Table of Contents
Introduction
The chassis frame is an essential component of any vehicle, serving as the backbone that provides structural support and helps distribute the weight of the vehicle. Understanding the definition, types, and materials used in chassis frames is crucial for anyone involved in the automotive industry or interested in the mechanics of vehicles
Definition of Chassis Frame
The chassis frame, also known as the frame or backbone, is the structure on which the various components of a vehicle are mounted. It acts as a platform for supporting the engine, drivetrain, suspension, and bodywork. The chassis frame provides strength, rigidity, and structural integrity to the vehicle while withstanding various forces and vibrations encountered during operation.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | – Serves as the main support structure for the car. |
| – Provides rigidity and stability. | |
| Material Used | – Steel (most common). |
| – Aluminum (for lightweight demands). | |
| – Carbon fiber (for premium/sporty vehicles). | |
| Types | 1. Ladder Frame |
| 2. Monocoque/Unibody | |
| 3. Backbone Frame | |
| 4. Space Frame | |
| Components | – Cross Members (horizontal structural sections). |
| – Longitudinal Main Members (run lengthwise). | |
| – Subframes (support engine, suspension components, etc.). | |
| Advantages | – Provides a base for mounting various automobile components. |
| – Affects the handling and ride quality of the vehicle. | |
| – Contributes to safety in case of collisions. | |
| Maintenance | – Regular inspection for rust or damage. |
| – Repairs as needed to ensure structural integrity. | |
| Modern Innovations | – Hybrid frames (combining characteristics of different types). |
| – Enhanced corrosion resistance treatments. | |
| – Advanced manufacturing techniques for weight reduction and improved strength. | |
| Environmental Considerations | – Recycling initiatives (especially for steel and aluminum frames). |
| – Reducing weight to enhance fuel efficiency. |
Types of Chassis Frames
There are different types of chassis frames, each designed to suit specific vehicle applications. Here are some of the most common types:
a) Ladder Frame:
This is the oldest and most basic type of chassis frame. It consists of two parallel longitudinal beams (rails) connected by several cross members. Ladder frames are commonly found in trucks and body-on-frame SUVs, offering excellent strength and durability.
b) Monocoque (Unibody) Frame:
Unlike ladder frames, monocoque frames integrate the body and frame into a single unit. The structural rigidity is derived from the body panels, eliminating the need for a separate frame. Monocoque frames are commonly used in passenger cars, offering improved fuel efficiency, reduced weight, and enhanced handling.
c) Space Frame:
Space frames are lightweight and made up of interconnected tubes or beams, forming a lattice-like structure. They are often used in high-performance sports cars and supercars due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Space frames offer superior rigidity and can withstand high torsional forces, ensuring optimal handling and performance.
d) Backbone Frame:
Backbone frames consist of a single large structural member running along the centerline of the vehicle. This design provides excellent torsional rigidity while allowing flexibility in other areas. Backbone frames are commonly found in small cars and motorcycles, offering a cost-effective solution with good ride quality.
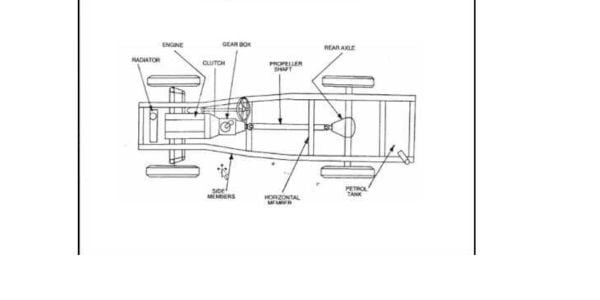
Materials Used in Chassis Frames
Chassis frames are constructed using a variety of materials, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. Here are the most common materials used:
a) Steel:
Steel is the most widely used material for chassis frames due to its high strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Different types of steel, such as mild steel, high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel, and advanced high-strength steel (AHSS), are utilized to achieve varying levels of strength and weight reduction.
b) Aluminum:
Aluminum is a lightweight material that offers excellent corrosion resistance and a high strength-to-weight ratio. It is commonly used in high-end vehicles where weight reduction is crucial, as it helps improve fuel efficiency and performance. However, aluminum is generally more expensive than steel.
c) Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP):
CFRP is a composite material composed of carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix. It offers exceptional strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties. CFRP is commonly used in high-performance and luxury vehicles due to its ability to reduce weight significantly while maintaining structural integrity. However, CFRP is expensive and requires specialized manufacturing processes.
d) Other Materials:
Chassis frames may also incorporate other materials such as magnesium alloys or hybrid structures that combine different materials to optimize strength, weight, and cost factors.

The Various Assemblies Fitted on a Chassis Frame
A chassis frame serves as the foundation of any vehicle, providing structural support and housing various assemblies that are crucial for its proper functioning. These assemblies are designed to work in harmony, ensuring safety, stability, and overall performance.
