Table of Contents
Definition: Batteries use sponge lead and lead peroxide to convert chemical energy into electrical energy. This type of battery is called the lead-acid battery. Lead-acid batteries are often used in power stations and substations because of their high cell voltage and low cost.
Construction of lead-acid batteries
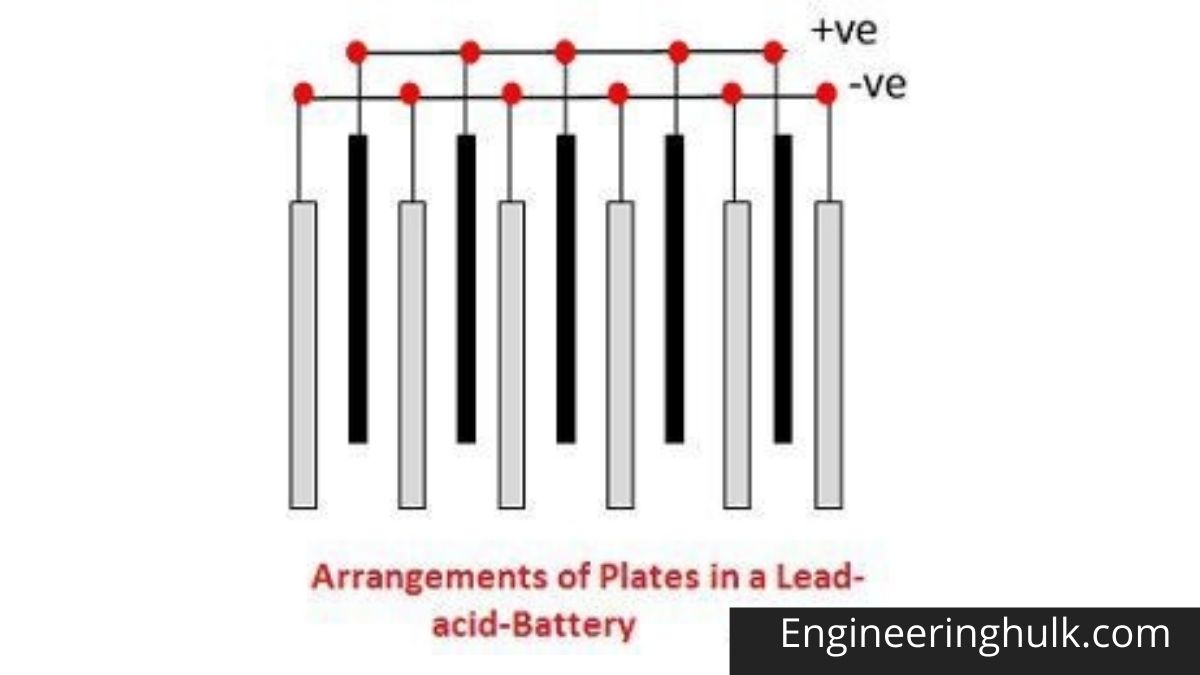
The different parts of lead-acid batteries are shown below. Containers and plates are a major component of lead-acid batteries. The container stores chemical energy which is converted into electrical energy with the help of a plate.
1. Container –
The container of lead-acid battery is made of glass, lead-lined wood, ebonite, hard rubber of bituminous compound, ceramic material, or molded plastic and placed on top to prevent electrolyte leakage. At the base of the container, there are four ribs, two of which support the positive plate and the other the negative plate.
The prism acts as a support for the plates and at the same time protects them from short-circuits. Materials made of battery containers must be resistant to sulfuric acid, not deformed or porous, or contain impurities that can damage the electrolyte.
2. Plates –
Lead-acid cell plates come in a variety of designs, all of which have some form of a grid consisting of lead and active ingredients. A grid is required to conduct electrical current and to distribute current evenly in the active material. If the current is not evenly distributed, the active material will slow down and fall out.
