Table of Contents
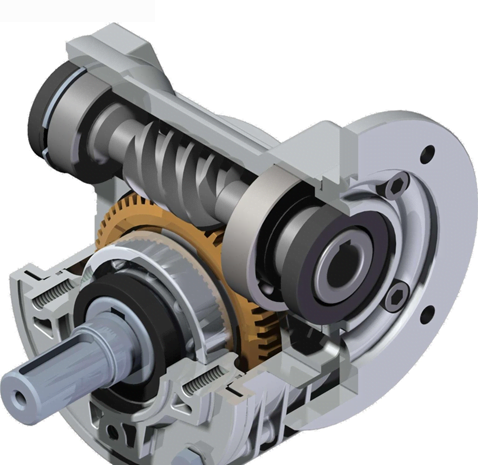
Gears are a crucial part of many automobile vehicles. Gears help increase delivered torque by providing a reduction in gear and adjusting the direction of rotation like the axle of the rear wheels of motor vehicles. Following are some basic types of gears & how they differ from each other.
Spur gears in Types of Final Drive
Spur gears are mounted in series on parallel shafts to achieve large gear reductions in the types of the final drive.
The most common gears are spur gears and are used in series for large reductions. Spur gear teeth are straight and mounted in parallel on different axes. Spur gears are used in washing machines, screwdrivers, winding alarms, and other devices.
These are particularly noisy, due to the engagement and collision of the gear teeth. Each impact produces loud noises and vibrations, which is why spur gears are not used in machinery such as automobiles. A typical gear ratio range is 1: 1 to 6: 1
Helical Gears in Types of Final Drive
Helical gears run smoother and quieter than spur gears due to the way the teeth interact. The teeth of a worm gear cut at an angle to the face of the gear. When two of the teeth begin to engage, contact is gradual, starting at one end of the tooth and maintaining contact while the gear rotates fully engaged. The helix angle range is about 15-30 degrees.
The thrust load varies directly with the magnitude of the tangent of the helix angle. The helical gear is the most widely used gear in transmissions. They also generate large amounts of thrust and use bearings to support the thrust load. Helical gears can be used to adjust the angle of rotation by 90 degrees. When mounted on perpendicular shafts, its average gear ratio range is 3: 2 to 10: 1.
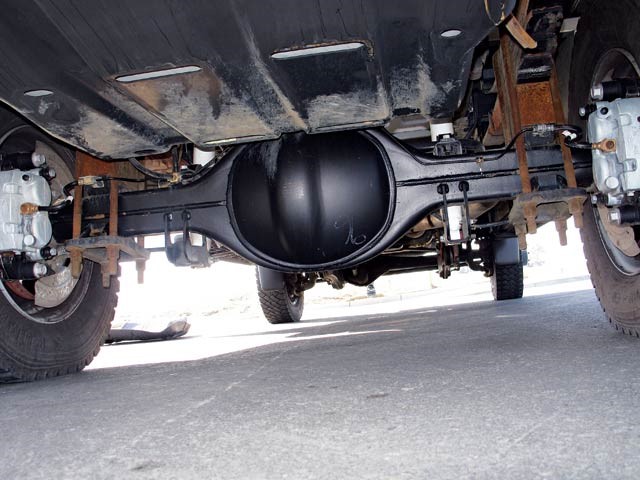
Bevel Gears in Types of Final Drive
Bevel gears are used to change the direction of rotation of a shaft. Bevel gears have teeth that come in a straight spiral. Spurs have similar characteristics to spur gears and also punch when engaged. As with spur gears, the normal gear ratio range for spur bevel gears is 3: 2 to 5: 1.
Worm Gears in Types of Final Drive
Helical gears are used in large gear reductions. The typical gear ratio is between 5: 1 and 300: 1. The setting is designed so that the worm can turn the gear, but the gear cannot turn the worm. The angle of the worm is shallow, and as a result, the gear is held in place due to the friction between the two. The gear is found in applications such as transport systems where the locking function can act as a brake
FAQ
What is the final drive in automobiles?
