Table of Contents
MCB full form:
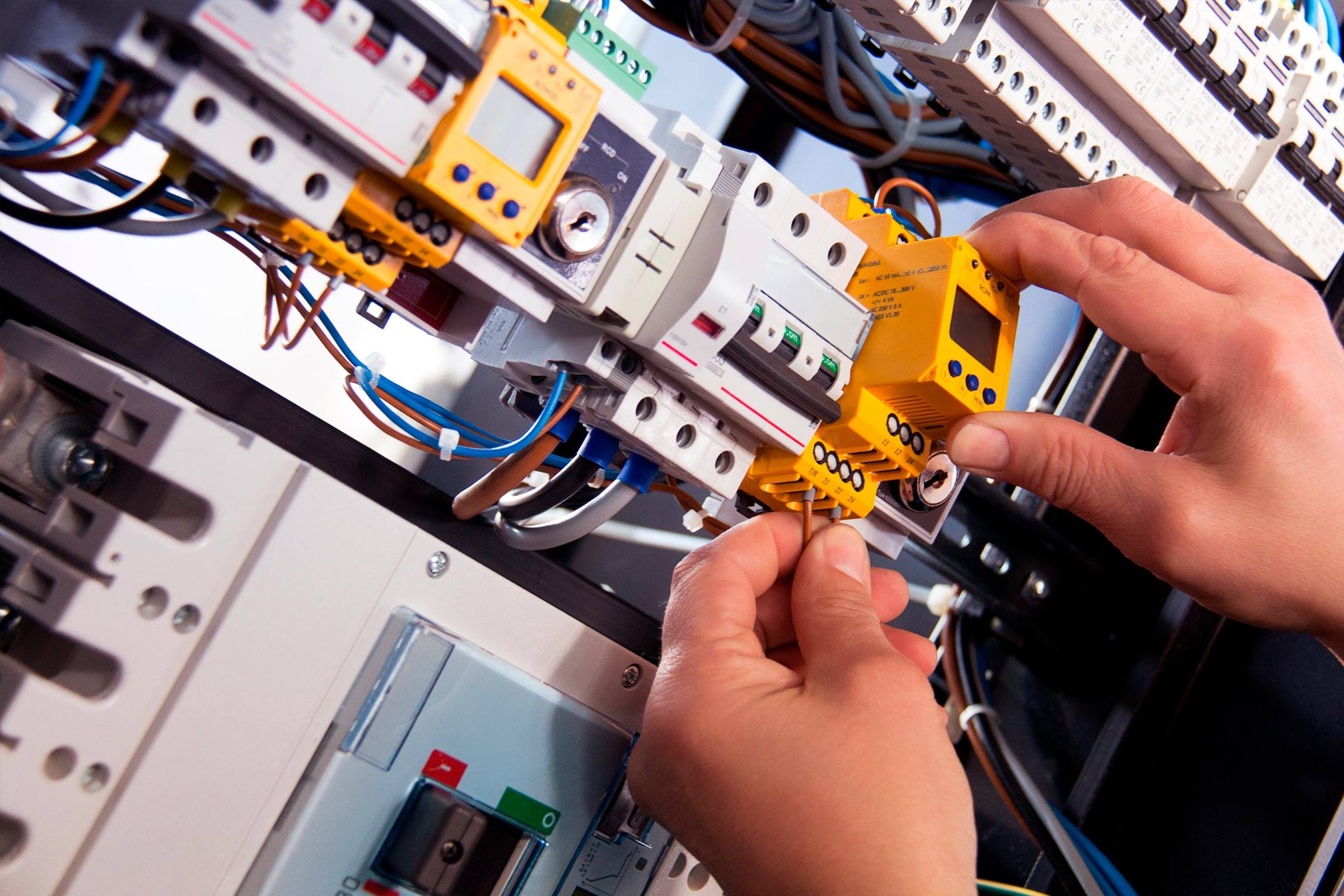
MCB full form is Miniature Circuit Breaker. It is a device used to provide overcurrent protection and prevent overloads and short circuits in electrical systems.
