Table of Contents
All alternators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. According to this act, a conductor, magnetic field, and mechanical energy are required to generate electricity
The main parts of an alternator are, apparently, a stator and a rotor. But, unlike other machines, in most alternators, the field exciter rotates and the armature coil becomes stationary.

Stator
The DC machine of the alternator is not to serve the route for the opposite magnetic flux in the stator. Instead, the stator armature is used for rotation. The stator core is made of steel alloy or lamination of magnetic iron, to reduce the AD current loss.
Why is the armature winding fixed in the alternator?
At higher voltages, static armature windings are easier to insulate, which can be 30 kV or more.
The high-voltage output can be extracted directly from the static armature. Where for rotary armature, there will be a large brush contact drop at high voltages, as well as sparking on the brush surface.
The field exciter is mounted on a rotating rotor, and the low DC voltage can be safely transferred.
The armature winding can be braced well to prevent deformation caused by high centrifugal force.
Rotor
There are two types of rotors used in AC generators/alternators:
(i) main and (ii) cylindrical type
Main pole type: The main pole type rotor is used in low and medium-speed alternators. This type of rotor has a large number of projected poles (called main poles), bolted in a magnetic cycle. These poles are also laminated to reduce AD current losses. Alternators characteristic of this type of rotor are large in diameter and short in axial length.
Cylindrical type: Cylindrical type rotors are used in high-speed alternators, especially in turbo-alternators. This type of rotor consists of a smooth and solid steel cylinder with slots on the outer circumference. These slots have field windings.
Working principle
The working principle of an alternator is very simple. This is like the basic principle of a DC generator. It also depends on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction which states that the relative motion between the conductor and the magnetic field occurs in the conductor within the electromagnetic field.
DC supply is provided for rotor rotation through slip ring and brush arrangement. Having understood the basic principles of alternators, let us now take a look at the basic operating principles of practical alternators.
In discussing the basic functions of alternators, we have considered that the magnetic field is constant and the conductors (armature) are rotating. But generally in the practical construction of alternators, the armature conductors are stationary and field magnets rotate between them.
The rotor of an alternator or asynchronous generator is mechanically connected to a shaft or turbine blade, which is designed to rotate at synchronous speed Ns under some mechanical force resulting in cutting off the magnetic flux of the static armature conductors placed on the stator.
As a direct result of this flow, an induced emf cut and the current begins to flow through the armature conductors which flow in one direction for the first half cycle and then for the second half cycle in each direction with a fixed time delay for each winding.
These special events result in a 3φ power flow from the alternator which is then sent to distribution stations for domestic and industrial use.
Factors affecting battery life
1. Electrolyte levels
2. Overcharging
3. Low charge
4. Bicycle
5. Terminals carbon/corrosion/impurities/residues
6. Mounting
FAQ
What is the purpose of an alternator in a car?
The alternator is responsible for generating electrical power to charge the battery and provide electricity for the vehicle’s electrical systems while the engine is running.
How does an alternator work?
An alternator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a rotor, which rotates inside a stator, producing an alternating current (AC). This AC is then converted into direct current (DC) by the rectifier diodes in the alternator.
Can an alternator overcharge the battery?
Yes, it is possible for an alternator to overcharge the battery. Modern vehicles use voltage regulators to control the charging output of the alternator and prevent overcharging. If the voltage regulator malfunctions, it can lead to excessive charging and damage the battery.
What are the signs of a failing alternator?
Some common signs of a failing alternator include dimming or flickering lights, a dead battery, strange noises coming from the alternator, warning lights on the dashboard, and difficulty starting the engine.
Can a bad alternator drain the battery?
Yes, a faulty alternator can cause the battery to drain. If the alternator fails to recharge the battery properly while the engine is running, the battery’s charge will deplete over time, leading to a drained battery.
How long does an alternator typically last?
The lifespan of an alternator can vary depending on factors such as usage, maintenance, and the quality of the component. Generally, alternators can last anywhere from 80,000 to 150,000 miles (128,000 to 240,000 kilometers) or around 7 to 12 years.
Can a car run without an alternator?
No, a car cannot run for an extended period without an alternator. The battery’s initial charge may power the vehicle for a short time, but without the alternator to replenish the battery, the electrical systems will eventually drain the battery, causing the engine to shut off.
Can I replace the alternator myself?
Replacing an alternator typically requires intermediate to advanced mechanical skills. It involves disconnecting the battery, removing the drive belt, disconnecting electrical connections, removing mounting bolts, and installing the new alternator. It is advisable to consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance if you are not experienced with such repairs.
Are there different types of alternators?
Yes, there are different types of alternators used in cars. The most common type is the three-phase alternator, which generates three-phase AC. Some vehicles also use a single-phase alternator. Additionally, there are variations in the design and output capacity of alternators based on the specific vehicle make and model.
Can aftermarket alternators be used as replacements?
Yes, aftermarket alternators can be used as replacements for the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) alternators. However, it is important to ensure that the aftermarket alternator is compatible with your vehicle’s electrical system and meets the necessary specifications. It is often recommended to purchase alternators from reputable suppliers to ensure quality and compatibility.



















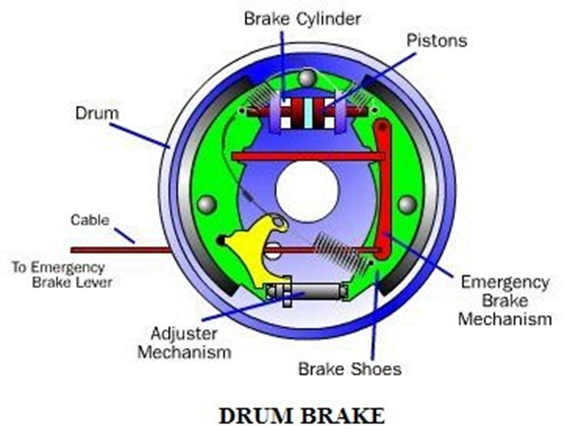
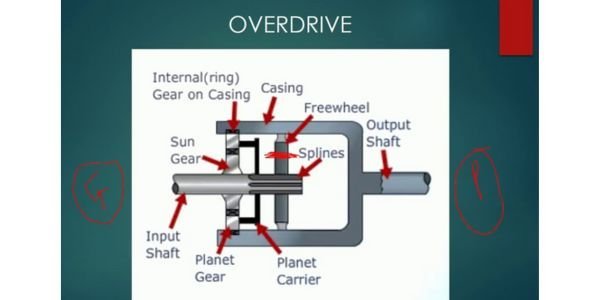
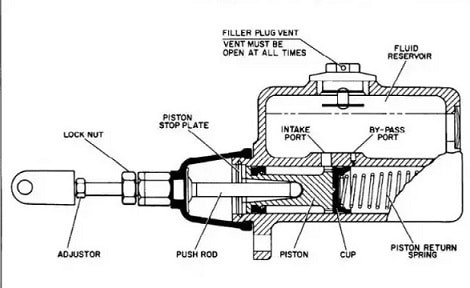

Comment on “Alternator in Automobile Engineering”