The grids are made of an alloy of lead and antimony. They are usually made with a transverse rib that crosses the locations at a right angle or diagonal. The positive and negative plate grids are of the same design, but the negative plate grids are lighter because they are not as essential for uniform current conduction.
3. Active Material –
The material in a cell that takes an active part in a chemical reaction (absorption or evolution of electrical energy) during charging or discharging is called the active material of the cell. The functional elements of lead acid are
Lead peroxide (PbO2) – forms the positive active material. PbO2 is dark chocolate in color.
Lead sponge – forms the negative active material. It is grey in color.
Dilute sulfuric acid (H2SO4) – is used as an electrolyte. It contains 31% sulfuric acid.
Lead peroxide and lead sponges, which form the negative and positive active materials, have little mechanical strength and therefore can be used alone.
4. Separators –
The Separators are thin sheets of non-conductive material made of chemically treated lead, porous rubbers or fibreglass mats and are placed between the positive and negative to insulate them from each other. Separators are vertically grooved on one side and smooth on the other side.
5. Battery Terminals –
A battery has two terminals, the positive and the negative. The positive terminal with a diameter of 17.5 mm at the top is slightly larger than the negative terminal, which is 16 mm in diameter.
Working principle of lead-acid battery
When sulfuric acid dissolves, its molecules split into positive hydrogen ions (2H+) and negative sulfate ions (SO4—) and move freely. If the two electrodes are immersed in solutions and connected to the DC source, the hydrogen ions are positively charged and moved towards the electrodes and connected to the negative terminal of the source.
The SO4- ions being negatively charged moved towards the electrodes connected to the positive terminal of the supply network (ie anode).
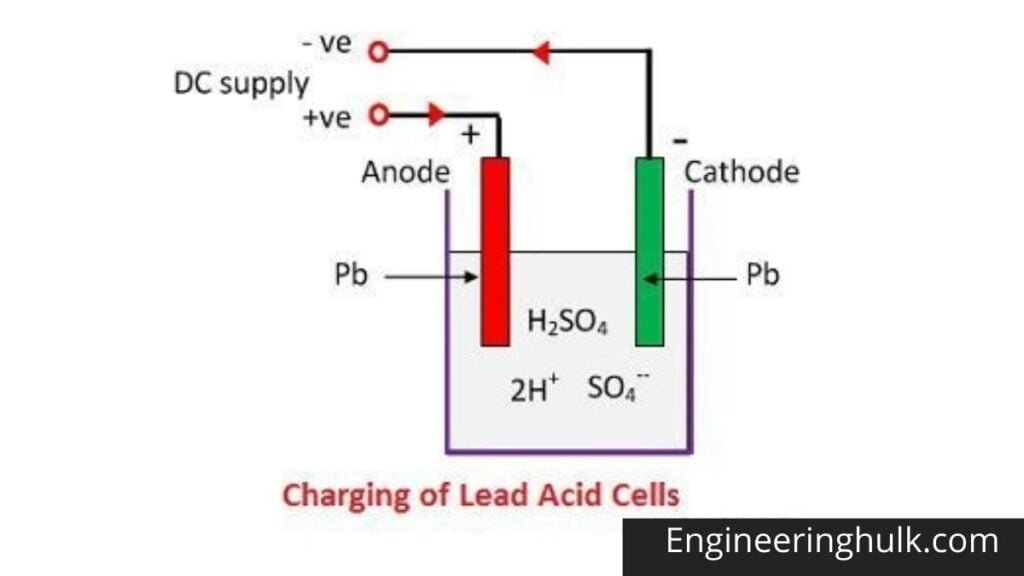
Each hydrogen ion takes an electron from the cathode, and each sulfate ion takes the two negative ions from the anodes and reacts with water to form sulfuric acid and hydrogen.
Oxygen from the above equation reacts with lead oxide and forms lead peroxide (PbO2).
If the DC power supply is disconnected and the voltmeter connects between the electrodes, it will show the potential difference between them. If the wire connects the electrodes, then the current will flow from the positive plate to the negative plate through an external circuit, ie the cell is capable of supplying electrical energy.