It is a type of electrical switch that is used to protect against overcurrents, and it is able to detect when the current flow in an electrical circuit is too high and automatically disconnects the flow. MCBs are used in both domestic and industrial settings and are available in a variety of different sizes and configurations.
They are typically rated for current, voltage, and short circuit breaking capacity. MCBs are typically connected to the circuit at the main panel and are used to protect all of the circuits downstream from it.
The overview of MCB:
The MCB or Miniature Circuit Breaker is a protective device that is used to protect electrical systems and components from damage caused by overloads or short circuits.
It is also used to prevent overloads or short circuits from occurring in the first place. MCBs are small, lightweight, and typically have a reset button or switch. They are installed in electrical circuits and are designed to detect and interrupt any abnormal current flow.
The MCB can be used in a variety of applications, such as residential, commercial, and industrial. MCBs come in a variety of types, each designed to meet a specific application’s needs. Common types of MCBs include thermal-magnetic breakers, adjustable breakers, electronic breakers, and residual current devices (RCD).
MCBs are typically rated in amperes and are available in a range of amperages, ranging from 0.5A to 63A. The primary function of the MCB is to detect and interrupt any current flow that is outside the normal range of operation.
When an overcurrent or short circuit is detected, the circuit breaker will trip, interrupting the current flow and protecting the electrical system or component from damage. The MCB can also be used to protect against other electrical problems, such as arc faults and ground faults.
MCBs are also used to control the flow of power to various circuits. For example, a circuit breaker can be used to control the power to a specific appliance or circuit, preventing it from being overloaded.
In summary, the MCB is a protective device that is used to protect electrical systems and components from overloads, short circuits, and other electrical problems.
It is designed to detect and interrupt any current flow outside the normal range of operation and to control the flow of power to various circuits. MCBs are available in a variety of types, each designed to meet a specific application’s needs and are rated in amperes.
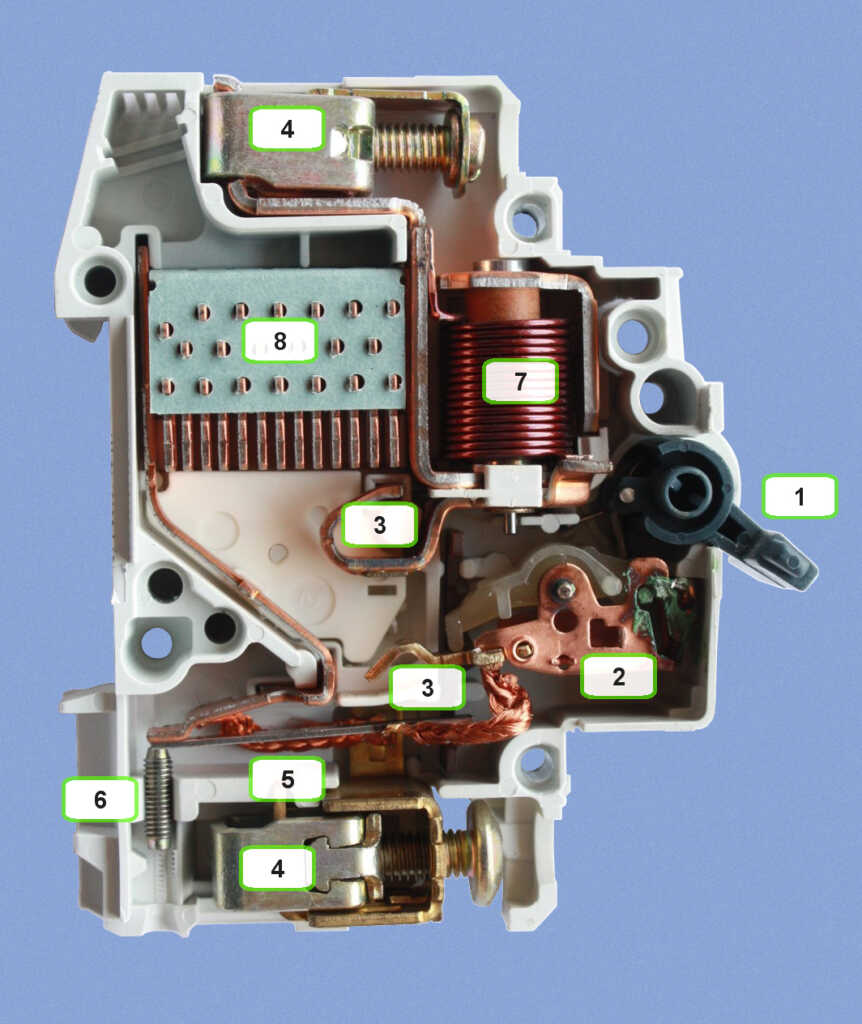
The definition of MCB:
A miniature circuit breaker (MCB) is a type of electrical protection device used to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit.
