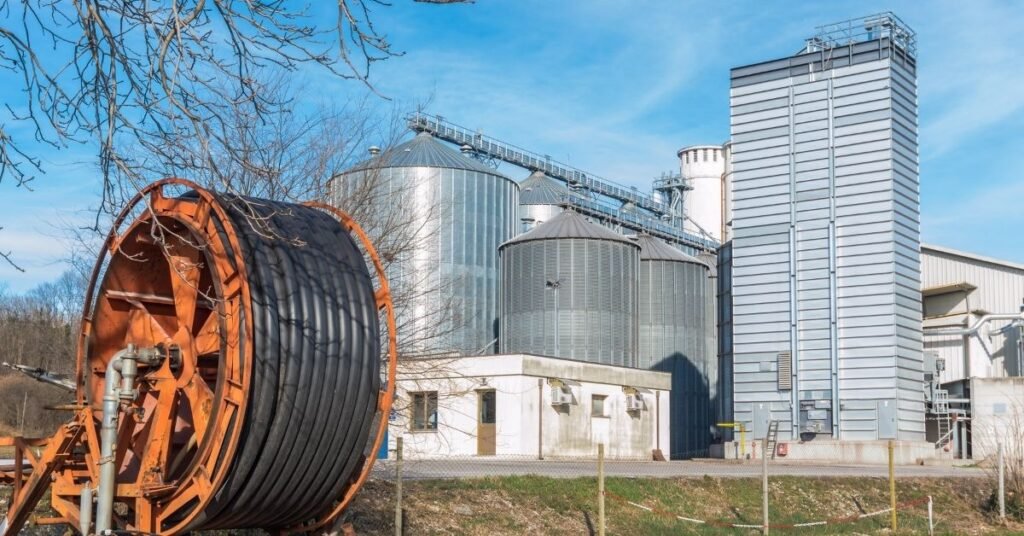

The modernization of coal production has led to large increases in production efficiencies, with large-scale industrial production in Brazil now reaching efficiencies in excess of 30% (by weight). There are three basic types of charcoal production: a) internally heated (by controlled combustion of the raw material), b) externally heated (using wood or fossil fuels), and c) circulating gas heat (retort or gas). biomass conversion technologies used to produce chemicals).
Internally heated coal ovens are the most common form of coal oven. It is estimated that 10 to 20% of the wood (by weight) is sacrificed, an additional 60% (by weight) is lost due to the conversion and release of gases from these kilns into the atmosphere. Externally heated reactors allow the complete exclusion of oxygen and therefore provide better quality coal on a larger scale. However, they require the use of an external fuel source, which can be supplied by the “producer gas” once pyrolysis has started. Hot gas recirculation systems offer the potential to generate large amounts of coal and associated by-products but are currently limited by the high investment costs for large-scale plants.
Gasification
The high temperatures and a controlled environment mean that practically all the raw material is converted into gas. This happens in two stages. In the first stage, the biomass conversion technologies are partially burned to form production gas and coal. In the second step, the CO2 and H2O produced in the first step are chemically reduced by the coal, forming CO and H2. The composition of the gas is from 18 to 20% of H2, an equal share of CO, from 2 to 3% of CH4, from 8 to 10% of CO2 and the rest of nitrogen.
These phases are spatially separated in the gasifier, with the design of the gasifier highly dependent on the characteristics of the raw material. Gasification requires temperatures of about 800 ° C and is carried out in closed or open gasifiers. These gasifiers can operate at atmospheric or higher pressure. The energy density of the gas is generally less than 5.6 MJ / m3, which is low compared to natural gas at 38 MJ / m3 {WEC, 1992}, providing only 60% of the rated power of diesel when used in a diesel engine edited {Makunda, 1992}. Gasifiers were widely used for transportation to Europe during World War II due to oil shortages, with a predominance of a closed lid design.
An important future role is foreseen for the production of electricity from biomass plantations and agricultural residues using large gasifiers with direct coupling to gas turbines. The potential efficiency gains using such gasifier/gas turbine hybrid systems make them extremely attractive for electricity generation once commercial viability has been demonstrated. These systems exploit cheap and low-quality raw materials (waste and wood produced with short rotation techniques) and the high efficiencies of modern gas turbines to produce electricity at a cost comparable or lower to that of electricity derived from fossil fuels.
Net CO2 emissions into the atmosphere are avoided if biomass growth is managed to match consumption. The use of BIG / STIG (Steam Injection Gas Turbine Integrated Biomass Gasifier) and BIG / GTCC (Combined Cycle Gas Turbine Integrated Biomass Gasifier) is expected as mature biomass conversion technologies to enable energy conversion efficiencies 40% to 55%. Modern coal-fired power plants have an efficiency of around 35% or less. Combined heat and power systems can eventually provide energy with efficiencies of 50% to 80%. The use of low-quality raw materials combined with high conversion efficiencies makes these systems economically competitive with low-cost coal plants and energetically competitive with natural gas plants.




























Comment on “Biomass conversion technologies Noted”