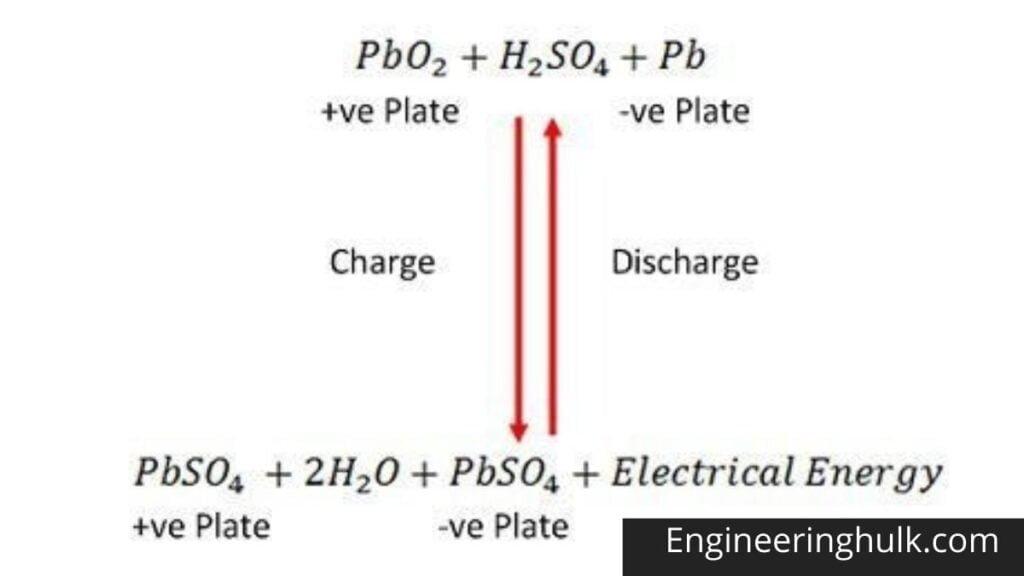
Chemical Action During Discharge
When the cell is fully discharged, the anode is lead peroxide (PbO2) and the cathode is lead sponge metal (Pb). When the electrodes are connected through a resistance, the cell discharges, and electrons flow in an opposite direction to that during charging. Hydrogen ions move to the anode and reach the anode, receive an electron from the anode, and become hydrogen atoms.
The hydrogen atom comes into contact with a PbO2, so it attacks and forms lead sulphate (PbSO4), whitish in color and aqueous according to the chemical equation.

Each sulphate ion (SO4—) moves towards the cathode and reaching there gives up two electrons becomes radical SO4, attack the metallic lead cathode, and form lead sulphate whitish in color according to the chemical equation.
Chemical Action during Recharging
For recharging, the anode and cathode are connected to the positive and the negative terminal of the DC supply mains. The molecules of the sulfuric acid break up into ions of 2H+ and SO4—.
The positively charged hydrogen ions move toward the cathodes, receive two electrons from there, and form a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom reacts with lead sulphate cathode forming lead and sulfuric acid according to the chemical equation.