It is designed to automatically trip and disconnect a circuit when it detects an electrical fault condition. MCBs are designed to operate at a specific current rating and can be used to protect against overloads caused by increases in current beyond their rated capacity.
MCBs are also used to protect against short circuits, which occur when a high-current flow occurs between two points in an electrical system.
MCBs provide a cost-effective and safe method for protecting electrical circuits and equipment. They are often used in residential and commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and other electrical systems.
The classification of MCBs:
As per usage, MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) are electrical devices used to protect electrical circuits from overload or short circuits. They can be classified according to their usage:
1. Single Pole MCB – This type of MCB is used to protect a single-phase circuit.
2. Double Pole MCB – This type of MCB is used to protect a two-phase circuit.
3. Three-Pole MCB – This type of MCB is used to protect a three-phase circuit.
4. Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) – This type of MCB is used to detect and interrupt the flow of residual current.
5. Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) – This type of MCB is used to detect and interrupt the flow of current from the earth.
6. Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) – This type of MCB is used to detect and interrupt arc faults in a circuit.
7. Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) – This type of MCB is used to protect motors from overload and short circuits.
8. Surge Protective Device (SPD) – This type of MCB is used to protect circuits from transient overvoltages caused by lightning or other sources.
The classification of MCB as per the mechanism:
Miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) are a type of protective device used in electrical circuits to detect and prevent excess current flow. They protect electrical circuits from overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. MCBs are classified as either thermal-magnetic or electronic according to their operating mechanism.
Thermal-magnetic MCBs are the most common type of MCB. They use a combination of a bimetallic strip and a magnetic coil to detect and react to overcurrents. The bimetallic strip is made from two strips of different metals that expand and contract at different rates when heated. The current flowing through the circuit causes a heating effect on the strip, which causes it to expand and open the circuit.
The magnetic coil is also heated by the current and produces a magnetic field that acts to trip the circuit in the event of an overcurrent. Electronic MCBs are a newer type of MCB that use a semiconductor device to detect overcurrents. They are much more sensitive than thermal-magnetic MCBs and can detect even small levels of overcurrent.
The semiconductor device is usually a trial, which switches off the circuit when the current exceeds the preset level. Electronic MCBs are more expensive than thermal-magnetic MCBs but are becoming increasingly popular due to their high level of accuracy and reliability.
In summary, MCBs are classified according to their operating mechanism, as either thermal-magnetic or electronic. Thermal-magnetic MCBs use a combination of a bimetallic strip and a magnetic coil to detect and react to overcurrents, while electronic MCBs use a semiconductor device to detect overcurrents. Both types of MCBs are used to protect electrical circuits from overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
The classification of MCBs as per the number of poles:
MCBs or Miniature Circuit Breakers can be classified according to the number of poles they have. A pole is a conducting connection from the breaker to the circuit it is protecting.
Single pole MCBs are typically used to protect lighting circuits and are rated at 10A or 16A.
Two pole MCBs are used to protect larger electrical circuits, such as those supplying power to a washing machine or oven, and are rated at 20A or 32A.
Three pole MCBs are used to protect circuits with three-phase power and are rated at 20A, 32A, or 40A.
Four-pole MCBs are also available but are less common and are used to protect circuits with four-phase power. They are typically rated at 40A or 63A.