1. Engine Assembly:
The engine assembly, often referred to as the powertrain, is one of the primary components fitted on a chassis frame. It comprises the engine, transmission, driveshaft, and other related parts. The engine generates power by converting fuel into mechanical energy, while the transmission transfers this power to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. The engine assembly is mounted securely onto the chassis frame, providing stability and minimizing vibrations.
2. Suspension System:
The suspension system plays a critical role in ensuring a smooth and comfortable ride. It consists of various components, including springs, shock absorbers, control arms, and anti-roll bars. These assemblies are strategically placed on the chassis frame to absorb shocks, maintain tire contact with the road, and provide stability during acceleration, braking, and cornering. A well-designed suspension system enhances vehicle handling and reduces the impact of road irregularities.
3. Brake System:
The brake system is responsible for decelerating or stopping the vehicle efficiently and safely. It comprises several key components, such as brake calipers, rotors, pads, and hydraulic lines. The assemblies are mounted on the chassis frame and synchronized to ensure optimal braking performance. When the driver applies pressure to the brake pedal, the hydraulic system transmits force to the brake calipers, causing the pads to clamp onto the rotors and slow down the wheels.
4. Steering System:
The steering system enables the driver to control the direction of the vehicle. It consists of various components, including the steering column, rack and pinion, steering gear, and tie rods. These assemblies are mounted on the chassis frame and work together to transfer the driver’s input to the wheels, allowing for precise steering control. The steering system ensures smooth maneuverability and responsiveness, contributing to overall vehicle safety.
5. Fuel and Exhaust Systems:
The fuel and exhaust systems are integral to the vehicle’s performance and environmental compliance. The fuel system includes components such as fuel tanks, fuel lines, fuel pumps, and injectors, which deliver fuel to the engine. The exhaust system, on the other hand, comprises the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe, which expel combustion byproducts safely.
These assemblies are fitted onto the chassis frame, ensuring proper routing and minimizing interference with other components.
6. Electrical System:
Modern vehicles rely heavily on the electrical system for various functions, including ignition, lighting, instrumentation, and communication. The electrical system includes the battery, alternator, wiring harnesses, fuses, relays, and control modules. These assemblies are strategically placed on the chassis frame to ensure efficient power distribution and electrical connectivity throughout the vehicle.
FAQ
How do car chassis frames contribute to vehicle durability?
A well-designed and robust car chassis frame ensures the durability and longevity of the vehicle. It provides a stable platform for various components and systems, minimizing vibrations, fatigue, and structural failures, ultimately enhancing the overall lifespan of the vehicle.
What role does suspension play in a car chassis frame?
Suspension components, such as springs, shock absorbers, and control arms, are mounted to the car chassis frame. The chassis frame, along with the suspension system, determines the ride quality, handling, and stability of the vehicle.
Can car chassis frames be repaired if damaged?
In most cases, car chassis frames can be repaired, depending on the extent of the damage. Repairing a chassis frame requires specialized equipment and expertise, and it is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and consult professionals for proper repairs.
How do safety features like crumple zones affect car chassis frames?
Modern car chassis frames often incorporate crumple zones, which are engineered to deform during an impact, absorbing and dissipating energy to protect occupants. These zones are strategically placed in areas that are likely to crumple, minimizing the transfer of forces to the passenger compartment.
How has the design of car chassis frames evolved over the years?
Over the years, car chassis frames have evolved to be lighter, stronger, and more rigid. Advancements in materials, such as high-strength steel and composites, have allowed for improved structural integrity while reducing weight and enhancing fuel efficiency.
What is the difference between a ladder frame and a monocoque frame?
A ladder frame is a traditional design where the chassis consists of two parallel longitudinal rails connected by cross-members, providing excellent strength and durability. On the other hand, a monocoque frame integrates the body structure with the chassis, eliminating the need for a separate frame and offering weight savings.
What are the different types of car chassis frames?
There are several types of car chassis frames, including ladder frames, monocoque (unibody) frames, space frames, and backbone frames. Each type has its own construction and characteristics, suited for different vehicle applications.
How does the design of a car chassis frame affect vehicle performance?
The design of the chassis frame plays a crucial role in determining a vehicle’s handling, stability, and safety. Factors such as weight distribution, torsional rigidity, and suspension mounting points impact the overall performance of the vehicle.
What materials are commonly used in car chassis frames?
Car chassis frames are typically made from high-strength steel, which offers a balance of strength and weight. Some manufacturers also use aluminum or carbon fiber composites to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency.
What is a car chassis frame?
A car chassis frame is the structural backbone of a vehicle that supports its components, including the engine, suspension, body, and other systems. It provides rigidity, strength, and stability to the vehicle.
Also, read Types of Fits
















Comment on “Car Chassis Frame: Definition, Types, & Materials Explained”
Comments are closed.