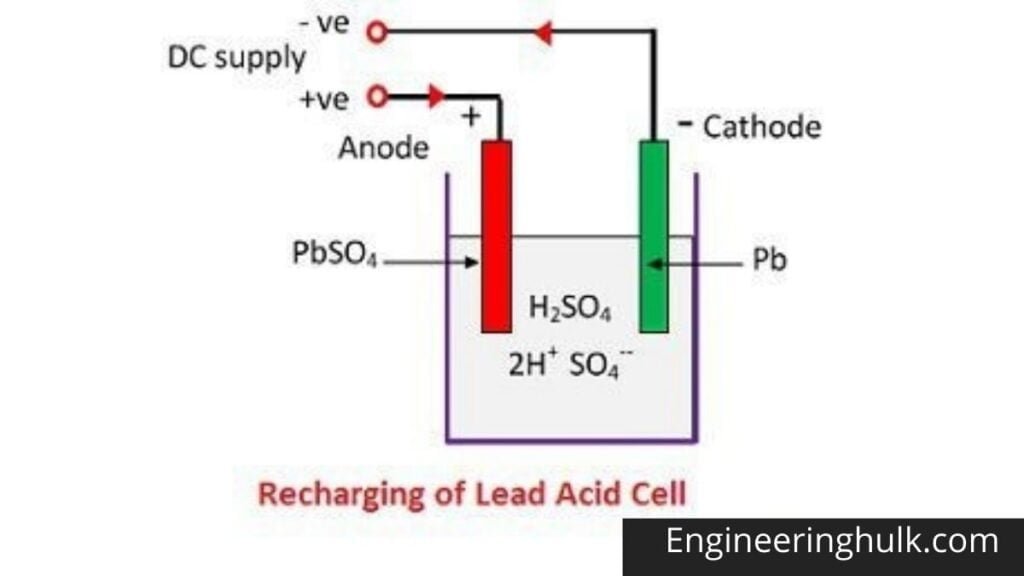
SO4— Ion moves to the anode, gives up its two additional electrons, becomes a radical SO4, reacts with the lead sulfate anode, and forms lead peroxide and lead sulfuric acid according to the chemical equation that is represented by a single reversible equation given below.
FAQ
What is a lead-acid battery in cars?
A lead-acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery commonly used in automotive applications. It consists of lead plates immersed in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid, which facilitates the chemical reactions to store and release electrical energy.
How does a lead-acid battery work?
When a lead-acid battery is charged, a chemical reaction occurs that converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The sulfuric acid in the electrolyte reacts with the lead plates, creating lead sulfate and releasing electrons. During discharge, the process is reversed, with lead sulfate breaking down and releasing electrical energy.
What are the advantages of lead-acid batteries in cars?
Lead-acid batteries have several advantages, including relatively low cost, high energy density, and the ability to deliver high current outputs. They are also known for their robustness and ability to perform well in a wide range of temperatures.
What are the disadvantages of lead-acid batteries?
Lead-acid batteries have some limitations. They are heavy and have a lower energy-to-weight ratio compared to newer battery technologies like lithium-ion. They also require regular maintenance, such as checking and topping up the electrolyte levels and ensuring proper ventilation.
How long do lead-acid batteries last in cars?
The lifespan of a lead-acid battery in a car can vary depending on various factors, including usage patterns, maintenance, and environmental conditions. On average, a well-maintained lead-acid battery can last anywhere from 3 to 5 years.
Can lead-acid batteries be recycled?
Yes, lead-acid batteries are highly recyclable. The lead and other components can be extracted and reused to manufacture new batteries. Recycling lead-acid batteries is crucial as it helps prevent environmental pollution and conserves valuable resources.
Can lead-acid batteries be recharged?
Yes, lead-acid batteries can be recharged. They are designed to be rechargeable and can undergo multiple charge-discharge cycles. It’s important to use a compatible battery charger and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Can lead-acid batteries freeze?
Yes, lead-acid batteries can freeze if they are exposed to extremely low temperatures for extended periods without being properly charged. Freezing can cause damage to the battery and reduce its performance. It’s important to store and use lead-acid batteries in environments that are within their recommended temperature range.
Can lead-acid batteries produce hydrogen gas?
During the charging process, lead-acid batteries can produce hydrogen gas as a byproduct. This is a normal occurrence, but it is important to ensure proper ventilation when charging or using lead-acid batteries to prevent the accumulation of hydrogen gas, which can be flammable and pose safety risks.
Are there alternatives to lead-acid batteries in cars?
Yes, there are alternative battery technologies used in cars, with lithium-ion batteries being the most prominent. Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, lighter weight, and longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries. They are commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, but they are more expensive than lead-acid batteries.