The classification of MCB as per the Trip cures:
MCB is classified into three categories based on the trip cure:
1. Instantaneous Trip Cure: This type of MCB trips instantly when the current exceeds a specific value. It is very fast in response and it has a very little time delay. It is used in applications where safety is of utmost importance.
2. Short Delay Trip Cure: This type of MCB trips after a certain time delay when the current exceeds a specific value. It is used in applications where the equipment needs to be protected from damage due to overloading.
3. Long Delay Trip Cure: This type of MCB trips after a long time delay when the current exceeds a specific value. It is used in applications where it is necessary to allow the circuit to operate for a longer period of time before tripping. This type of MCB is used for the control and protection of motors, transformers, etc.
The working principle of MCB:
A miniature circuit breaker (MCB) is an electrical device designed to protect an electrical circuit from being damaged by an overload or short circuit. It works by automatically disconnecting the circuit when a predetermined amount of current, as determined by the rating of the breaker, is exceeded.
This helps to prevent any damage to the circuit and the connected devices, as well as preventing any potential fire hazards. The working principle of an MCB is relatively simple. When the current in a circuit exceeds the breaker’s amperage rating, a bi-metallic strip inside the device warps, causing a contact to break and disconnect the circuit.
The bi-metallic strip is made of two different types of metal, each with a different thermal expansion rate. When the current increases, the bi-metallic strip warps, causing the contacts to separate and break the circuit.
Once the current drops back to a safe level, the bi-metallic strip cools and the contacts close again, allowing the circuit to be reconnected. This makes MCBs ideal for protecting circuits from damage due to overloads or short circuits.
An MCB is designed to trip or disconnect the circuit at a certain amperage level, which is determined by the breaker’s rating. The rating of the breaker is typically printed on the device itself and is typically expressed in amps. For example, a 15 amp breaker should trip or disconnect the circuit when the current exceeds 15 amps.
MCBs are a crucial part of any electrical system and are used to protect the circuit and the connected devices from damage due to overcurrents or short circuits. By automatically disconnecting the circuit when the current in the circuit exceeds the rating of the breaker, MCBs can help to protect against fire hazards and electrical damage.
The drawbacks of MCB:
1. MCBs or Miniature Circuit Breakers are limited in their ability to provide short-circuit protection. These are designed to protect from overloads or short circuits, but they cannot provide the same level of protection as a full-sized circuit breaker.
2. MCBs are not suitable for applications that require frequent switching. They are best used for static load applications such as lighting or small appliances.
3. MCBs are more expensive than other types of circuit breakers, and they require more space.
4. MCBs are not designed to provide over-current protection, and they may be unable to protect against damage caused by high currents.
5. MCBs may be difficult to install, especially if you are not familiar with electrical systems.
6. MCBs may require regular maintenance in order to ensure they are working correctly.
7. MCBs can be damaged by surges and lightning strikes. 8. MCBs may not be able to detect ground faults, which could lead to a fire or other damage.
The conclusion about the usage of MCB:
The usage of MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is a cost-effective and efficient way of protecting electrical circuits from damage due to overloads and short circuits. MCBs are designed to trip automatically when a fault occurs and provide a fast, safe, and reliable means of disconnecting the electrical circuit.
MCBs are also used as a safety precaution to prevent hazardous electric shock and fire. They are available in a range of sizes and ratings to suit all applications.
The use of MCBs has become increasingly popular due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. MCBs are a cost-effective way of protecting electrical circuits from overload and short circuit damage and providing a reliable and safe means of disconnecting an electrical circuit in the event of a fault.
Furthermore, MCBs provide greater protection against electric shock and fire than standard circuit breakers, making them an ideal choice for domestic and commercial applications.
In conclusion, the usage of MCB is a cost-effective and efficient way of protecting electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. They provide a reliable and safe means of disconnecting an electrical circuit in the event of a fault and are available in a range of sizes and ratings to suit all applications.
MCBs provide greater protection against electric shock and fire than standard circuit breakers, making them an ideal choice for domestic and commercial applications.


























Comment on “MCB full form”
Comments are closed.