The final drive in automobiles is the last component in the drivetrain system, responsible for transmitting power from the transmission to the wheels.
How does the final drive work?
The final drive contains gears that increase or decrease torque and rotational speed to match the engine’s output with the desired wheel speed.
What is the purpose of the final drive?
The main purpose of the final drive is to allow the engine’s power to be appropriately converted and delivered to the wheels for vehicle movement.
Where is the final drive located in a car?
The final drive is usually located at the rear axle, powering the rear wheels in rear-wheel-drive vehicles. In front-wheel-drive cars, it is integrated into the transaxle.
What is the difference between a final drive and a differential?
The final drive is a part of the entire differential assembly. The differential distributes power to the two wheels, while the final drive specifically handles the gear reduction.
Can the final drive ratio be changed?
Yes, the final drive ratio can be changed to alter the vehicle’s performance characteristics, such as improving acceleration or increasing fuel efficiency.
How does the final drive ratio affect the car’s performance?
A higher final drive ratio (numerically lower) offers better acceleration but may sacrifice top speed, while a lower ratio (numerically higher) can improve fuel efficiency and top speed at the cost of acceleration.
Are there different types of final drive systems?
Yes, there are various types, including open differentials, limited-slip differentials (LSD), and electronic locking differentials, each providing different traction and handling characteristics.
What maintenance does the final drive require?
Regular maintenance involves checking and changing the gear oil at recommended intervals to ensure proper lubrication and prevent wear.
Can a faulty final drive cause problems in a car?
Yes, a faulty final drive can lead to issues like poor traction, strange noises, or vibrations, and may result in costly repairs if not addressed promptly.
Can you improve off-road performance with a different final drive ratio?
Yes, choosing a lower final drive ratio can enhance off-road performance by providing more torque and better control in challenging terrain.
Is the final drive relevant in electric vehicles?
Yes, electric vehicles also have a final drive or reduction gearbox that adjusts the motor’s high-speed, low-torque output to the wheels for optimal performance.



















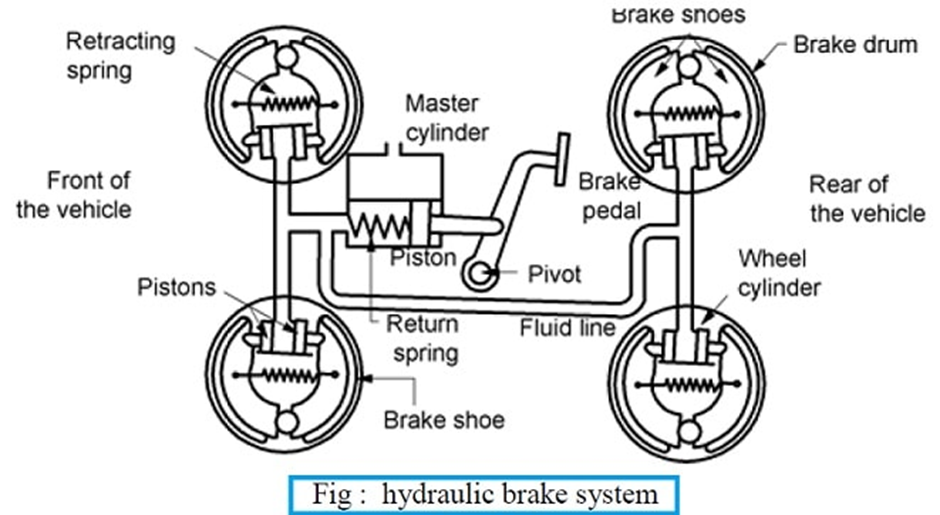
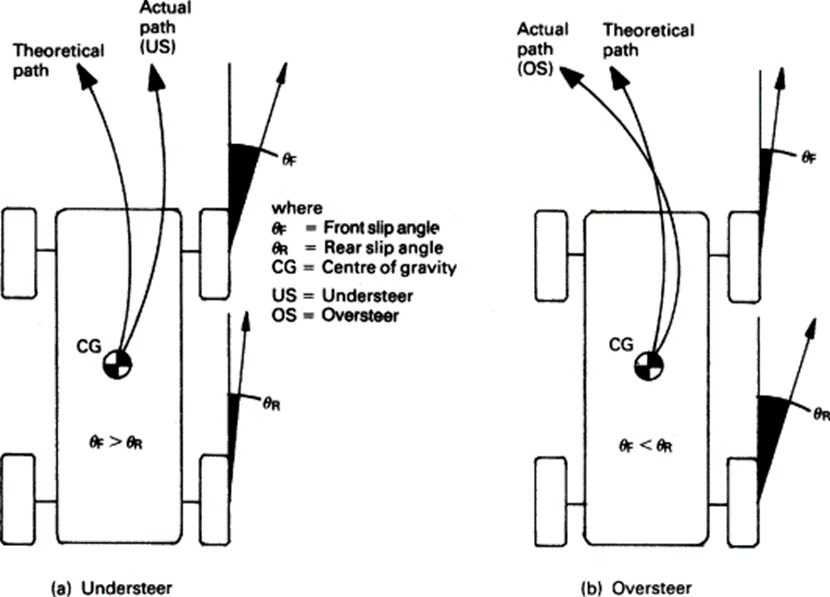
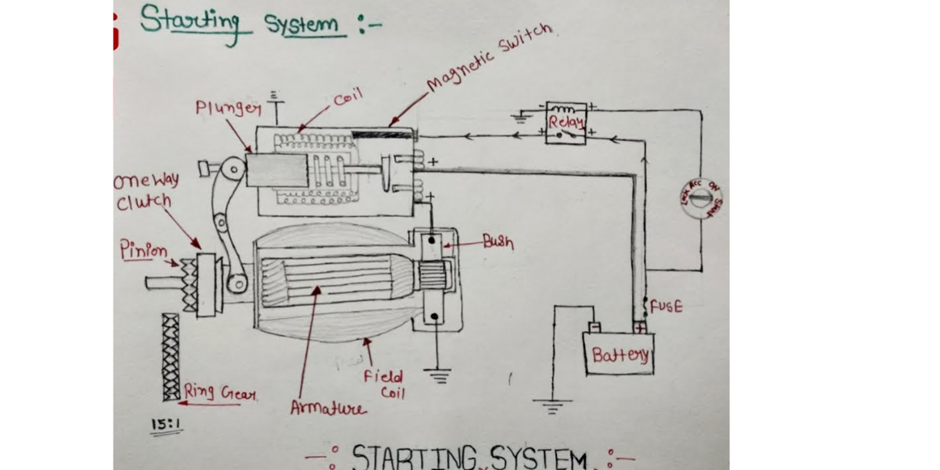

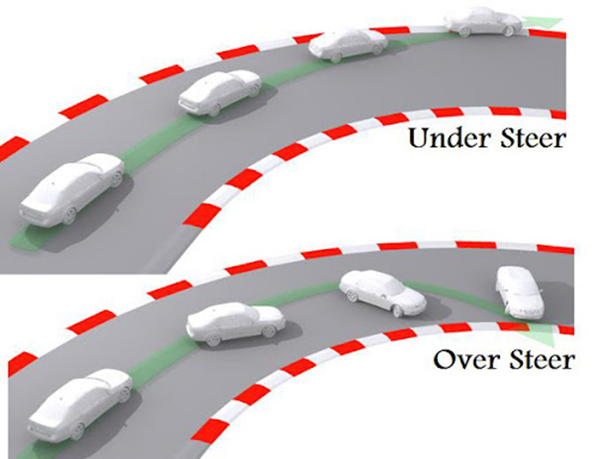
Comment on “Types of Final Drive in Automobiles”